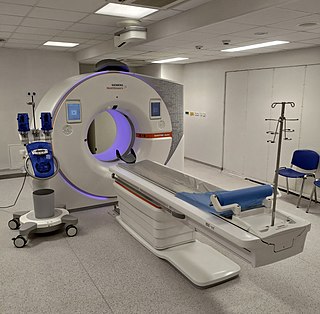
A computed tomography scan is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists.
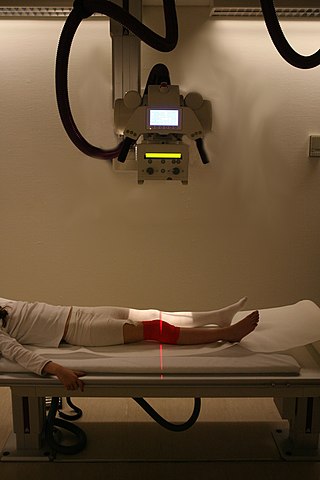
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical and industrial radiography. Similar techniques are used in airport security,. To create an image in conventional radiography, a beam of X-rays is produced by an X-ray generator and it is projected towards the object. A certain amount of the X-rays or other radiation are absorbed by the object, dependent on the object's density and structural composition. The X-rays that pass through the object are captured behind the object by a detector. The generation of flat two-dimensional images by this technique is called projectional radiography. In computed tomography, an X-ray source and its associated detectors rotate around the subject, which itself moves through the conical X-ray beam produced. Any given point within the subject is crossed from many directions by many different beams at different times. Information regarding the attenuation of these beams is collated and subjected to computation to generate two-dimensional images on three planes which can be further processed to produce a three-dimensional image.
The Hounsfield scale, named after Sir Godfrey Hounsfield, is a quantitative scale for describing radiodensity. It is frequently used in CT scans, where its value is also termed CT number.

Electron beam computed tomography (EBCT) is a specific form of computed tomography (CT) in which the X-ray tube is not mechanically spun in order to rotate the source of X-ray photons. This different design was explicitly developed to better image heart structures that never stop moving, performing a complete cycle of movement with each heartbeat.

Tomographic reconstruction is a type of multidimensional inverse problem where the challenge is to yield an estimate of a specific system from a finite number of projections. The mathematical basis for tomographic imaging was laid down by Johann Radon. A notable example of applications is the reconstruction of computed tomography (CT) where cross-sectional images of patients are obtained in non-invasive manner. Recent developments have seen the Radon transform and its inverse used for tasks related to realistic object insertion required for testing and evaluating computed tomography use in airport security.

In radiography, X-ray microtomography uses X-rays to create cross-sections of a physical object that can be used to recreate a virtual model without destroying the original object. It is similar to tomography and X-ray computed tomography. The prefix micro- is used to indicate that the pixel sizes of the cross-sections are in the micrometre range. These pixel sizes have also resulted in creation of its synonyms high-resolution X-ray tomography, micro-computed tomography, and similar terms. Sometimes the terms high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) and micro-CT are differentiated, but in other cases the term high-resolution micro-CT is used. Virtually all tomography today is computed tomography.
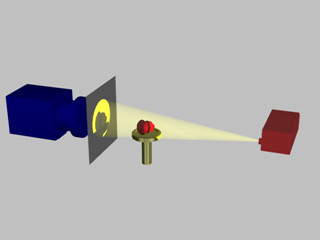
In microtomography X-ray scanners, cone beam reconstruction is one of two common scanning methods, the other being Fan beam reconstruction.
Image-guided radiation therapy is the process of frequent imaging, during a course of radiation treatment, used to direct the treatment, position the patient, and compare to the pre-therapy imaging from the treatment plan. Immediately prior to, or during, a treatment fraction, the patient is localized in the treatment room in the same position as planned from the reference imaging dataset. An example of IGRT would include comparison of a cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) dataset, acquired on the treatment machine, with the computed tomography (CT) dataset from planning. IGRT would also include matching planar kilovoltage (kV) radiographs or megavoltage (MV) images with digital reconstructed radiographs (DRRs) from the planning CT.

Tomosynthesis, also digital tomosynthesis (DTS), is a method for performing high-resolution limited-angle tomography at radiation dose levels comparable with projectional radiography. It has been studied for a variety of clinical applications, including vascular imaging, dental imaging, orthopedic imaging, mammographic imaging, musculoskeletal imaging, and chest imaging.

