Burkina Faso is a landlocked Sahel country that shares borders with six nations. It lies between the Sahara desert and the Gulf of Guinea, south of the loop of the Niger River, mostly between latitudes 9° and 15°N, and longitudes 6°W and 3°E. The land is green in the south, with forests and fruit trees, and semi-arid in the north. Most of central Burkina Faso lies on a savanna plateau, 198–305 metres (650–1,001 ft) above sea level, with fields, brush, and scattered trees. Burkina Faso's game preserves – the most important of which are Arly, Nazinga, and W National Park—contain lions, elephants, hippopotamus, monkeys, common warthogs, and antelopes. Previously the endangered painted hunting dog, Lycaon pictus occurred in Burkina Faso, but, although the last sightings were made in Arli National Park, the species is considered extirpated from Burkina Faso.

Lomé is the capital and largest city of Togo. It has an urban population of 837,437 while there were 1,477,660 permanent residents in its metropolitan area as of the 2010 census. Located on the Gulf of Guinea at the southwest corner of the country, with its entire western border along the easternmost point of Ghana's Volta Region, Lomé is the country's administrative and industrial center, which includes an oil refinery. It is also the country's chief port, from where it exports coffee, cocoa, copra, and oil palm kernels.

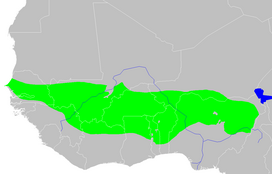
The Sahel is the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition in Africa between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a semi-arid climate, it stretches across the south-central latitudes of Northern Africa between the Atlantic Ocean and the Red Sea.

The Llanos is a vast tropical grassland plain situated to the east of the Andes in Colombia and Venezuela, in northwestern South America. It is an ecoregion of the tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome.

The Sudanian savanna is a broad belt of tropical savanna that runs east and west across the African continent, from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Ethiopian Highlands in the east. The Sahel, a belt of drier grasslands and acacia savannas, lies to the north, between the Sudanian savanna and the Sahara Desert. To the south the forest-savanna mosaic forms a transition zone between the Sudanian savanna and the Guineo-Congolian forests that lie nearer the equator.

The East Sudanian savanna is a hot, dry, tropical savanna ecoregion of Central and East Africa.

The Northern Congolian forest–savanna mosaic is a forest and savanna ecoregion of central Africa. It extends east and west across central Africa, covering parts of Cameroon, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, South Sudan, and Uganda. It is part of the belt of transitional forest-savanna mosaic that lie between Africa's moist equatorial Guineo-Congolian forests and the tropical dry forests, savannas, and grasslands to the north and south.

The South Saharan steppe and woodlands, also known as the South Sahara desert, is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion of northern Africa. This band is a transitional region between the Sahara's very arid center to the north, and the wetter Sahelian Acacia savanna ecoregion to the south. In pre-modern times, the grasslands were grazed by migratory gazelles and other ungulates after the rainfalls. More recently, over-grazing by domestic livestock have degraded the territory. Despite the name of the ecoregion, there are few 'woodlands' in the area; those that exist are generally acacia and shrubs along rivers and in wadis.

The Lake Chad flooded savanna is a flooded grasslands and savannas ecoregion in Africa. It includes the seasonally- and permanently-flooded grasslands and savannas in the basin of Lake Chad in Central Africa, and covers portions of Cameroon, Chad, Niger, and Nigeria.

The Carpentaria tropical savanna is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion in northern Australia.

The Victoria Plains tropical savanna is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion in northwestern Australia.

The Southern Acacia–Commiphora bushlands and thickets is a tropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion in Tanzania and Kenya. It includes portions of Serengeti National Park and Ngorongoro Conservation Area, which are designated World Heritage Sites and biosphere reserves for their outstanding wildlife and landscapes. It is one of three Acacia–Commiphora bushlands and thickets ecoregions in eastern Africa.

The Northern Acacia–Commiphora bushlands and thickets are a tropical grasslands, savannas and shrublands ecoregion in eastern Africa. The ecoregion is mostly located in Kenya, extending north into southeastern South Sudan, northeastern Uganda and southwestern Ethiopia and south into Tanzania along the Kenya-Tanzania border.

The Southwestern Arabian foothills savanna, also known as the Southwestern Arabian Escarpment shrublands and woodlands, is a desert and xeric shrubland ecoregion of the southern Arabian Peninsula, covering portions of Saudi Arabia, Yemen, and Oman.

The Victoria Basin forest–grassland mosaic is an ecoregion that lies mostly in Uganda and extends into neighboring countries. The ecoregion is centered north and west of Lake Victoria, with an outlier on the border of Ethiopia and South Sudan.

The Mitchell Grass Downs is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion in northeastern Australia. It is a mostly treeless grassland, characterised by Mitchell grasses .