Related Research Articles
Spinning is the twisting technique where the fiber is drawn out, twisted, and wound onto a bobbin.

Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus Gossypium in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. Under natural conditions, the cotton bolls will increase the dispersal of the seeds.
![Textile Material produced by twining, weaving, felting, knotting, or otherwise processing [[natural or synthetic fibers]]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c5/Karachi_-_Pakistan-market.jpg/320px-Karachi_-_Pakistan-market.jpg)
A textile is a flexible material made by creating an interlocking network of yarns or threads, which are produced by spinning raw fibres into long and twisted lengths. Textiles are then formed by weaving, knitting, crocheting, knotting, tatting, felting, bonding, or braiding these yarns together.

Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibres, suitable for use in the production of textiles, sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery, or ropemaking. Thread is a type of yarn intended for sewing by hand or machine. Modern manufactured sewing threads may be finished with wax or other lubricants to withstand the stresses involved in sewing. Embroidery threads are yarns specifically designed for needlework.
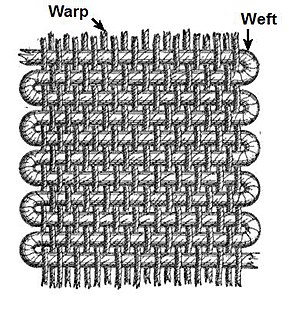
Warp and weft are the two basic components used in weaving to turn thread or yarn into fabric. The lengthwise or longitudinal warp yarns are held stationary in tension on a frame or loom while the transverse weft is drawn through and inserted over and under the warp. A single thread of the weft crossing the warp is called a pick. Terms vary. Each individual warp thread in a fabric is called a warp end or end.

Aditya Birla Management Corporation Pvt. Ltd., d/b/a Aditya Birla Group, is an Indian multinational conglomerate, headquartered in Worli, Maharashtra, India. It operates in 36 countries with more than 140,000 employees. The group was founded by Seth Shiv Narayan Birla in 1857. The group has interests in viscose staple fibre, metals, cement, viscose filament yarn, branded apparel, carbon black, chemicals, fertilisers, insulators, financial services and telecom.

Acrylic fibers are synthetic fibers made from a polymer (polyacrylonitrile) with an average molecular weight of ~100,000, about 1900 monomer units. For a fiber to be called "acrylic" in the US, the polymer must contain at least 85% acrylonitrile monomer. Typical comonomers are vinyl acetate or methyl acrylate. DuPont created the first acrylic fibers in 1941 and trademarked them under the name Orlon. It was first developed in the mid-1940s but was not produced in large quantities until the 1950s. Strong and warm acrylic fiber is often used for sweaters and tracksuits and as linings for boots and gloves, as well as in furnishing fabrics and carpets. It is manufactured as a filament, then cut into short staple lengths similar to wool hairs, and spun into yarn.

Textile manufacturing is a major industry. It is largely based on the conversion of fibre into yarn, then yarn into fabric. These are then dyed or printed, fabricated into cloth which is then converted into useful goods such as clothing, household items, upholstery and various industrial products.
The manufacture of textiles is one of the oldest of human technologies. To make textiles, the first requirement is a source of fibre from which a yarn can be made, primarily by spinning. The yarn is processed by knitting or weaving, which turns yarn into cloth. The machine used for weaving is the loom. For decoration, the process of colouring yarn or the finished material is dyeing. For more information of the various steps, see textile manufacturing.
Platt Brothers, also known as Platt Bros & Co Ltd, was a British company based at Werneth in Oldham, North West England. The company manufactured textile machinery and were iron founders and colliery proprietors. By the end of the 19th century, the company had become the largest textile machinery manufacturer in the world, employing more than 12,000 workers.

Textile fibers, threads, yarns and fabrics are measured in a multiplicity of units.

Combing is a method for preparing carded fibre for spinning. Combing is divided into linear and circular combing. The Noble comb is an example of circular combing. The French comb is an example of linear combing. The process of combing is accompanied by gilling, a process of evening out carded or combed top making it suitable for spinning. Combing separates out short fibres by means of a rotating ring or rectilinear row of steel pins. The fibres in the 'top' it produces have been straightened and lie parallel to each other. When combing wool, the discarded short fibres are called noils, and are ground up into shoddy.
Textile manufacturing is one of the oldest human activities. The oldest known textiles date back to about 5000 B.C. In order to make textiles, the first requirement is a source of fibre from which a yarn can be made, primarily by spinning. The yarn is processed by knitting or weaving to create cloth. The machine used for weaving is the loom. Cloth is finished by what are described as wet process to become fabric. The fabric may be dyed, printed or decorated by embroidering with coloured yarns.

Ainsworth Mill, Breightmet is a mercerising mill near the Breightmet neighborhood of Bolton, Greater Manchester. It was bought by the Lancashire Cotton Corporation in the 1940s as an attempt to develop a cotton finishing presence.

Thread is a type of yarn but similarly used for sewing. It can be made out of many different materials including cotton, wool, linen, nylon, and silk.

RadiciGroup is an Italian corporation with a network of production and sales sites located in Europe, North America, South America and Asia. RadiciGroup is one of the world’s leading producers of a wide range of chemical intermediates, polyamide polymers, engineering plastics, synthetic fibres and nonwovens.
The textile industry is the largest manufacturing industry in Pakistan. Pakistan is the 8th largest exporter of textile commodities in Asia. Textile sector contributes 8.5% to the GDP of Pakistan. In addition, the sector employs about 45% of the total labor force in the country. Pakistan is the 4th largest producer of cotton with the third largest spinning capacity in Asia after China and India and contributes 5% to the global spinning capacity. At present, there are 1,221 ginning units, 442 spinning units, 124 large spinning units and 425 small units which produce textile.
S. P. Oswal is an Indian industrialist and the present head of the Vardhman Group name="Vardhman">"Vardhman". Retrieved 11 August 2014.</ref> The Government of India honoured him in 2010, with the Padma Bhushan, the third highest civilian award, for his services to the fields of trade and industry.

Cotton production in Pakistan is integral to the economic development of the country. The nation is largely dependent on the cotton industry and its related textile sector, and the crop has been given a principal status in the country. Cotton is grown as an industrial crop in 15% of the nation's land during the monsoon months of May to August, known as the Kharif period, and is grown at a smaller scale between February and April. Record production of cotton was reported at 15 million bales of 470 pounds (210 kg) each in the form of phutti during 2014–15, which was an 11% rise compared to the previous season (2013–14). Production-wise, as of 2012–13, Pakistan occupied the fourth position among the cotton growers of the world, the first three being China, India and the United States, in that order. In respect of exports of raw cotton, Pakistan holds third position and is the fourth in consumption. It is the largest exporter of cotton yarn.
Ludhiana is Punjab, India city's and largest industrial hub. It is the biggest city north of Delhi. It is known for hosiery and bicycle manufacturing.
References
- ↑ "S. P. Oswal" . Retrieved 11 August 2014.
- "Vardhman Group History". Official website. 21 June 2011. Archived from the original on 21 June 2011. Retrieved 21 June 2011.
- "Vardhman Group Performance". Official website. 21 June 2011. Retrieved 30 June 2011.
- "Vardhman Group Performance". Official website. 21 June 2011. Retrieved 30 June 2011.