Industrial computed tomography (CT) scanning is any computer-aided tomographic process, usually X-ray computed tomography, that uses irradiation to produce three-dimensional internal and external representations of a scanned object. Industrial CT scanning has been used in many areas of industry for internal inspection of components. Some of the key uses for industrial CT scanning have been flaw detection, failure analysis, metrology, assembly analysis and reverse engineering applications. Just as in medical imaging, industrial imaging includes both nontomographic radiography and computed tomographic radiography.

Cone beam computed tomography is a medical imaging technique consisting of X-ray computed tomography where the X-rays are divergent, forming a cone.

Rotational angiography is a medical imaging technique based on x-ray, that allows to acquire CT-like 3D volumes during hybrid surgery or during a catheter intervention using a fixed C-Arm. The fixed C-Arm thereby rotates around the patient and acquires a series of x-ray images that are then reconstructed through software algorithms into a 3D image. Synonyms for rotational angiography include flat-panel volume CT and cone-beam CT.
Three-dimensional X-ray diffraction (3DXRD) is a microscopy technique using hard X-rays to investigate the internal structure of polycrystalline materials in three dimensions. For a given sample, 3DXRD returns the shape, juxtaposition, and orientation of the crystallites ("grains") it is made of. 3DXRD allows investigating micrometer- to millimetre-sized samples with resolution ranging from hundreds of nanometers to micrometers. Other techniques employing X-rays to investigate the internal structure of polycrystalline materials include X-ray diffraction contrast tomography (DCT) and high energy X-ray diffraction (HEDM).

X-ray computed tomography operates by using an X-ray generator that rotates around the object; X-ray detectors are positioned on the opposite side of the circle from the X-ray source.

In a medical facility, such as a hospital or clinic, a gantry holds radiation detectors and/or a radiation source used to diagnose or treat a patient's illness. Radiation sources may produce gamma radiation, x-rays, electromagnetic radiation, or magnetic fields depending on the purpose of the device.
Wojciech (Wojtek) Zbijewski is an American biomedical engineering and medical physics working in the fields of Computed tomography (CT), Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), image reconstruction in CT, and applications of CT and CBCT in orthopedics. He is faculty at the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
Jeffrey Harold Siewerdsen is an American physicist and biomedical engineer who is a Professor of Imaging Physics at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center as well as Biomedical Engineering, Computer Science, Radiology, and Neurosurgery at Johns Hopkins University.He is among the original inventors of cone-beam CT-guided radiotherapy as well as weight-bearing cone-beam CT for musculoskeletal radiology and orthopedic surgery. His work also includes the early development of flat-panel detectors on mobile C-arms for intraoperative cone-beam CT in image-guided surgery. He developed early models for the signal and noise performance of flat-panel detectors and later extended such analysis to dual-energy imaging and 3D imaging performance in cone-beam CT. He founded the ISTAR Lab in the Department of Biomedical Engineering, the Carnegie Center for Surgical Innovation at Johns Hopkins Hospital, and the Surgical Data Science Program at the Institute for Data Science in Oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Photon-counting computed tomography (PCCT) is a form of X-ray computed tomography (CT) in which X-rays are detected using a photon-counting detector (PCD) which registers the interactions of individual photons. By keeping track of the deposited energy in each interaction, the detector pixels of a PCD each record an approximate energy spectrum, making it a spectral or energy-resolved CT technique. In contrast, more conventional CT scanners use energy-integrating detectors (EIDs), where the total energy deposited in a pixel during a fixed period of time is registered. These EIDs thus register only photon intensity, comparable to black-and-white photography, whereas PCDs register also spectral information, similar to color photography.
Spectral imaging is an umbrella term for energy-resolved X-ray imaging in medicine. The technique makes use of the energy dependence of X-ray attenuation to either increase the contrast-to-noise ratio, or to provide quantitative image data and reduce image artefacts by so-called material decomposition. Dual-energy imaging, i.e. imaging at two energy levels, is a special case of spectral imaging and is still the most widely used terminology, but the terms "spectral imaging" and "spectral CT" have been coined to acknowledge the fact that photon-counting detectors have the potential for measurements at a larger number of energy levels.
X-ray diffraction computed tomography is an experimental technique that combines X-ray diffraction with the computed tomography data acquisition approach. X-ray diffraction (XRD) computed tomography (CT) was first introduced in 1987 by Harding et al. using a laboratory diffractometer and a monochromatic X-ray pencil beam. The first implementation of the technique at synchrotron facilities was performed in 1998 by Kleuker et al.











