Related Research Articles

A primer is a short, single-stranded nucleic acid used by all living organisms in the initiation of DNA synthesis. A synthetic primer may also be referred to as an oligo, short for oligonucleotide. DNA polymerase enzymes are only capable of adding nucleotides to the 3’-end of an existing nucleic acid, requiring a primer be bound to the template before DNA polymerase can begin a complementary strand. DNA polymerase adds nucleotides after binding to the RNA primer and synthesizes the whole strand. Later, the RNA strands must be removed accurately and replace them with DNA nucleotides forming a gap region known as a nick that is filled in using an enzyme called ligase. The removal process of the RNA primer requires several enzymes, such as Fen1, Lig1, and others that work in coordination with DNA polymerase, to ensure the removal of the RNA nucleotides and the addition of DNA nucleotides. Living organisms use solely RNA primers, while laboratory techniques in biochemistry and molecular biology that require in vitro DNA synthesis usually use DNA primers, since they are more temperature stable. Primers can be designed in laboratory for specific reactions such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR). When designing PCR primers, there are specific measures that must be taken into consideration, like the melting temperature of the primers and the annealing temperature of the reaction itself. Moreover, the DNA binding sequence of the primer in vitro has to be specifically chosen, which is done using a method called basic local alignment search tool (BLAST) that scans the DNA and finds specific and unique regions for the primer to bind.

Protein biosynthesis is a core biological process, occurring inside cells, balancing the loss of cellular proteins through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critical functions as enzymes, structural proteins or hormones. Protein synthesis is a very similar process for both prokaryotes and eukaryotes but there are some distinct differences.

In genetics, a promoter is a sequence of DNA to which proteins bind to initiate transcription of a single RNA transcript from the DNA downstream of the promoter. The RNA transcript may encode a protein (mRNA), or can have a function in and of itself, such as tRNA or rRNA. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, upstream on the DNA . Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long, the sequence of which is highly dependent on the gene and product of transcription, type or class of RNA polymerase recruited to the site, and species of organism.
The central dogma of molecular biology deals with the flow of genetic information within a biological system. It is often stated as "DNA makes RNA, and RNA makes protein", although this is not its original meaning. It was first stated by Francis Crick in 1957, then published in 1958:
The Central Dogma. This states that once "information" has passed into protein it cannot get out again. In more detail, the transfer of information from nucleic acid to nucleic acid, or from nucleic acid to protein may be possible, but transfer from protein to protein, or from protein to nucleic acid is impossible. Information here means the precise determination of sequence, either of bases in the nucleic acid or of amino acid residues in the protein.
In genetics, an operon is a functioning unit of DNA containing a cluster of genes under the control of a single promoter. The genes are transcribed together into an mRNA strand and either translated together in the cytoplasm, or undergo splicing to create monocistronic mRNAs that are translated separately, i.e. several strands of mRNA that each encode a single gene product. The result of this is that the genes contained in the operon are either expressed together or not at all. Several genes must be co-transcribed to define an operon.

In molecular biology, RNA polymerase, or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions that synthesize RNA from a DNA template.
In genetics, a transcription terminator is a section of nucleic acid sequence that marks the end of a gene or operon in genomic DNA during transcription. This sequence mediates transcriptional termination by providing signals in the newly synthesized transcript RNA that trigger processes which release the transcript RNA from the transcriptional complex. These processes include the direct interaction of the mRNA secondary structure with the complex and/or the indirect activities of recruited termination factors. Release of the transcriptional complex frees RNA polymerase and related transcriptional machinery to begin transcription of new mRNAs.
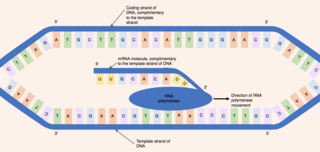
When referring to DNA transcription, the coding strand is the DNA strand whose base sequence is identical to the base sequence of the RNA transcript produced. It is this strand which contains codons, while the non-coding strand contains anticodons. During transcription, RNA Pol II binds to the non-coding template strand, reads the anti-codons, and transcribes their sequence to synthesize an RNA transcript with complementary bases.

In molecular biology, a reading frame is a way of dividing the sequence of nucleotides in a nucleic acid molecule into a set of consecutive, non-overlapping triplets. Where these triplets equate to amino acids or stop signals during translation, they are called codons.

