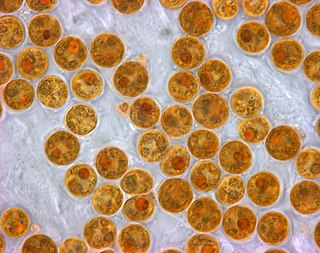
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus Symbiodinium, but some are known from the genus Amphidinium, and other taxa, as yet unidentified, may have similar endosymbiont affinities. "Zooxanthella" was originally a genus name given in 1881 by Karl Brandt to Zooxanthella nutricula which has been placed in the Peridiniales. Another group of unicellular eukaryotes that partake in similar endosymbiotic relationships in both marine and freshwater habitats are green algae zoochlorellae.

Acoelomorpha is a subphylum of very simple and small soft-bodied animals with planula-like features which live in marine or brackish waters. They usually live between grains of sediment, swimming as plankton, or crawling on other organisms, such as algae and corals. With the exception of two acoel freshwater species, all known acoelomorphs are marine.

Symsagittifera roscoffensis, also called the Roscoff worm, the mint-sauce worm, or the shilly-shally worm, is a marine acoel worm. The origin and nature of the green color of this worm stimulated the intrigued zoologists in the 1870's. It was discovered that the coloring resulted from the symbiosis between the animal and a green micro-algae, the species Tetraselmis convolutae, hosted under its epidermis. It is the photosynthetic activity of the micro-algae in hospite that provides the essential nutrients for the worm. This partnership is called photosymbiosis, from "photo", "light", and symbiosis "who lives with". These photosynthetic marine animals live in colonies on the tidal zone.

Convolutidae is a family of acoels, belonging to the phylum Xenacoelomorpha. This family contains more than a third of all known acoel species.

Acoela, or the acoels, is an order of small and simple invertebrates in the subphylum Acoelomorpha of phylum Xenacoelomorpha, a deep branching bilaterian group of animals, which resemble flatworms. Historically they were treated as an order of turbellarian flatworms. About 400 species are known, but probably many more not yet described.

Symbiodinium is a genus of dinoflagellates that encompasses the largest and most prevalent group of endosymbiotic dinoflagellates known and have photosymbiotic relationships with many species. These unicellular microalgae commonly reside in the endoderm of tropical cnidarians such as corals, sea anemones, and jellyfish, where the products of their photosynthetic processing are exchanged in the host for inorganic molecules. They are also harbored by various species of demosponges, flatworms, mollusks such as the giant clams, foraminifera (soritids), and some ciliates. Generally, these dinoflagellates enter the host cell through phagocytosis, persist as intracellular symbionts, reproduce, and disperse to the environment. The exception is in most mollusks, where these symbionts are intercellular. Cnidarians that are associated with Symbiodinium occur mostly in warm oligotrophic (nutrient-poor), marine environments where they are often the dominant constituents of benthic communities. These dinoflagellates are therefore among the most abundant eukaryotic microbes found in coral reef ecosystems.

Xenacoelomorpha is a small phylum of bilaterian invertebrate animals, consisting of two sister groups: xenoturbellids and acoelomorphs. This new phylum was named in February 2011 and suggested based on morphological synapomorphies, which was then confirmed by phylogenomic analyses of molecular data.

Litophyton arboreum, also known as broccoli coral, is a common soft coral (octocoral) found from the Red Sea to the Western Pacific. It grows up to 80 cm, usually on seaward reef slopes or hard bottoms. The color of L. arboreum varies from pale olive-green to yellow or grey. L. arboreum are anthozoans in the order Alcyonacea in the family Nephtheidae. The L. arboreum was originally classified in 1775 by Peter Forsskål, a Swedish Linnaean naturalist. As of 2016, the entire genus Litophyton was reclassified using phylogenetic data, in contrast to its original morphological classification.
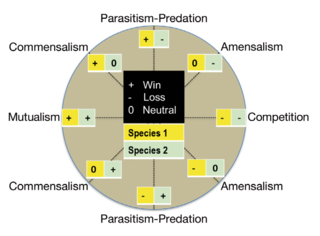
Microbial symbiosis in marine animals was not discovered until 1981. In the time following, symbiotic relationships between marine invertebrates and chemoautotrophic bacteria have been found in a variety of ecosystems, ranging from shallow coastal waters to deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Symbiosis is a way for marine organisms to find creative ways to survive in a very dynamic environment. They are different in relation to how dependent the organisms are on each other or how they are associated. It is also considered a selective force behind evolution in some scientific aspects. The symbiotic relationships of organisms has the ability to change behavior, morphology and metabolic pathways. With increased recognition and research, new terminology also arises, such as holobiont, which the relationship between a host and its symbionts as one grouping. Many scientists will look at the hologenome, which is the combined genetic information of the host and its symbionts. These terms are more commonly used to describe microbial symbionts.

Anthelia glauca, the giant anthelia, is a species of soft coral in the family Xeniidae. It is a colonial species and is found in shallow water in the Indo-Pacific region.
Waminoa brickneri is a species of acoel from the coral reefs around the northern Red Sea and the second described species in the genus.
Waminoa litus is a species of dinoflagellate-bearing acoel which is epizoic on living corals. This species is unique in that it transmits its endosymbiotic dinoflagellates (zooxanthellae) vertically via eggs, regardless of the heterogeneity of the zooxanthellae. Two dinoflagellate genera have been found to simultaneously live in the parenchyma of W. litus: Symbiodinium and Amphidinium.

Zoanthus sansibaricus is a species of zoanthid generally found in the Indo-pacific but also off the western coast of South America. The range of habitation has been noted in intertidal zones along with areas below 7 m, but shows phenotypical and morphological differences based on depth and shading. Shaded individuals contain larger polyps compared to unshaded. It can be divided into three reproductive categories, male, female and asexual. Spawning has been observed within the middle of July, using lunar phases as an indicator. Various subclades are theorized to appear based on the time of year.
Robert Kent Trench was an American Biologist who was a professor at the University of California, Santa Barbara. His research considered corals and symbiotic algae, with a focus on the adaption of zooxanthellae. He was awarded the 1994 International Society of Endocytobiology Miescher-Ishida Prize.

Mary Alice Coffroth is an American marine biologist who is a professor at the State University of New York at Buffalo. She is known for her use of molecular tools to examine coral larval ecology, recruitment and cnidarian-dinoflagellate symbiosis.
Hofstenia, or panther worms, is a genus of acoels belonging to the family Hofsteniidae.

Symbiodiniaceae is a family of marine dinoflagellates notable for their symbiotic associations with reef-building corals, sea anemones, jellyfish, marine sponges, giant clams, acoel flatworms, and other marine invertebrates. Symbiotic Symbiodiniaceae are sometimes colloquially referred to as Zooxanthellae, though the latter term can be interpreted to include other families of symbiotic algae as well. While many Symbiodiniaceae species are endosymbionts, others are free living in the water column or sediment.

Photosymbiosis is a type of symbiosis where one of the organisms is capable of photosynthesis.
Siphamia tubifer, also known as the sea urchin cardinalfish, is a small (~7 cm) coral reef fish in the family Apogonidae. Its geographic range extends from East Africa to the French Polynesian Islands.
Miguel Mies is a Brazilian academic, oceanographer, and researcher. He is currently a professor at the Oceanographic Institute of the University of São Paulo (IO-USP) and leads the Coral Reefs and Climate Change Laboratory (LARC). He also serves as the research coordinator for the Coral Vivo Project and is the vice president of the Coral Vivo Institute.











