The term carotene (also carotin, from the Latin carota, "carrot") is used for many related unsaturated hydrocarbon substances having the formula C40Hx, which are synthesized by plants but in general cannot be made by animals (with the exception of some aphids and spider mites which acquired the synthesizing genes from fungi). Carotenes are photosynthetic pigments important for photosynthesis.

Food additives are substances added to food to preserve flavor or enhance taste, appearance, or other sensory qualities. Some additives, such as vinegar (pickling), salt (salting), smoke (smoking) and sugar (crystallization), have been used for centuries to preserve food. This allows for longer-lasting foods, such as bacon, sweets or wines.
The International Numbering System for Food Additives (INS) is an international naming system for food additives, aimed at providing a short designation of what may be a lengthy actual name. It is defined by Codex Alimentarius, the international food standards organisation of the World Health Organization (WHO) and Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations (UN). The information is published in the document Class Names and the International Numbering System for Food Additives, first published in 1989, with revisions in 2008 and 2011. The INS is an open list, "subject to the inclusion of additional additives or removal of existing ones on an ongoing basis".

E numbers, short for Europe numbers, are codes for substances used as food additives, including those found naturally in many foods, such as vitamin C, for use within the European Union (EU) and European Free Trade Association (EFTA). Commonly found on food labels, their safety assessment and approval are the responsibility of the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The fact that an additive has an E number implies that its use was at one time permitted in products for sale in the European Single Market; some of these additives are no longer allowed today.

Food coloring, color additive or colorant is any dye, pigment, or substance that imparts color when it is added to food or beverages. Colorants can be supplied as liquids, powders, gels, or pastes. Food coloring is commonly used in commercial products and in domestic cooking.

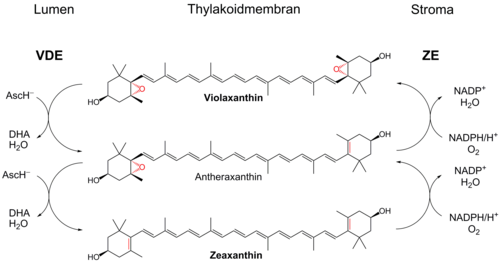
Xanthophylls are yellow pigments that occur widely in nature and form one of two major divisions of the carotenoid group; the other division is formed by the carotenes. The name is from Greek: xanthos (ξανθός), meaning "yellow", and phyllon (φύλλον), meaning "leaf"), due to their formation of the yellow band seen in early chromatography of leaf pigments.
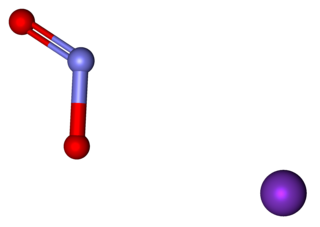
Potassium nitrite (distinct from potassium nitrate) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula KNO2. It is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ and nitrite ions NO2−, which forms a white or slightly yellow, hygroscopic crystalline powder that is soluble in water.

Sodium propanoate or sodium propionate is the sodium salt of propionic acid which has the chemical formula Na(C2H5COO). This white crystalline solid is deliquescent in moist air.

Potassium propanoate or potassium propionate has formula K(C2H5COO). Its melting point is 410 °C. It is the potassium salt of propanoic acid.

Green S is a green synthetic coal tar triarylmethane dye with the molecular formula C27H25N2O7S2Na.

Ascorbyl palmitate is an ester formed from ascorbic acid and palmitic acid creating a fat-soluble form of vitamin C. In addition to its use as a source of vitamin C, it is also used as an antioxidant food additive. It is approved for use as a food additive in the EU, the U.S., Canada, Australia, and New Zealand.

Calcium benzoate refers to the calcium salt of benzoic acid. When used in the food industry as a preservative, its E number is E213 ; it is approved for use as a food additive in the EU, USA and Australia and New Zealand.

Calcium ascorbate is a compound with the molecular formula CaC12H14O12. It is the calcium salt of ascorbic acid, one of the mineral ascorbates. It is approximately 10% calcium by mass.

Sodium ascorbate is one of a number of mineral salts of ascorbic acid (vitamin C). The molecular formula of this chemical compound is C6H7NaO6. As the sodium salt of ascorbic acid, it is known as a mineral ascorbate. It has not been demonstrated to be more bioavailable than any other form of vitamin C supplement.
β-Cryptoxanthin is a natural carotenoid pigment. It has been isolated from a variety of sources including the fruit of plants in the genus Physalis, orange rind, winter squashes such as butternut, papaya, egg yolk, butter, apples, and bovine blood serum.

Flavoxanthin is a natural xanthophyll pigment with a golden-yellow color found in small quantities in a variety of plants. As a food additive it used under the E number E161a as a food coloring although it is not approved for use in the EU or USA. It is listed as food additive 161a in Australia and New Zealand where it is approved for usage as an ingredient in food products.
Rubixanthin, or natural yellow 27, is a natural xanthophyll pigment with a red-orange color found in rose hips. As a food additive it used under the E number E161d as a food coloring; it is not approved for use in the USA or EU but is approved in Australia and New Zealand where it is listed as 161d.
Rhodoxanthin is a xanthophyll pigment with a purple color that is found in small quantities in a variety of plants including Taxus baccata and Lonicera morrowii. It is also found in the feathers of some birds. As a food additive it is used under the E number E161f as a food coloring. It is not approved for use in the EU or US; however, it is approved in Australia and New Zealand.
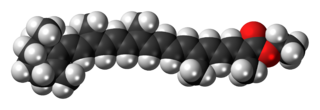
Food orange 7, the ethyl ester of beta-apo-8'-carotenic acid, is a carotenoid with an orange-red color. It is found in small quantities in some plants, but is often produced commercially from apocarotenal (E160e). It is used as a food coloring under the E number E160f and is approved for use in Australia and New Zealand. It was approved for use in the EU, but was delisted in November 2011 as it was no longer being manufactured.

Anthocyanins, also called anthocyans, are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that, depending on their pH, may appear red, purple, blue, or black. In 1835, the German pharmacist Ludwig Clamor Marquart named a chemical compound that gives flowers a blue color, Anthokyan, in his treatise "Die Farben der Blüthen". Food plants rich in anthocyanins include the blueberry, raspberry, black rice, and black soybean, among many others that are red, blue, purple, or black. Some of the colors of autumn leaves are derived from anthocyanins.