The Republic of Texas, or simply Texas, was a sovereign state in North America that existed from March 2, 1836, to February 19, 1846. It shared borders with Mexico, the Republic of the Rio Grande, and the United States of America.

Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the United States government for the relocation of Native Americans who held original Indian title to their land as an independent nation-state. The concept of an Indian territory was an outcome of the U.S. federal government's 18th- and 19th-century policy of Indian removal. After the American Civil War (1861–1865), the policy of the U.S. government was one of assimilation.

The Territory of Oklahoma was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 2, 1890, until November 16, 1907, when it was joined with the Indian Territory under a new constitution and admitted to the Union as the state of Oklahoma.

In the United States before 1865, a slave state was a state in which slavery and the internal or domestic slave trade were legal, while a free state was one in which they were prohibited. Between 1812 and 1850, it was considered by the slave states to be politically imperative that the number of free states not exceed the number of slave states, so new states were admitted in slave–free pairs. There were, nonetheless, some slaves in most free states up to the 1840 census, and the Fugitive Slave Clause of the U.S. Constitution, as implemented by the Fugitive Slave Act of 1793 and the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850, provided that a slave did not become free by entering a free state and must be returned to his or her owner.

Thomas Jefferson Rusk was an early political and military leader of the Republic of Texas, serving as its first Secretary of War as well as a general at the Battle of San Jacinto. He was later a US politician and served as a Senator from Texas from 1846 until his suicide. He served as the President pro tempore of the United States Senate in 1857.

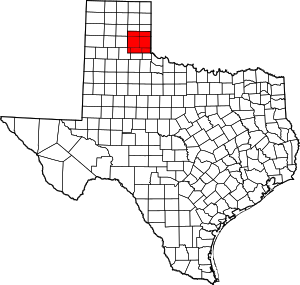
Greer County, a county created by the Texas legislature on February 8, 1860, was land claimed by both Texas and the United States. The region of Greer County is now in present-day Oklahoma.

A certified copy is a copy of a primary document that has on it an endorsement or certificate that it is a true copy of the primary document. It does not certify that the primary document is genuine, only that it is a true copy of the primary document.

Encinal County was a former Texas county. Its area is now completely contained in the present Webb County.

The Texas Department of Transportation is a Texas state government agency responsible for construction and maintenance of the state's immense state highway system and the support of the state's maritime, aviation, rail, and public transportation systems. TxDOT previously administered vehicle registration prior to the creation of the Texas Department of Motor Vehicles in November 2009.

The Salt Fork Red River is a sandy-braided stream about 311 km (193 mi) long, heading on the Llano Estacado of West Texas about 2.9 km (1.8 mi) north of Claude of Armstrong County, Texas, flowing east across the Texas Panhandle and Western Oklahoma to join the Red River about 21 km (13 mi) south of Altus of Jackson County, Oklahoma.
Miller County was a county that existed from April 1, 1820 to 1838, first as part of Arkansas Territory and later the State of Arkansas. It included much of what is southeastern Oklahoma and the northeastern counties in Texas. It was named for James Miller, the first governor of the Arkansas Territory.

The history of slavery in Texas began slowly at first during the first few phases in Texas' history. Texas was a colonial territory, then part of Mexico, later Republic in 1836, and U.S. state in 1845. The use of slavery expanded in the mid-nineteenth century as White American settlers, primarily from the Southeastern United States, crossed the Sabine River and brought enslaved people with them. Slavery was present in Spanish America and Mexico prior to the arrival of American settlers, but it was not highly developed, and the Spanish did not rely on it for labor during their years in Spanish Texas.
Preston, also known as Preston Bend, is an unincorporated community and census-designated place located on the Red River in Grayson County, Texas, United States. It grew in the 19th century at the intersection of several military and trade roads and was an important crossing on the Shawnee cattle trail. Preston lost prominence after the MK&T railroad bypassed the town to the east, leading to a decline in traveler and cattle drive traffic. Much of its former town site is submerged beneath the waters of Lake Texoma. Its population was 2,096 as of the 2010 census.
Following the defeat of the Confederate States in the American Civil War, Texas was mandated to rejoin the United States of America. Union Army soldiers officially occupied the state starting on June 19, 1865. For the next nine years, Texas was governed by a series of provisional governors as the state went through Reconstruction. As stated by the Texas State Library and Archive Commission, in 1869, the United States Congress passed an act allowing the citizens of Texas to vote on a new State Constitution. Later that same year, President Grant approved their Constitution. Texas fully rejoined the Union on March 30, 1870, when President Grant signed the act to readmit Texas to Congressional Representation. Texas later repealed the State Constitution of 1869 and enacted the Texas State Constitution of 1876 on February 15, 1876, which remains their current state constitution though with numerous amendments.

Buchel County was a former Texas county. Its area is now completely contained in the present Brewster County.

An Organic Act is a generic name for a statute used by the United States Congress to describe a territory, in anticipation of being admitted to the Union as a state. Because of Oklahoma's unique history an explanation of the Oklahoma Organic Act needs a historic perspective. In general, the Oklahoma Organic Act may be viewed as one of a series of legislative acts, from the time of Reconstruction, enacted by Congress in preparation for the creation of a united State of Oklahoma. The Organic Act created Oklahoma Territory, and Indian Territory that were Organized incorporated territories of the United States out of the old "unorganized" Indian Territory. The Oklahoma Organic Act was one of several acts whose intent was the assimilation of the tribes in Oklahoma and Indian Territories through the elimination of tribes' communal ownership of property.
Legal forms of gambling in the U.S. state of North Carolina include the North Carolina Education Lottery, three Indian casinos, charitable bingo and raffles, and low-stakes "beach bingo". North Carolina has long resisted expansion of gambling, owing to its conservative Bible Belt culture.
John B. Harrison was a justice of the Oklahoma Supreme Court from 1927 to 1929.