
AutoCAD is a 2D and 3D computer-aided design (CAD) software application developed by Autodesk. It was first released in December 1982 for the CP/M and IBM PC platforms as a desktop app running on microcomputers with internal graphics controllers. Initially a DOS application, subsequent versions were later released for other platforms including Classic Mac OS (1992), Microsoft Windows (1993) and macOS (2010), iOS (2010), and Android (2011).

Adobe Illustrator is a vector graphics editor and design software developed and marketed by Adobe. Originally designed for the Apple Macintosh, development of Adobe Illustrator began in 1985. Along with Creative Cloud, Illustrator CC was released. The latest version, Illustrator 2025, was released on October 14, 2024, and is the 29th generation in the product line. Adobe Illustrator was reviewed as the best vector graphics editing program in 2021 by hpMagazine.
Autodesk, Inc. is an American multinational software corporation that provides software products and services for the architecture, engineering, construction, manufacturing, media, education, and entertainment industries. Autodesk is headquartered in San Francisco, California, and has offices worldwide. Its U.S. offices are located in the states of California, Oregon, Colorado, Texas, Michigan, New Hampshire and Massachusetts. Its Canada offices are located in the provinces of Ontario, Quebec, and Alberta.
Spatial network analysis software packages are analytic software used to prepare graph-based analysis of spatial networks. They stem from research fields in transportation, architecture, and urban planning. The earliest examples of such software include the work of Garrison (1962), Kansky (1963), Levin (1964), Harary (1969), Rittel (1967), Tabor (1970) and others in the 1960s and 70s. Specific packages address their domain-specific needs, including TransCAD for transportation, GIS for planning and geography, and Axman for Space syntax researchers.

Rhinoceros is a commercial 3D computer graphics and computer-aided design (CAD) application software that was developed by TLM, Inc, dba Robert McNeel & Associates, an American, privately held, and employee-owned company that was founded in 1978. Rhinoceros geometry is based on the NURBS mathematical model, which focuses on producing mathematically precise representation of curves and freeform surfaces in computer graphics.

Archicad is an architectural BIM CAD software for Mac and Windows developed by the Hungarian company Graphisoft. Archicad offers computer aided solutions for common aspects of aesthetics and engineering during the design process of the built environment-buildings, interiors, urban areas, etc.

Graphisoft SE is a European multinational corporation that designs software, and is headquartered in Budapest, Hungary. As a subsidiary of Nemetschek, Graphisoft develops Building Information Modeling software products for architects, interior designers and planners. Graphisoft has subsidiaries in Germany, France, Switzerland, United States, United Kingdom, Spain, Japan and a representative office in Singapore. The company's flagship product is Archicad — an architectural design software developed since 1984 for Windows and Mac platforms.

Autodesk Revit is a building information modeling software for architects, structural engineers, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) engineers, and contractors. The original software was developed by Charles River Software, founded in 1997, renamed Revit Technology Corporation in 2000 and acquired by Autodesk in 2002. The software allows users to design a building and structure and its components in 3D, annotate the model with 2D drafting elements and access building information from the building model's database. Revit is 4D building information modeling (BIM) application capable with tools to plan and track various stages in the building's lifecycle, from concept to construction and later maintenance and/or demolition.
Open Design Alliance is a nonprofit organization creating software development kits (SDKs) for engineering applications. ODA offers interoperability tools for CAD, BIM, and Mechanical industries including .dwg, .dxf, .dgn, Autodesk Revit, Autodesk Navisworks, and .ifc files and additional tools for visualization, web development, 3D PDF publishing and modeling.

TurboCAD is a CAD software application for 2D and 3D design and drafting which runs on MacOS and Microsoft Windows operating systems.
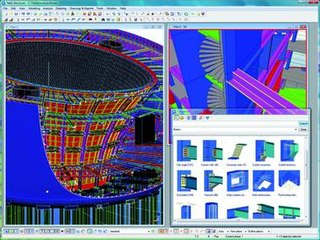
Tekla Structures is a building information modeling software able to model structures that incorporate different kinds of building materials, including steel, concrete, timber and glass. Tekla allows structural drafters and engineers to design a building structure and its components using 3D modeling, generate 2D drawings and access building information. Tekla Structures was formerly known as Xsteel.

IntelliCAD is a CAD editor and development platform with an Application Programming Interface API published by the IntelliCAD Technology Consortium ("ITC") through shared development. IntelliCAD emulates the basic interface and functions of AutoCAD, however, it is particularly able to incorporate and interchange freely between a wide variety of file types.

BricsCAD® is a software application for computer-aided design (CAD), developed by Bricsys nv. The company was founded in 2002 by Erik de Keyser, a longtime CAD entrepreneur. In 2011 Bricsys acquired the intellectual property rights from Ledas for constraints-based parametric design tools, permitting the development of applications in the areas of direct modeling and assembly design. Bricsys is headquartered in Ghent, Belgium, and has additional development centers in Nizhny Novgorod and Novosibirsk, Russia; Bucharest, Romania and Singapore. Bricsys is a founding member of the Open Design Alliance, and joined the BuildingSMART International consortium in December 2016.

ArcGIS CityEngine is a commercial three-dimensional (3D) modeling program developed by Esri R&D Center Zurich and specialises in the generation of 3D urban environments. Using a procedural modeling approach, it supports the creation of detailed large-scale 3D city models. CityEngine works with architectural object placement and arrangement in the same manner that software like VUE manages terrain, ecosystems and atmosphere mapping. Unlike the traditional 3D modeling methodology which uses Computer-Aided Design (CAD) tools and techniques, CityEngine takes a different approach to shape generation via a rule-based system. It can also use Geographic Information System (GIS) datasets due to its integration with the wider Esri/ArcGIS platform. Due to this unique feature set, CityEngine has been used in academic research and built environment professions, e.g., urban planning, architecture, visualization, game development, entertainment, archeology, military and cultural heritage. CityEngine can be used within Building Information Model (BIM) workflows as well as visualizing the data of buildings in a larger urban context, enhancing its working scenario toward real construction projects.

Grasshopper is a visual programming language and environment that runs within the Rhinoceros 3D computer-aided design (CAD) application. The program was created by David Rutten at Robert McNeel & Associates. Programs are created by dragging components onto a canvas. The outputs of these components are then connected to the inputs of subsequent components.
Chief Architect Software is a developer of 3D architectural home design software for builders, interior designers, architects, and DIY home enthusiasts. Chief Architect uses BIM tools to create a 3D model of the structure and automatically generates all of the building systems of the home. For the professional architectural and building market, it publishes the Chief Architect product line. For the consumer DIY market, it publishes the Home Designer product line.

C3D Toolkit is a proprietary cross-platform geometric modeling kit software developed by Russian C3D Labs. It's written in C++. It can be licensed by other companies for use in their 3D computer graphics software products. The most widely known software in which C3D Toolkit is typically used are computer aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and computer-aided engineering (CAE) systems.
Sonata was a 3D building design software application developed in the early 1980s and now regarded as the forerunner of today's building information modelling applications.

The BIM Collaboration Format (BCF) is a structured file format suited to issue tracking with a building information model. The BCF is designed primarily for defining views of a building model and associated information on collisions and errors connected with specific objects in the view. The BCF allows users of different BIM software, and/or different disciplines to collaborate on issues with the project. The use of the BCF to coordinate changes to a BIM is an important aspect of OpenBIM.

Vectorworks, Inc. is a U.S.-based software development company that focuses on CAD and BIM software for the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC), landscape, and entertainment industries. Vectorworks is owned by the Nemetschek Group, a multinational company. It operates as an independent subsidiary of Nemetschek Group.












