Related Research Articles

Aquaculture, also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants. Aquaculture involves cultivating freshwater, brackish water and saltwater populations under controlled or semi-natural conditions, and can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is the harvesting of wild fish. Mariculture, commonly known as marine farming, refers specifically to aquaculture practiced in seawater habitats and lagoons, as opposed to freshwater aquaculture. Pisciculture is a type of aquaculture that consists of fish farming to obtain fish products as food.

Mariculture or marine farming is a specialized branch of aquaculture involving the cultivation of marine organisms for food and other animal products, in enclosed sections of the open ocean, fish farms built on littoral waters, or in artificial tanks, ponds or raceways which are filled with seawater. An example of the latter is the farming of marine fish, including finfish and shellfish like prawns, or oysters and seaweed in saltwater ponds. Non-food products produced by mariculture include: fish meal, nutrient agar, jewellery, and cosmetics.

The Chesapeake Bay is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Eastern Shore of Maryland, the Eastern Shore of Virginia, and the state of Delaware. The mouth of the Bay at its southern point is located between Cape Henry and Cape Charles. With its northern portion in Maryland and the southern part in Virginia, the Chesapeake Bay is a very important feature for the ecology and economy of those two states, as well as others surrounding within its watershed. More than 150 major rivers and streams flow into the Bay's 64,299-square-mile (166,534 km2) drainage basin, which covers parts of six states, New York, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, and West Virginia, and all of Washington, D.C.

Smith Island is a collection of three distinct island communities – Tylerton, Rhodes Point, and Ewell, Maryland – on the Chesapeake Bay, on the border of Maryland and Virginia territorial waters in the United States. The island is the last inhabited island in Maryland that is not accessible by vehicle. Most of the islands are eroding due to tidal currents and sea level rise; a study conducted in 2008 by the DNR reported that Smith Island is expected to completely erode by 2100 if no action is taken.

Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not all oysters, are in the superfamily Ostreoidea.

The eastern oyster —also called the Atlantic oyster, American oyster, or East Coast oyster—is a species of true oyster native to eastern North and South America. Other names in local or culinary use include the Wellfleet oyster, Virginia oyster, Malpeque oyster, Blue Pointoyster, Chesapeake Bay oyster, and Apalachicola oyster. C. virginica ranges from northern New Brunswick south through parts of the West Indies to Venezuela. It is farmed in all of the Maritime provinces of Canada and all Eastern Seaboard and Gulf states of the United States, as well as Puget Sound, Washington, where it is known as the Totten Inlet Virginica. It was introduced to the Hawaiian Islands in the 19th century and is common in Pearl Harbor.

Oyster farming is an aquaculture practice in which oysters are bred and raised mainly for their pearls, shells and inner organ tissue, which is eaten. Oyster farming was practiced by the ancient Romans as early as the 1st century BC on the Italian peninsula and later in Britain for export to Rome. The French oyster industry has relied on aquacultured oysters since the late 18th century.

Fanny Bay is a small hamlet in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It is located on Baynes Sound on the east coast of Vancouver Island. In 2001, its population was listed as 815. It is best known for its fine oysters. The area is served by the Island Highway and Island Rail Corridor.
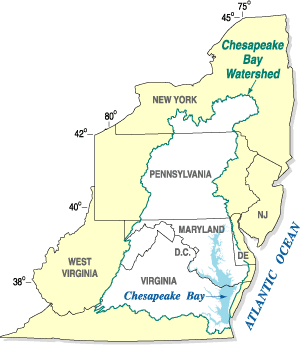
The Chesapeake Bay Program is the regional partnership that directs and conducts the restoration of the Chesapeake Bay in the United States. As a partnership, the Chesapeake Bay Program brings together members of various state, federal, academic and local watershed organizations to build and adopt policies that support Chesapeake Bay restoration. By combining the resources and unique strengths of each individual organization, the Chesapeake Bay Program is able to follow a unified plan for restoration. The program office is located in Annapolis, Maryland.


The Virginia Institute of Marine Science (VIMS) is one of the largest marine research and education centers in the United States. Founded in 1940, VIMS is unique among marine science institutions in its legal mandate to provide research, education, and advisory services to government, citizens, and industry. Funding for VIMS comes from the Commonwealth of Virginia, grants and contracts from federal and state agencies, and private giving. The School of Marine Science (SMS) at VIMS is the graduate school in marine science for the College of William & Mary. VIMS offers M.S., Ph.D., and professional M.A. degrees in marine science. The school has 52 faculty members, an enrollment of 80-100 students, and includes 4 academic departments. VIMS' main campus is located in Gloucester Point, Virginia.

