
Lobopodians are members of the informal group Lobopodia, or the formally erected phylum Lobopoda Cavalier-Smith (1998). They are panarthropods with stubby legs called lobopods, a term which may also be used as a common name of this group as well. While the definition of lobopodians may differ between literatures, it usually refers to a group of soft-bodied, marine worm-like fossil panarthropods such as Aysheaia and Hallucigenia. However, other genera like Kerygmachela and Pambdelurion are often referred to as “gilled lobopodians”.

Opabinia regalis is an extinct, stem group arthropod found in the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale Lagerstätte of British Columbia. Opabinia was a soft-bodied animal, measuring up to 7 cm in body length, and its segmented trunk had flaps along the sides and a fan-shaped tail. The head shows unusual features: five eyes, a mouth under the head and facing backwards, and a clawed proboscis that probably passed food to the mouth. Opabinia probably lived on the seafloor, using the proboscis to seek out small, soft food. Fewer than twenty good specimens have been described; 3 specimens of Opabinia are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they constitute less than 0.1% of the community.

Aysheaia is an extinct genus of soft-bodied lobopodian, known from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada

Dinocaridida is a proposed fossil taxon of basal arthropods, which flourished during the Cambrian period and survived up to Early Devonian. Characterized by a pair of frontal appendages and series of body flaps, the name of Dinocaridids refers to the suggested role of some of these members as the largest marine predators of their time. Dinocaridids are occasionally referred to as the 'AOPK group' by some literatures, as the group compose of Radiodonta, Opabiniidae, and the "gilled lobopodians" Pambdelurion and Kerygmachelidae. It is most likely paraphyletic, with Kerygmachelidae and Pambdelurion more basal than the clade compose of Opabiniidae, Radiodonta and other arthropods.

Anomalocaris is an extinct genus of radiodont, an order of early-diverging stem-group marine arthropods.

Kerygmachela kierkegaardi is a kerygmachelid gilled lobopodian from the Cambrian Stage 3 aged Sirius Passet Lagerstätte in northern Greenland. Its anatomy strongly suggests that it, along with its relative Pambdelurion whittingtoni, was a close relative of radiodont and euarthropods. The generic name "Kerygmachela" derives from the Greek words Kerygma (proclamation) and Chela (claw), in reference to the flamboyant frontal appendages. The specific name, "kierkegaardi" honors Danish philosopher Søren Kierkegaard.
A number of assemblages bear fossil assemblages similar in character to that of the Burgess Shale. While many are also preserved in a similar fashion to the Burgess Shale, the term "Burgess Shale-type fauna" covers assemblages based on taxonomic criteria only.

The Wheeler Shale is a Cambrian (c. 507 Ma) fossil locality world-famous for prolific agnostid and Elrathia kingii trilobite remains and represents a Konzentrat-Lagerstätte. Varied soft bodied organisms are locally preserved, a fauna and preservation style normally associated with the more famous Burgess Shale. As such, the Wheeler Shale also represents a Konservat-Lagerstätten.

Hadranax is a genus of large lobopodian known from the lower Cambrian Sirius Passet Lagerstätte. This genus is characterized from other lobopodians due to multiple groups of four nodes running along its trunk region, similar to Kerygmachela, and a pair of extremely large frontal appendages that were possibly as long as the animal's entire body. This lobopodian is one of the rarer members of the Sirius Passet fauna, with only around three fragmentary specimens being known.

Radiodonta is an extinct order of stem-group arthropods that was successful worldwide during the Cambrian period. Radiodonts are distinguished by their distinctive frontal appendages, which are morphologically diverse and were used for a variety of functions. Radiodonts were among the earliest large predators, but they also included sediment sifters and filter feeders. Some of the most famous species of radiodonts are the Cambrian taxa Anomalocaris canadensis, Hurdia victoria, Peytoia nathorsti, Titanokorys gainesi, Cambroraster falcatus and Amplectobelua symbrachiata. The later surviving members include the subfamily Aegirocassisinae from the Early Ordovician of Morocco and the Early Devonian member Schinderhannes bartelsi from Germany.

