
Herpetology is a branch of zoology concerned with the study of amphibians and reptiles. Birds, which are cladistically included within Reptilia, are traditionally excluded here; the separate scientific study of birds is the subject of ornithology.

The tiger snake is a large and highly venomous snake of southern Australia, including its coastal islands and Tasmania. These snakes are often observed and locally well known by their banding, black and yellow like a tiger, although the species can be highly variable in coloration and patterning. All populations are classified within the genus Notechis (Elapidae). Their diverse characteristics have been classified either as distinct species or by subspecies and regional variation.

East Sister Island is a 15 hectare island in Ontario, Canada, located within Lake Erie. It has no long-term human population and is maintained as a Provincial Nature Reserve.

Leptophis ahaetulla, commonly known as the lora or parrot snake, is a species of medium-sized slender snake of the family Colubridae. The species is native to Central America and northern South America.

The eastern brown snake, often referred to as the common brown snake, is a species of extremely venomous snake in the family Elapidae. The species is native to eastern and central Australia and southern New Guinea. It was first described by André Marie Constant Duméril, Gabriel Bibron, and Auguste Duméril in 1854. The adult eastern brown snake has a slender build and can grow to 2 m (7 ft) in length. The colour of its surface ranges from pale brown to black, while its underside is pale cream-yellow, often with orange or grey splotches. The eastern brown snake is found in most habitats except dense forests, often in farmland and on the outskirts of urban areas, as such places are populated by its main prey, the house mouse. The species is oviparous. The International Union for Conservation of Nature classifies the snake as a least-concern species, though its status in New Guinea is unclear.

The queen snake is a species of nonvenomous semiaquatic snake, a member of the subfamily Natricinae of the family Colubridae. The species is endemic to North America.

Gerarda prevostiana, commonly known as the cat-eyed water snake, Gerard's water snake, and the glossy marsh snake, is a species of snake in the family Homalopsidae. The species is endemic to Asia. It is the only species in the genus Gerarda.

Günther's black snake is a species of poorly known lamprophiid snake endemic to central Africa. It is the only member of the genus, Bothrolycus. This snake is notable as one of the few snakes with notable sexual dimorphism, as well as possessing a small pit anterior to the eye. While superficially similar to the thermal pits of vipers, its function remains unknown.

The smooth earth snake is a species of nonvenomous natricine colubrid snake native to the eastern half of the United States.

Snakes, like other reptiles, have skin covered in scales. Snakes are entirely covered with scales or scutes of various shapes and sizes, known as snakeskin as a whole. A scale protects the body of the snake, aids it in locomotion, allows moisture to be retained within, alters the surface characteristics such as roughness to aid in camouflage, and in some cases even aids in prey capture. The simple or complex colouration patterns are a property of the underlying skin, but the folded nature of scaled skin allows bright skin to be concealed between scales then revealed in order to startle predators.

In snakes, the dorsal scales are the longitudinal series of plates that encircle the body, but do not include the ventral scales.

In snakes, the anal scale or anal plate is the scale just in front of and covering the cloacal opening. This scale can be either single or paired. When paired, the division is oblique. The anal scale is preceded by the ventral scales and followed by the subcaudal scales.
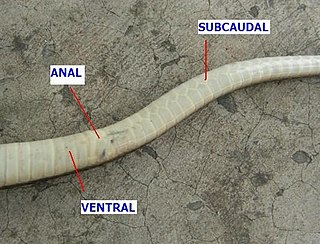
In snakes, the subcaudal scales are the enlarged plates on the underside of the tail. These scales may be either single or divided (paired) and are preceded by the anal scale.

The Chinese cobra, also called the Taiwan cobra, is a species of cobra in the family Elapidae, found mostly in southern China and a couple of neighboring nations and islands. It is one of the most prevalent venomous snakes in China, which has caused many snakebite incidents to humans.

The many-banded krait, also known as the Taiwanese krait or the Chinese krait, is a highly venomous species of elapid snake found in much of central and southern China and Southeast Asia. The species was first described by the scientist Edward Blyth in 1861. Averaging 1 to 1.5 m in length, it is a black or bluish-black snake with many white bands across its body. The many-banded krait mostly inhabits marshy areas throughout its geographical distribution, though it does occur in other habitat types.

The crayfish snake, also known commonly as the glossy crayfish snake, the glossy swampsnake, the glossy water snake, and the striped water snake, is a species of semiaquatic snake in the subfamily Natricinae of the family Colubridae. The species is endemic to the southeastern United States, and preys mainly on crayfish.

In snakes, the paraventral scales are the longitudinal rows of dorsal scales that contact the ventral scales. These are the first rows of dorsal scales on either side of the body and are usually slightly larger than the scales located more dorsally. In species that have mostly keeled scales, the paraventrals are usually smooth or only weakly keeled.

Atractaspis aterrima, commonly known as the slender burrowing asp or mole viper, is a species of fossorial, venomous snake in the family Atractaspididae. The specific epithet, aterrima, meaning "blackest", is the superlative form of the Latin adjective ater, meaning "black".

The thickhead ground snake is a nonvenomous colubrid snake species, with no recognized subspecies, endemic to central Colombia.

The desert egernia, unadorned desert-skink or desert skink is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The desert egernia is endemic to the continent of Australia, and is widespread, with populations recorded in all mainland states and territories except the Australian Capital Territory. The desert egernia is found in dry, desert areas with deep, uncompacted sandy/loamy soils and little significant vegetation cover.




















