Related Research Articles

The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of Lentivirus that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive. Without treatment, the average survival time after infection with HIV is estimated to be 9 to 11 years, depending on the HIV subtype.
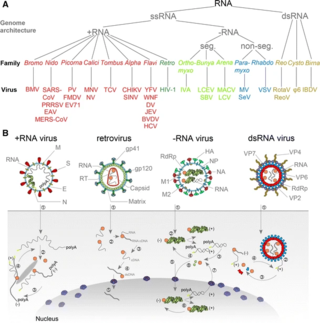
An RNA virus is a virus—other than a retrovirus—that has ribonucleic acid (RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include the common cold, influenza, SARS, MERS, COVID-19, Dengue Virus, hepatitis C, hepatitis E, West Nile fever, Ebola virus disease, rabies, polio, mumps, and measles.

Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials, a larger group which also includes antibiotic, antifungal and antiparasitic drugs, or antiviral drugs based on monoclonal antibodies. Most antivirals are considered relatively harmless to the host, and therefore can be used to treat infections. They should be distinguished from virucides, which are not medication but deactivate or destroy virus particles, either inside or outside the body. Natural virucides are produced by some plants such as eucalyptus and Australian tea trees.

Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection period, people often have mild or no symptoms. Early symptoms can include fever, dark urine, abdominal pain, and yellow tinged skin. The virus persists in the liver, becoming chronic, in about 70% of those initially infected. Early on, chronic infection typically has no symptoms. Over many years however, it often leads to liver disease and occasionally cirrhosis. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will develop serious complications such as liver failure, liver cancer, or dilated blood vessels in the esophagus and stomach.
Hepatitis D is a type of viral hepatitis caused by the hepatitis delta virus (HDV). HDV is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E. HDV is considered to be a satellite because it can propagate only in the presence of the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Transmission of HDV can occur either via simultaneous infection with HBV (coinfection) or superimposed on chronic hepatitis B or hepatitis B carrier state (superinfection).
Coinfection is the simultaneous infection of a host by multiple pathogen species. In virology, coinfection includes simultaneous infection of a single cell by two or more virus particles. An example is the coinfection of liver cells with hepatitis B virus and hepatitis D virus, which can arise incrementally by initial infection followed by superinfection.

The hepatitis E virus (HEV) is the causative agent of hepatitis E. It is of the species Orthohepevirus A.

Martin Andreas Nowak is an Austrian-born professor of mathematics and biology at Harvard University. He is one of the leading researchers in evolutionary dynamics. Nowak has made contributions to the fields of evolutionary theory, cooperation, viral dynamics, and cancer dynamics.
GB virus C (GBV-C), formerly known as hepatitis G virus (HGV) and also known as human pegivirus – HPgV is a virus in the family Flaviviridae and a member of the Pegivirus, is known to infect humans, but is not known to cause human disease. Reportedly, HIV patients coinfected with GBV-C can survive longer than those without GBV-C, but the patients may be different in other ways. Research is active into the virus' effects on the immune system in patients coinfected with GBV-C and HIV.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) co-infection is a multi-faceted, chronic condition that significantly impacts public health. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 2 to 15% of those infected with HIV are also affected by HCV, increasing their risk of morbidity and mortality due to accelerated liver disease. The burden of co-infection is especially high in certain high-risk groups, such as intravenous drug users and men who have sex with men. These individuals who are HIV-positive are commonly co-infected with HCV due to shared routes of transmission including, but not limited to, exposure to HIV-positive blood, sexual intercourse, and passage of the Hepatitis C virus from mother to infant during childbirth.
A viral quasispecies is a population structure of viruses with a large number of variant genomes. Quasispecies result from high mutation rates as mutants arise continually and change in relative frequency as viral replication and selection proceeds.

A virus is a tiny infectious agent that reproduces inside the cells of living hosts. When infected, the host cell is forced to rapidly produce thousands of identical copies of the original virus. Unlike most living things, viruses do not have cells that divide; new viruses assemble in the infected host cell. But unlike simpler infectious agents like prions, they contain genes, which allow them to mutate and evolve. Over 4,800 species of viruses have been described in detail out of the millions in the environment. Their origin is unclear: some may have evolved from plasmids—pieces of DNA that can move between cells—while others may have evolved from bacteria.
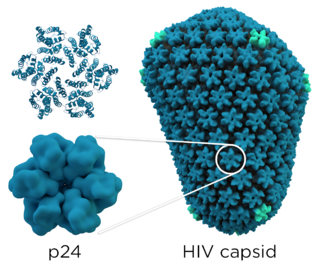
The P24 capsid protein is the most abundant HIV protein with each virus containing approximately 1,500 to 3,000 p24 molecules. It is the major structural protein within the capsid, and it is involved in maintaining the structural integrity of the virus and facilitating various stages of the viral life cycle, including viral entry into host cells and the release of new virus particles. Detection of p24 protein is used in various diagnostic assays, including antigen tests, to identify the presence of HIV in a person's blood. These tests are designed to detect viral antigens, such as p24, only in the acute phase of HIV infection. After approximately 50 days of infection, the p24 antigen is often cleared from the bloodstream entirely.

