Related Research Articles

The Epipalaeolithic Near East designates the Epipalaeolithic in the prehistory of the Near East. It is the period after the Upper Palaeolithic and before the Neolithic, between approximately 20,000 and 10,000 years Before Present (BP). The people of the Epipalaeolithic were nomadic hunter-gatherers who generally lived in small, seasonal camps rather than permanent villages. They made sophisticated stone tools using microliths—small, finely-produced blades that were hafted in wooden implements. These are the primary artifacts by which archaeologists recognise and classify Epipalaeolithic sites.
The Levant is the area in Southwest Asia, south of the Taurus Mountains, bounded by the Mediterranean Sea in the west, the Arabian Desert in the south, and Mesopotamia in the east. It stretches 400 mi (640 km) north to south from the Taurus Mountains to the Sinai desert, and 70–100 mi (110–160 km) east to west between the sea and the Arabian desert. The term is also sometimes used to refer to modern events or states in the region immediately bordering the eastern Mediterranean Sea: the Hatay Province of Turkey, Cyprus, Syria, Lebanon, Palestine, and Jordan.
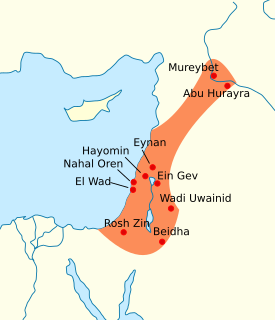
The Natufian culture is a Late Epipaleolithic archaeological culture of the Levant, dating to around 15,000 to 11,500 years ago. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentary or semi-sedentary population even before the introduction of agriculture. The Natufian communities may be the ancestors of the builders of the first Neolithic settlements of the region, which may have been the earliest in the world. Some evidence suggests deliberate cultivation of cereals, specifically rye, by the Natufian culture, at Tell Abu Hureyra, the site of earliest evidence of agriculture in the world. The world's oldest evidence of bread-making has been found at Shubayqa 1, a 14,500-year-old site in Jordan's northeastern desert. In addition, the oldest known evidence of beer, dating to approximately 13,000 BP, was found at the Raqefet Cave in Mount Carmel near Haifa in Israel.
The 10th millennium BC spanned the years 10,000 BC to 9001 BC. It marks the beginning of the transition from the Palaeolithic to the Neolithic via the interim Mesolithic and Epipaleolithic periods, which together form the first part of the Holocene epoch that is generally believed to have begun c. 9700 BC and is the current geological epoch. It is impossible to precisely date events that happened around the time of this millennium and all dates mentioned here are estimates mostly based on geological and anthropological analysis.

Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (PPNA) denotes the first stage of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, in early Levantine and Anatolian Neolithic culture, dating to c. 12,000 – c. 10,800 years ago, that is, 10,000–8,800 BCE. Archaeological remains are located in the Levantine and Upper Mesopotamian region of the Fertile Crescent.

Pella was an ancient city in northwest Jordan. It is located in a rich water source within the eastern foothills of the Jordan Valley, close to the modern village of Ṭabaqat Faḥl some 27 km (17 mi) south of the Sea of Galilee. The site is situated 130 km (81 mi) north of Amman: a drive of about an hour and a half, and an by car from Irbid, in the north of the country. Pella's ruins - predominantly temples, churches, and housing - have been partially excavated by teams of archaeologists; they attract thousands of tourists annually but especially in spring, during which time the area is awash with spring flowers.
In cultural anthropology, sedentism is the practice of living in one place for a long time. As of 2022, the large majority of people belong to sedentary cultures. In evolutionary anthropology and archaeology, sedentism takes on a slightly different sub-meaning, often applying to the transition from nomadic society to a lifestyle that involves remaining in one place permanently. Essentially, sedentism means living in groups permanently in one place. The invention of agriculture led to sedentism in many cases, but the earliest sedentary settlements were pre-agricultural.
Tell Hammeh is a relatively small tell in the central Jordan Valley, Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, located where the Zarqa River valley opens into the Jordan Valley. It is the site of the earliest bloomery smelting of iron, from around 930 BC. It is close to several of the larger tells in this part of the Jordan Valley as well as to the natural resources desirable in metal production: access to water, outcrops of marly clays, and above all the only iron ore deposit of the wider region at Mugharet al-Warda.
Tell el-Hammeh is a medium-size archaeological tell (mound) in the West Bank, at the southern fringe of the Beit She'an valley. It has been identified with the Canaanite city state of Hammath, mentioned in a late-13th century BCE Egyptian inscription.