Hurdia is an extinct genus of hurdiid radiodont that lived 505 million years ago during the Cambrian Period. Fossils have been found in North America, China and the Czech Republic.

Stanleycaris is an extinct genus of hurdiid radiodont from the Cambrian. The type species is Stanleycaris hirpex. Stanleycaris was described from the Stephen Formation near the Stanley Glacier and Burgess Shale locality of Canada, as well as Wheeler Formation of United States. A second species, S. qingjiangensis is known from the Qingjiang biota of China. The genus was characterized by the rake-like frontal appendages with robust inner spines.

Cucumericrus ("cucumber-leg") is an extinct genus of stem-arthropod. The type and only species is Cucumericrus decoratus, with fossils discovered from the Maotianshan Shales of Yunnan, China.

Caryosyntrips ("nutcracker") is an extinct genus of stem-arthropod which known from Canada, United States and Spain during the middle Cambrian. It was first named by Allison C. Daley and Graham E. Budd in 2010, being the type species Caryosyntrips serratus.

Diania is an extinct genus of lobopodian panarthropod found in the Lower Cambrian Maotianshan shale of China, represented by a single species - D. cactiformis. Known during its investigation by the nickname "walking cactus", this organism belongs to a group known as the armoured lobopodians, and has a simple worm-like body with robust, spiny legs. Initially, the legs were thought to have a jointed exoskeleton and Diania was suggested to be evolutionarily close to early arthropods, but many later studies have rejected this interpretation.
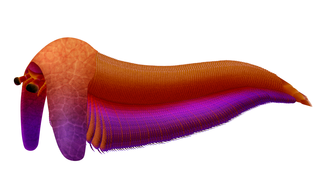
Erratus is an extinct genus of marine arthropod from the Cambrian of China. Its type and only species is Erratus sperare. Erratus is likely one of the most basal known arthropods, and its discovery has helped scientists understand the early evolution of arthropod trunk appendages. Some of the stem-arthropods like radiodonts did not have legs, instead they had flap like appendages that helped them swim. Erratus on the other hand had not only flaps but also a set of primitive legs. It also supported the theory that the gills of aquatic arthropods probably evolved into the wings and lungs of terrestrial arthropods later in the Paleozoic.
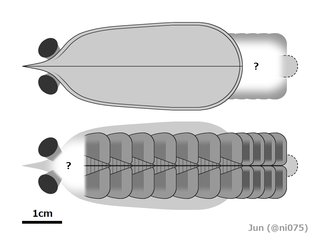
Balhuticaris is a genus of extinct bivalved hymenocarine arthropod that lived in the Cambrian aged Burgess Shale in what is now British Columbia around 506 million years ago. This extremely multisegmented arthropod is the largest member of the group, and it was even one of the largest animals of the Cambrian, with individuals reaching lengths of 245 mm (9 in). Fossils of this animal suggests that gigantism occurred in more groups of Arthropoda than had been previously thought. It also presents the possibility that bivalved arthropods were very diverse, and filled in a lot of ecological niches.

Parvibellus is an extinct genus of panarthropod animal known from the Cambrian of China. It is known from only a single species, P. atavus, found in the Cambrian Stage 3 aged Chengjiang Biota of Yunnan, China.

Kerygmachelidae is a family of gilled lobopodians from the Cambrian period. Currently three genera are included in the family: Kerygmachela from the lower Cambrian of Greenland, Utahnax from the middle Cambrian of Utah, and Mobulavermis from the lower-middle Cambrian of Nevada. These animals are characterized by well developed frontal appendages similar to other dinocaridids like the radiodonts, except the ones present in these genera are horizontal to one another, and do not curve downward. These animals were most likely nektonic predators, using their large trunk flaps to swim in the water column, and using their frontal appendages to grab small-sized prey. Unlike other groups referred to as Lobopodians, this family lacks the distinctive legs (lobopods) that are usually seen in Lobopodian groups.

Mobulavermis is an extinct genus of Cambrian kerygmachelid lobopodian from the Pioche Shale, the Combined Metals Member of the Pioche Formation in Nevada; USA. The type species is M. adustus, known from the holotype and paratype.





















