Utara Coal Mine is a coal mine along the Utara River of Iriomote, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan, where mining was in operation between 1935 and 1943. In 2007, it was designated as a Heritage of Industrial Modernization in Japan.
Contents


Utara Coal Mine is a coal mine along the Utara River of Iriomote, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan, where mining was in operation between 1935 and 1943. In 2007, it was designated as a Heritage of Industrial Modernization in Japan.


One of the main coal mining companies within Iriomote Island, Marumitsu Mining Company, found thick layers of coal along Utara River in 1935. Earlier, the predecessor of Marumitsu Mining Company, Takasaki Mining Company was established in 1924 by Kōichirō Noda, a contractor with 50 workers, Kimiichi Oguri, an accountant general, and Shōsaburō Takasaki, a money lender in Naha. [1] [2] The company changed their name to Marumitsu Goumei Company in 1933. First, they mined coal along Nakara River but then they investigated other areas and found good layers of coal along Utara River in 1935. In 1936, they started to mining there with a large lodging house for 400 single workers and more than 10 houses for couples. There were two thick layers of coal in the Utara Mine; one was 60 cm thick and the other 40 cm thick. Coal was sent first by Minecart and later by boat on the Utara river carrying 20 to 30 tons each. In 1938, the mine was producing 2,500 tons monthly. Facilities for workers were extraordinarily good, compared with other mines. Sanitary conditions were greatly improved; glass was used for the prevention of mosquitoes and hence malaria. There were large bathrooms, good water supplies and a doctor's office. There was a 300-seat theater for movies; and dramas were played by workers there. There were three festivals for the workers. Children were educated at a school called Midori Gakuen (Green School). However, the involvement in the Pacific War in 1941 increased the demand for coal, leading to a worsening of mining conditions; men were drafted into military service and the mining operation was discontinued in 1943. The buildings of the mine were destroyed by American air raids. The president of the company, Kōichirō Noda gave up the mine and was engaged in agriculture. The Midori School was made a forerunner to Uehara Elementary School, Taketomi, Okinawa. [3]
In 2007, the ruins of the Utara Mine were designated as a Heritage of Industrial Modernization in Japan and a road was improved.

Okinawa Prefecture is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan and has a population of 1,457,162 and a geographic area of 2,281 km2.

The Iriomote cat is a subspecies of the leopard cat that lives exclusively on the Japanese island of Iriomote. It has been listed as critically endangered on the IUCN Red List since 2008, as the only population comprises fewer than 250 adult individuals and is considered declining. As of 2007, there were an estimated 100–109 individuals remaining.
A mining accident is an accident that occurs during the process of mining minerals or metals. Thousands of miners die from mining accidents each year, especially from underground coal mining, although accidents also occur in hard rock mining. Coal mining is considered much more hazardous than hard rock mining due to flat-lying rock strata, generally incompetent rock, the presence of methane gas, and coal dust. Most of the deaths these days occur in developing countries, and rural parts of developed countries where safety measures are not practiced as fully. A mining disaster is an incident where there are five or more fatalities.
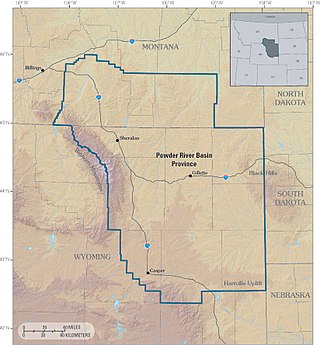
The Powder River Basin is a geologic structural basin in southeast Montana and northeast Wyoming, about 120 miles (190 km) east to west and 200 miles (320 km) north to south, known for its extensive coal reserves. The former hunting grounds of the Oglala Lakota, the area is very sparsely populated and is known for its rolling grasslands and semiarid climate.