Wadi Ara was a Palestinian village located 38.5 km south of the city of Haifa. It is named after the nearby stream that is known in Arabic as Wadi 'Ara. The village was particularly small with a population of 230 and a land area of approximately 9,800 dunums.

The Tall Zira'a is an archaeological tell in Jordan. Surveys and geophysical investigations showed the site's great potential for excavations.

The Mushabian culture is an archaeological culture suggested to have originated among the Iberomaurusians in North Africa, though once thought to have originated in the Levant.

Nahal Oren is an archaeological site on the northern bank of the wadi of Nahal Oren (Hebrew)/Wadi Fallah (Arabic) on Mount Carmel, 10 km (6.2 mi) south of Haifa, Israel. The site comprises a cave and the small terrace in front of it, which steeply descends towards the wadi floor. The site was first excavated in 1941. Kebaran, Natufian (Epipaleolithic) and Pre-Pottery Neolithic A and B industries were found.
The Nachcharini cave is located at a height of 2,100 m (6,889.76 ft) on the Nachcharini Plateau in the Anti-Lebanon mountains near the Lebanese/Syrian border and among the most elevated Natufian and Khiamian hunter-gatherer occupation sites found to date.

Beidha, also sometimes Bayda, is a major Neolithic archaeological site a few kilometres north of Petra near Siq al-Barid in Jordan. It is included in Petra's inscription as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Aammiq is a village in the Western Beqaa District in Lebanon. It is also the name of an archaeological site.
Iraq ed-Dubb, or the Cave of the Bear, is an early Neolithic archeological site 7 km (4.3 mi) northwest of Ajlun in the Jordan Valley, in modern-day Jordan. The settlement existed before 8,000 BCE and experimented with the cultivation of founder crops, side by side with the harvesting of wild cereals. Along with Tell Aswad in Syria, the site shows the earliest reference to domestic hulled barley between 10,000 and 8,800 BCE. The site is located on a forested limestone escarpment above the Wadi el-Yabis in northwest Jordan. An oval-shaped stone structure was excavated along with two burials and a variety of animal and plant remains.
Tell Abu al-Kharaz is an archeological tell in the Irbid Governorate of modern-day Jordan. Tell Abu al-Kharaz was the site of a fortified town during the Bronze and Iron Ages; it is located in the Jordan Valley, 4 kilometers east of the Jordan River.

Wadi al-Far'a or Tirzah Stream is a stream in the northern West Bank that empties into the Jordan River south of Damia Bridge. It is the largest stream in the West Bank. Wadi al-Far'a is located in the rugged area of the West Bank and cuts east through the Jordan Valley, passing through the Palestinian village of Wadi al-Far'a. The Tirzah Reservoir is used to collect the floodwater of Wadi al-Far'a before it flows into the Jordan River.

Azraq 18 is an Epipalaeolithic archaeological site in the Azraq oasis, eastern Jordan. First recorded in a survey by Andrew Garrard and Nicholas Stanley-Price in 1975, and excavated by Garrard in 1985, it is one of many sites of prehistoric occupation around the perennial springs that feed the oasis. Of these, Azraq 18 is the only one associated with the Late Epipalaeolithic Natufian culture, which is dated to between around 15,000 to 11,500 years ago.
References
- 1 2 Edwards, Phillip C. (2015). "Ice Age villagers of the Levant: renewed excavations at the Natufian site of Wadi Hammeh 27, Jordan". Antiquity. 89 (347).