Aquaculture started to take off in New Zealand in the 1980s. It is dominated by mussels, oysters and salmon. In 2007, aquaculture generated about NZ$360 million in sales on an area of 7,700 hectares. $240 million was earned in exports.

Aquaculture in Australia is the country's fastest-growing primary industry, accounting for 34% of the total gross value of production of seafood. 10 species of fish are farmed in Australia, and production is dominated by southern bluefin tuna, Atlantic salmon and barramundi. Mud crabs have also been cultivated in Australia for many years, sometimes leading to over-exploitation. Traditionally, this aquaculture was limited to pearls, but since the early 1970s, there has been significant research and commercial development of other forms of aquaculture, including finfish, crustaceans, and molluscs.

Oyster reef restoration refers to the reparation and reconstruction of degraded oyster reefs. Environmental changes, modern fishing practices, over harvesting, water pollution, and other factors, have resulted in damage, disease, and ultimately, a large decline in global population and prevalence of oyster habitats. Aside from ecological importance, oyster farming is an important industry in many regions around the world. Both natural and artificial materials have been used in efforts to increase population and regenerate reefs.

South Korea is a major center of aquaculture production, and the world's third largest producer of farmed algae as of 2020.

An oyster buy-boat, also known as deck boat, is an approximately 40–90 foot long wooden boat with a large open deck which serviced oyster tongers and dredgers. Similar in function to sardine carriers, buy boats circulated among the harvesters collecting their catches, then delivered their loads to a wholesaler or oyster processing house. This spared the fishermen the task and its downtime, allowing them to catch more oysters. Buy-boats also bought seed oysters, or spat, for planting in oyster beds.
The Suminoe oyster, is a species of true oyster which inhabits intertidal hard grounds and substrate, as well as muddy creeks of warm estuaries throughout the western Pacific. It is large and flat in appearance and almost identical in gross morphology to Crassostrea virginica.

Aquaculture in the United Kingdom is dominated by salmon farming, then by mussel production with trout being the third most important enterprise. Aquaculture in the United Kingdom represents a significant business for the UK, producing over 200,000 tonnes of fish whilst earning over £700 million in 2012 (€793 million).
Fish farming inWestern Australia is an experimental part of the state's seafood sector. Prominent operators and lessees include Indian Ocean Fresh Australia and Huon Aquaculture, and the primary commercial species are yellowtail kingfish in the Mid West aquaculture zone and barramundi in the Kimberley aquaculture zone. Pink snapper is another species considered as a sea cage fish farming prospect. The Mid West aquaculture zone lies between Geraldton and the Abrolhos Islands, and the Kimberly aquaculture zone is in Cone Bay north of Derby. The sector is represented by Erica Starling as spokesperson for the Marine Fishfarmers Association.
The Oyster Recovery Partnership ("ORP") is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization that leads conservation efforts of the native Eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica, in the Chesapeake Bay and Eastern United States. The organization's activities and programs include oyster restoration, shell recycling conservation, and sustainable fishery initiatives.
References
- 1 2 "How This Virginia Aquaculture Farm Raises Four Million Oysters for Market". WSJ. Retrieved September 11, 2023.
- ↑ Cameron, Steve. "How 3.5 million oysters are harvested at this Virginia farm every year". Business Insider. Retrieved September 11, 2023.
- ↑ "How This Virginia Aquaculture Farm Raises Four Million Oysters for Market". MarketWatch. Retrieved September 11, 2023.
- ↑ "Cage Oyster Farm Oyster Farm - Ward Oyster Co - Fresh Oysters For Sale". Ward Oyster Company - Aquaculture Oyster Farm. Retrieved September 11, 2023.
- ↑ "OUR AQUACULTURE OYSTER FARM - Ward Oyster Company". Ward Oyster Company - Aquaculture Oyster Farm. Retrieved September 11, 2023.
- ↑ "Ward Oyster Company". FishChoice. April 13, 2020. Retrieved September 11, 2023.
- ↑ "New oyster restoration project to take place in Chesapeake Bay". thefishsite.com. May 11, 2023. Retrieved September 11, 2023.