The Nanaimo mine explosion occurred on May 3, 1887, in Nanaimo, British Columbia killing 150 miners. Only seven miners survived and the mine burned for one full day.
The history of coal mining goes back thousands of years, with early mines documented in ancient China, the Roman Empire and other early historical economies. It became important in the Industrial Revolution of the 19th and 20th centuries, when it was primarily used to power steam engines, heat buildings and generate electricity. Coal mining continues as an important economic activity today, but has begun to decline due to the strong contribution coal plays in global warming and environmental issues, which result in decreasing demand and in some geographies, peak coal.
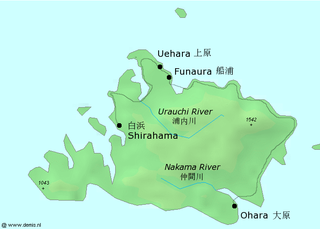
Iriomote Island is the largest of the Yaeyama Islands of Japan, and the second largest in Okinawa Prefecture after Okinawa Island itself.
Drift mining is either the mining of an ore deposit by underground methods, or the working of coal seams accessed by adits driven into the surface outcrop of the coal bed. A drift mine is an underground mine in which the entry or access is above water level and generally on the slope of a hill, driven horizontally into the ore seam.
Leigh Creek is a former coal-mining town in eastern central South Australia. At the 2016 census, Leigh Creek had a population of 245, a 55% decrease from 550 in the previous census in 2011.

Rail transport in Okinawa consists of only the Okinawa Urban Monorail, the only rail line providing rail transportation in Okinawa Prefecture. In the past, Okinawa Island had railroad, trams, and horse-drawn streetcar service. Moreover, Minamidaitōjima and other islands had rail lines to transport sugarcane and other commodities.

The West Virginia coal wars (1912–1921), also known as the mine wars, arose out of a dispute between coal companies and miners.
Calumet is a census-designated place in Mount Pleasant Township, Westmoreland County, Pennsylvania, United States. Although the United States Census Bureau included it as a census-designated place with the nearby community of Norvelt for the 2000 census, they are in reality two very different communities, each reflecting a different chapter in how the Great Depression affected rural Pennsylvanians. As of the 2010 census, Calumet-Norvelt was divided into two separate CDPs officially. Calumet was a typical "patch town," another name for a coal town, built by a single company to house coal miners as cheaply as possible. The closing of the Calumet mine during the Great Depression caused enormous hardship in an era when unemployment compensation and welfare payments were nonexistent. On the other hand, Norvelt was created during the depression by the US federal government as a model community, intended to increase the standard of living of laid-off coal miners.
The Consolidation Coal Company (CCC) was founded in 1875 in Iowa and purchased by the Chicago and North Western Railroad in 1880 in order to secure a local source of coal. The company operated in south central Iowa in Mahaska and Monroe counties until after World War I. Exhaustion of some resources, competition from overseas markets, and other changes led to the company's closing down its mines and leaving its major planned towns by the late 1920s. The CCC worked at Muchakinock in Mahaska County until the coal resources of that area were largely exhausted. In 1900, the company purchased 10,000 acres (40 km2) in southern Mahaska County and northern Monroe County, Iowa.
Corbin is a ghost town in British Columbia, Canada. It was a coal mining community located at the foot of Coal Mountain, south of the Crowsnest Pass in the southern Canadian Rockies.
The Iriomote Coal Mine was a producing coal mine in the northwestern area of Uchibanare and Iriomote Islands, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. At its peak, between 120,000 and 130,000 tons of coal were produced annually in the years 1936 and 1937 by 1,400 coal mine workers, but production ceased in 1960.
This is a list of events in the year 1894 in Japan. It corresponds to Meiji 27 (明治27年) in the Japanese calendar.

Tercio is a ghost town and former coal mine in Las Animas County, in the U.S. state of Colorado. The GNIS classifies it as a populated place. A post office called Tercio was established in 1902, and remained in operation until 1949. The community was the third coal mining community established by the Colorado Fuel and Iron company, hence the name.
In the mid-19th century, Colorado Springs was a center of mining industry activity. Coal was mined in 50 mines in the area and towns, now annexed to Colorado Springs, were established to support residents of the coal mining industry.

The Palencia mining basin is a Spanish coal mining area located on the southern slope of the Cantabrian mountain range. It owes its name to its location, in the north of the province of Palencia, in the region of Montaña Palentina. Its main exploitations are black coal and anthracite.