A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 11,000 of the millions of virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology.

Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, a species of the genus Orthohepadnavirus and a member of the Hepadnaviridae family of viruses. This virus causes the disease hepatitis B.
In biology, a pathogen, in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ.
Viral phylodynamics is defined as the study of how epidemiological, immunological, and evolutionary processes act and potentially interact to shape viral phylogenies. Since the coining of the term in 2004, research on viral phylodynamics has focused on transmission dynamics in an effort to shed light on how these dynamics impact viral genetic variation. Transmission dynamics can be considered at the level of cells within an infected host, individual hosts within a population, or entire populations of hosts.

HIV/AIDS research includes all medical research that attempts to prevent, treat, or cure HIV/AIDS, as well as fundamental research about the nature of HIV as an infectious agent and AIDS as the disease caused by HIV.

Ground squirrel hepatitis virus, abbreviated GSHV, is a partially double-stranded DNA virus that is closely related to human Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and Woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV). It is a member of the family of viruses Hepadnaviridae and the genus Orthohepadnavirus. Like the other members of its family, GSHV has high degree of species and tissue specificity. It was discovered in Beechey ground squirrels, Spermophilus beecheyi, but also infects Arctic ground squirrels, Spermophilus parryi. Commonalities between GSHV and HBV include morphology, DNA polymerase activity in genome repair, cross-reacting viral antigens, and the resulting persistent infection with viral antigen in the blood (antigenemia). As a result, GSHV is used as an experimental model for HBV.
In the field of epidemiology, source attribution refers to a category of methods with the objective of reconstructing the transmission of an infectious disease from a specific source, such as a population, individual, or location. For example, source attribution methods may be used to trace the origin of a new pathogen that recently crossed from another host species into humans, or from one geographic region to another. It may be used to determine the common source of an outbreak of a foodborne infectious disease, such as a contaminated water supply. Finally, source attribution may be used to estimate the probability that an infection was transmitted from one specific individual to another, i.e., "who infected whom".
References
- 1 2 Nowak, Martin; May, Robert (2001). Virus Dynamics: mathematical principles of immunology and virology. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780198504177. Archived from the original on 13 February 2015. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- ↑ Perelson, Alan S; Ribeiro, Ruy M (2013). "Modeling the within-host dynamics of HIV infection". BMC Biology. 11 (1): 96. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-11-96 . PMC 3765939 . PMID 24020860.
- ↑ Nowak, MA; Bonhoeffer, S; Hill, AM; Boehme, R; Thomas, HC; McDade, H (1996). "Viral dynamics in hepatitis B virus infection". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 93 (9): 4398–4402. Bibcode:1996PNAS...93.4398N. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.9.4398 . PMC 39549 . PMID 8633078.
- ↑ Ciupe, SM; Ribeiro, RM; Nelson, PW; Perelson, AS (2007). "Modeling the mechanisms of acute hepatitis B virus infection". Journal of Theoretical Biology. 247 (1): 23–35. Bibcode:2007JThBi.247...23C. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2007.02.017. PMC 1994818 . PMID 17428501.
- ↑ Neumann, A; Lam, NP; Dahari, H; Gretch, DR; Wiley, TE; Layden, TJ; Perelson, AS (1998). "Hepatitis C Viral Dynamics in Vivo and the Antiviral Efficacy of Interferon-α Therapy". Science. 282 (5386): 103–107. Bibcode:1998Sci...282..103N. doi:10.1126/science.282.5386.103. PMID 9756471.
- ↑ Chatterjee, A; Smith, PF; Perelson, AS (2013). "Hepatitis C Viral Kinetics: The Past, Present, and Future". Clinics in Liver Disease. 17 (1): 13–26. doi:10.1016/j.cld.2012.09.003. PMC 3584572 . PMID 23177280.