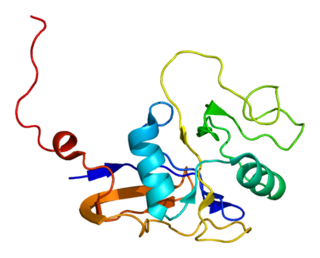
Kv7.1 (KvLQT1) is a potassium channel protein whose primary subunit in humans is encoded by the KCNQ1 gene. Kv7.1 is a voltage and lipid-gated potassium channel present in the cell membranes of cardiac tissue and in inner ear neurons among other tissues. In the cardiac cells, Kv7.1 mediates the IKs (or slow delayed rectifying K+) current that contributes to the repolarization of the cell, terminating the cardiac action potential and thereby the heart's contraction.
An internal ribosome entry site, abbreviated IRES, is an RNA element that allows for translation initiation in a cap-independent manner, as part of the greater process of protein synthesis. In eukaryotic translation, initiation typically occurs at the 5' end of mRNA molecules, since 5' cap recognition is required for the assembly of the initiation complex. The location for IRES elements is often in the 5'UTR, but can also occur elsewhere in mRNAs.

Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 1 also known as Kv1.1 is a shaker related voltage-gated potassium channel that in humans is encoded by the KCNA1 gene. The Isaacs syndrome is a result of an autoimmune reaction against the Kv1.1 ion channel.

Voltage-gated potassium channels (VGKCs) are transmembrane channels specific for potassium and sensitive to voltage changes in the cell's membrane potential. During action potentials, they play a crucial role in returning the depolarized cell to a resting state.

This family represents the internal ribosome entry site (IRES) of the hepatitis A virus. HAV IRES is a 450 nucleotide long sequence located in the 735 nt long 5’ UTR of Hepatitis A viral RNA genome. IRES elements allow cap and end-independent translation of mRNA in the host cell. The IRES achieves this by mediating the internal initiation of translation by recruiting a ribosomal 40S pre-initiation complex directly to the initiation codon and eliminates the requirement for eukaryotic initiation factor, eIF4F.
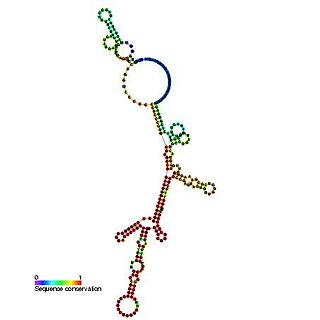
The Hepatitis C virus internal ribosome entry site, or HCV IRES, is an RNA structure within the 5'UTR of the HCV genome that mediates cap-independent translation initiation.

This family represents the Picornavirus internal ribosome entry site (IRES). IRES elements allow cap and end-independent translation of mRNA in the host cell. It has been found that La autoantigen (La) is required for Coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) IRES-mediated translation, and it has been suggested that La may be required for the efficient translation of the viral RNA in the pancreas.
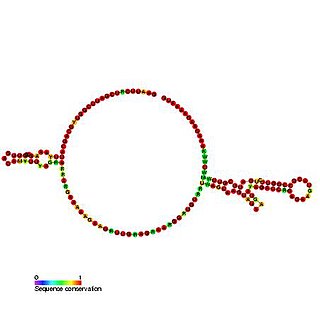
The Tobamovirus internal ribosome entry site (IRES) is an element that allows cap and end-independent translation of mRNA in the host cell. The IRES achieves this by mediating the internal initiation of translation by recruiting a ribosomal 43S pre-initiation complex directly to the initiation codon and eliminates the requirement for the eukaryotic initiation factor, eIF4F.

Potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 5, also known as KCNA5 or Kv1.5, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNA5 gene.

Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily D member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCND2 gene. It contributes to the cardiac transient outward potassium current (Ito1), the main contributing current to the repolarizing phase 1 of the cardiac action potential.

Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 4 also known as Kv1.4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNA4 gene. It contributes to the cardiac transient outward potassium current (Ito1), the main contributing current to the repolarizing phase 1 of the cardiac action potential.

Potassium voltage-gated channel, Shab-related subfamily, member 1, also known as KCNB1 or Kv2.1, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the KCNB1 gene.
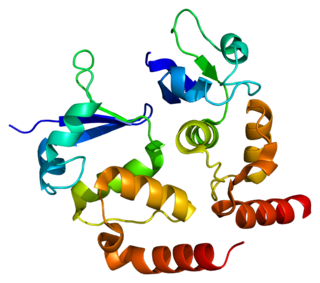
Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily D member 3 also known as Kv4.3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCND3 gene. It contributes to the cardiac transient outward potassium current (Ito1), the main contributing current to the repolarizing phase 1 of the cardiac action potential.

Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNAB1 gene.

Potassium voltage-gated channel, Shaw-related subfamily, member 4 (KCNC4), also known as Kv3.4, is a human gene.

Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily S member 3 (Kv9.3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNS3 gene. KCNS3 gene belongs to the S subfamily of the potassium channel family. It is highly expressed in pulmonary artery myocytes, placenta, and parvalbumin-containing GABA neurons in brain cortex. In humans, single-nucleotide polymorphisms of the KCNS3 gene are associated with airway hyperresponsiveness, whereas decreased KCNS3 mRNA expression is found in the prefrontal cortex of patients with schizophrenia.

Potassium voltage-gated channel, Shal-related subfamily, member 1 (KCND1), also known as Kv4.1, is a human gene.

Potassium voltage-gated channel, Shaw-related subfamily, member 3 also known as KCNC3 or Kv3.3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNC3.
Kaliotoxin (KTX) inhibits potassium flux through the Kv1.3 voltage-gated potassium channel and calcium-activated potassium channels by physically blocking the channel-entrance and inducing a conformational change in the K+-selectivity filter of the channel.

















