
The Centaur class aircraft carrier was the final iteration of the 1942 Design Light Fleet Carrier developed by the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy during the Second World War. They were designed in 1943 to operate higher-performance aircraft than the preceding Majestic-class aircraft carrier. Four ships were laid down in 1944-1945 and completed in 1953-1959. Rapid developments in carrier warfare and technology overtook the ships even as they were under construction, and the associated costs of modernization led to ships being completed to different specifications. Only the last ship, HMS Hermes (R12), was fitted as a modern fixed-wing carrier; she was also the last of the class to retire in 2017 as INS Viraat.

HMS Boscawan was a 70-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 3 April 1844 at Woolwich Dockyard. She was originally ordered in 1812 and begun as a 74-gun Vengeur-class ship of the line, but the order was cancelled and her frames placed instorage; an Admiralty order dated 3 March 1834 required that those frames be reworked to Sir William Symonds' design. She was named for Admiral Edward Boscawen.

The Thornycroft type leader or Shakespeare class were a class of five destroyer leaders designed by John I. Thornycroft & Company and built by them at Woolston, Southampton for the Royal Navy towards the end of World War I. They were named after historical naval leaders. Only Shakespeare and Spenser were completed in time for wartime service. The other three were completed after the war, Broke and Keppel after being towed to Royal dockyards for completion, and two further ships - Saunders and Spragge - were cancelled. The function of a leader was to carry the flag staff of a destroyer flotilla, therefore they were enlarged to carry additional crew, offices and signalling equipment, allowing a fifth gun to be carried. These ships were very similar to the Admiralty type leader, but had Thornycroft design characteristics, the most noticeable being the broad, slab-sided funnels.

The Océan-class ships of the line were a series of 118-gun three-decker ships of the line of the French Navy, designed by engineer Jacques-Noël Sané. Fifteen were completed from 1788 on, with the last one entering service in 1854; a sixteenth was never completed, and four more were never laid down.

The Caledonia-class ships of the line were a class of nine 120-gun first rates, designed for the Royal Navy by Sir William Rule. A tenth ship was ordered on 29 October 1827 to the same design, but was launched in 1833 as Queen to a fresh design by Sir William Symonds.

The Nelson-class ships of the line were a class of three 120-gun first rates, designed for the Royal Navy as a joint effort between the two Surveyors of the Navy at the time, Robert Seppings and Joseph Tucker.

HMS Vindictive was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built by Nicholas Diddams at Portsmouth Dockyard and launched on 30 November 1813 at Portsmouth.

The Téméraire-class ships of the line were a class of a hundred and twenty 74-gun ships of the line ordered between 1782 and 1813 for the French navy or its attached navies in dependent (French-occupied) territories. Although a few of these were cancelled, the type was and remains the most numerous class of capital ship ever built to a single design.

The Cherokee class was a class of brig-sloops of the Royal Navy, mounting ten guns. Brig-sloops were sloops-of-war with two masts rather than the three masts of ship sloops. Orders for 115 vessels were placed, including five which were cancelled and six for which the orders were replaced by ones for equivalent steam-powered paddle vessels.

The Cruizer class was an 18-gun class of brig-sloops of the Royal Navy. Brig-sloops were the same as ship-sloops except for their rigging. A ship-sloop was rigged with three masts whereas a brig-sloop was rigged as a brig with only a fore mast and a main mast.

The Lively class were a successful class of sixteen British Royal Navy 38-gun sailing frigates.

The Banterer-class sailing sixth rates were a series of six 22-gun post ships built to an 1805 design by Sir William Rule, which served in the Royal Navy during the Napoleonic War. The first four were launched in 1806 and the remaining two in 1807. One ship – the Banterer – was lost in 1808 and another – the Cyane – captured by the United States Navy in 1815; the remaining four were all deleted during 1816.

The Seringapatam-class frigates, were a class of British Royal Navy 46-gun sailing frigates.
The Apollo-class sailing frigates were a series of twenty-seven ships that the British Admiralty commissioned be built to a 1798 design by Sir William Rule. Twenty-five served in the Royal Navy during the Napoleonic Wars, two being launched too late.
HMS Constant was an Archer–class gun-brig of the Royal Navy, launched in 1801 for service against the French during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. She was variously stationed in English home waters, the Baltic, the Caribbean, and off the coast of Spain, and was responsible for the capture of at least seven enemy vessels during her fifteen years at sea. The Royal Navy sold Constant at Chatham Dockyard in 1816.
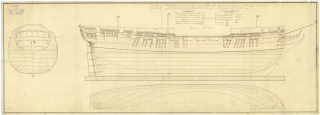
The Thames-class frigate was a 32-gun fifth-rate frigate class of eight ships of the Royal Navy based on the Richmond-class frigate designed by William Bately. The ships were ordered to the older design, which was of a smaller type of ship compared to more modern designs, so that they could be built quickly and cheaply in time to assist in defending against Napoleon's expected invasion of Britain. The class received several design changes to the Richmond class, being built of fir instead of oak, with these changes making the class generally slower and less weatherly than their predecessors, especially when in heavy weather conditions. The first two ships of the class, Pallas and Circe, were ordered on 16 March 1804 with two more ordered on 1 May and the final four on 12 July. The final ship of the class, Medea, was cancelled on 22 October before construction could begin but the other seven ships of the class were commissioned between 1804 and 1806.

The Perseverance-class frigate was a 36-gun, later 42-gun, 18-pounder fifth-rate frigate class of twelve ships of the Royal Navy, constructed in two batches. Designed by Surveyor of the Navy Sir Edward Hunt the first iteration, consisting of four ships, was constructed as a rival to the similar Flora-class frigate. Strongly built ships, the Perseverance class provided favourable gunnery characteristics and was highly manoeuvrable, but bought these traits with a loss of speed. The name ship of the class, Perseverance, was ordered in 1779 and participated in the American Revolutionary War, but her three sister ships were constructed too late to take part. The class continued in service after the war, but soon became outdated.
Nicholas Diddams (c.1760–1823) was a Master Shipwright mainly building for the Royal Navy.