Exonucleases are enzymes that work by cleaving nucleotides one at a time from the end (exo) of a polynucleotide chain. A hydrolyzing reaction that breaks phosphodiester bonds at either the 3′ or the 5′ end occurs. Its close relative is the endonuclease, which cleaves phosphodiester bonds in the middle (endo) of a polynucleotide chain. Eukaryotes and prokaryotes have three types of exonucleases involved in the normal turnover of mRNA: 5′ to 3′ exonuclease (Xrn1), which is a dependent decapping protein; 3′ to 5′ exonuclease, an independent protein; and poly(A)-specific 3′ to 5′ exonuclease.

Transcriptional modification or co-transcriptional modification is a set of biological processes common to most eukaryotic cells by which an RNA primary transcript is chemically altered following transcription from a gene to produce a mature, functional RNA molecule that can then leave the nucleus and perform any of a variety of different functions in the cell. There are many types of post-transcriptional modifications achieved through a diverse class of molecular mechanisms.
Cis-regulatory elements (CREs) or cis-regulatory modules (CRMs) are regions of non-coding DNA which regulate the transcription of neighboring genes. CREs are vital components of genetic regulatory networks, which in turn control morphogenesis, the development of anatomy, and other aspects of embryonic development, studied in evolutionary developmental biology.

In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression, DNA is first copied into RNA. RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for the synthesis of a protein.
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Depending on the context, sense may have slightly different meanings. For example, the negative-sense strand of DNA is equivalent to the template strand, whereas the positive-sense strand is the non-template strand whose nucleotide sequence is equivalent to the sequence of the mRNA transcript.
In genetics, a sense strand, or coding strand, is the segment within double-stranded DNA that carries the translatable code in the 5′ to 3′ direction, and which is complementary to the antisense strand of DNA, or template strand, which does not carry the translatable code in the 5′ to 3′ direction. The sense strand is the strand of DNA that has the same sequence as the mRNA, which takes the antisense strand as its template during transcription, and eventually undergoes translation into a protein. The antisense strand is thus responsible for the RNA that is later translated to protein, while the sense strand possesses a nearly identical makeup to that of the mRNA.

Directionality, in molecular biology and biochemistry, is the end-to-end chemical orientation of a single strand of nucleic acid. In a single strand of DNA or RNA, the chemical convention of naming carbon atoms in the nucleotide pentose-sugar-ring means that there will be a 5′ end, which frequently contains a phosphate group attached to the 5′ carbon of the ribose ring, and a 3′ end, which typically is unmodified from the ribose -OH substituent. In a DNA double helix, the strands run in opposite directions to permit base pairing between them, which is essential for replication or transcription of the encoded information.

Eukaryotic transcription is the elaborate process that eukaryotic cells use to copy genetic information stored in DNA into units of transportable complementary RNA replica. Gene transcription occurs in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Unlike prokaryotic RNA polymerase that initiates the transcription of all different types of RNA, RNA polymerase in eukaryotes comes in three variations, each translating a different type of gene. A eukaryotic cell has a nucleus that separates the processes of transcription and translation. Eukaryotic transcription occurs within the nucleus where DNA is packaged into nucleosomes and higher order chromatin structures. The complexity of the eukaryotic genome necessitates a great variety and complexity of gene expression control.
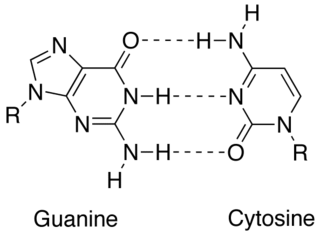
In molecular biology, complementarity describes a relationship between two structures each following the lock-and-key principle. In nature complementarity is the base principle of DNA replication and transcription as it is a property shared between two DNA or RNA sequences, such that when they are aligned antiparallel to each other, the nucleotide bases at each position in the sequences will be complementary, much like looking in the mirror and seeing the reverse of things. This complementary base pairing allows cells to copy information from one generation to another and even find and repair damage to the information stored in the sequences.
This glossary of cellular and molecular biology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts commonly used in the study of cell biology, molecular biology, and related disciplines, including molecular genetics, biochemistry, and microbiology. It is split across two articles:
This glossary of cellular and molecular biology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts commonly used in the study of cell biology, molecular biology, and related disciplines, including genetics, biochemistry, and microbiology. It is split across two articles:
References
- ↑ Harvey Lodish (2008). Molecular Cell Biology. W. H. Freeman. pp. 286–. ISBN 978-0-7167-7601-7.