
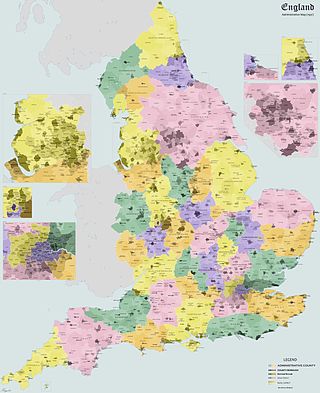
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term borough designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.

The districts of England are a level of subnational division of England used for the purposes of local government. As the structure of local government in England is not uniform, there are currently four principal types of district-level subdivision. There are a total of 296 districts made up of 36 metropolitan boroughs, 32 London boroughs, 164 two-tier non-metropolitan districts and 62 unitary authorities, as well as the City of London and the Isles of Scilly which are also districts, but do not correspond to any of these other categories. Some districts are styled as cities, boroughs or royal boroughs; these are purely honorific titles and do not alter the status of the district or the powers of their councils. All boroughs and cities are led by a mayor who in most cases is a ceremonial figure elected by the district council, but—after local government reform—is occasionally a directly elected mayor who makes most of the policy decisions instead of the council.

Until 1974, Denbighshire, or the County of Denbigh, was an administrative county in the north of Wales, later classed as one of the thirteen historic counties of Wales. It was a maritime county, that was bounded to the north by the Irish Sea, to the east by Flintshire, Cheshire and Shropshire, to the south by Montgomeryshire and Merionethshire, and to the west by Caernarfonshire.
A rural district was a type of local government area – now superseded – established at the end of the 19th century in England, Wales, and Ireland for the administration of predominantly rural areas at a level lower than that of the administrative counties.

In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government. Civil parishes can trace their origin to the ancient system of parishes, which for centuries were the principal unit of secular and religious administration in most of England and Wales. Civil and religious parishes were formally split into two types in the 19th century and are now entirely separate. Civil parishes in their modern form came into being through the Local Government Act 1894, which established elected parish councils to take on the secular functions of the parish vestry.
A county council is the elected administrative body governing an area known as a county. This term has slightly different meanings in different countries.

A municipal borough was a type of local government district which existed in England and Wales between 1836 and 1974, in Northern Ireland from 1840 to 1973 and in the Republic of Ireland from 1840 to 2002. Broadly similar structures existed in Scotland from 1833 to 1975 with the reform of royal burghs and creation of police burghs.

The Local Government Act 1894 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales outside the County of London. The Act followed the reforms carried out at county level under the Local Government Act 1888. The 1894 legislation introduced elected councils at district and parish level.
Sanitary districts were established in England and Wales in 1872 and in Ireland in 1878. The districts were of two types, based on existing structures:

The Local Government Act 1929 was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that made changes to the Poor Law and local government in England and Wales.

The Local Government Act 1958 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom affecting local government in England and Wales outside London. Among its provisions it included the establishment of Local Government Commissions to review the areas and functions of local authorities, and introduced new procedures for carrying these into action.

The Local Government Act 1933 was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that consolidated and revised existing legislation that regulated local government in England and Wales. It remained the principal legislation regulating local government until the Local Government Act 1972 took effect in 1974.

The County Borough of Leeds, and its predecessor, the Municipal Borough of Leeds, was a local government district in the West Riding of Yorkshire, England, from 1835 to 1974. Its origin was the ancient borough of Leeds, which was reformed by the Municipal Corporations Act 1835. In 1889, when West Riding County Council was formed, Leeds became a county borough outside the administrative county of the West Riding; and in 1893 the borough gained city status. The borough was extended a number of times, expanding from 21,593 acres (8,738 ha) in 1911 to 40,612 acres (16,435 ha) in 1961; adding in stages the former area of Roundhay, Seacroft, Shadwell and Middleton parishes and gaining other parts of adjacent districts. In 1971 Leeds was the fifth largest county borough by population in England. The county borough was abolished in 1974 and replaced with the larger City of Leeds, a metropolitan district of West Yorkshire.
Borough status is granted by royal charter to local government districts in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. The status is purely honorary, and does not give any additional powers to the council or inhabitants of the district. In Scotland, similarly chartered communities were known as royal burghs, although the status is no longer granted.
Successor parishes are civil parishes with a parish council, created in England in 1974. They replaced, with the same boundaries, a selected group of urban districts and municipal boroughs: a total of 300 successor parishes were formed from the former areas of 78 municipal boroughs and 221 urban districts.
The history of local government in England is one of gradual change and evolution since the Middle Ages. England has never possessed a formal written constitution, with the result that modern administration is based on precedent, and is derived from administrative powers granted to older systems, such as that of the shires.
Boards of improvement commissioners were ad hoc urban local government boards created during the 18th and 19th centuries in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and its predecessors the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland. Around 300 boards were created, each by a private Act of Parliament, typically termed an Improvement Act. The powers of the boards varied according to the acts which created them. They often included street paving, cleansing, lighting, providing watchmen or dealing with various public nuisances. Those with restricted powers might be called lighting commissioners, paving commissioners, police commissioners, etc.
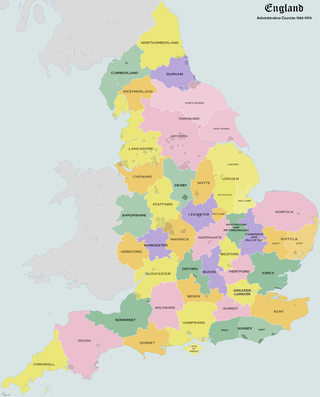
Administrative counties were subnational divisions of England used for local government from 1889 to 1974. They were created by the Local Government Act 1888, which established an elected county council for each area. Some geographically large historic counties were divided into several administrative counties, each with its own county council. The administrative counties operated until 1974, when they were replaced by a system of metropolitan and non-metropolitan counties under the Local Government Act 1972.
The History of local government districts in Buckinghamshire began in 1835 with the formation of poor law unions. This was followed by the creation of various forms of local government body. In 1894 the existing arrangements were replaced with a system of municipal boroughs, urban and rural districts, which remained in place until 1974.

A civil parish is a country subdivision, forming the lowest unit of local government in England. There are 218 civil parishes in the ceremonial county of Cornwall, which includes the Isles of Scilly. The county is effectively parished in its entirety; only the unpopulated Wolf Rock is unparished. At the 2001 census, there were 501,267 people living in the current parishes, accounting for the whole of the county's population. The final unparished areas of mainland Cornwall, around St Austell, were parished on 1 April 2009 to coincide with the structural changes to local government in England.











