
The rock hyrax, also called dassie, doop, Cape hyrax, rock rabbit, and coney, is a medium-sized terrestrial mammal native to Africa and the Middle East. Commonly referred to in South Africa as the dassie, it is one of the five living species of the order Hyracoidea, and the only one in the genus Procavia. Rock hyraxes weigh 4–5 kg (8.8–11.0 lb) and have short ears.
The Angolan long-eared bat is a species of vesper bat in the Vespertilionidae family. It can be found in moist savanna in Angola and Democratic Republic of the Congo.

Schreber's yellow bat or the giant house bat, is a species of vesper bat. It is found in Benin, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Nigeria, Senegal, Tanzania, Togo, and Zimbabwe. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, dry savanna, and moist savanna. It is an uncommon species and its biology is poorly known. It was first described in 1774 by the German naturalist Johann Christian Daniel von Schreber, who named it Vespertilio nigrita. It was later transferred to the genus Scotophilus, making it Scotophilus nigrita.
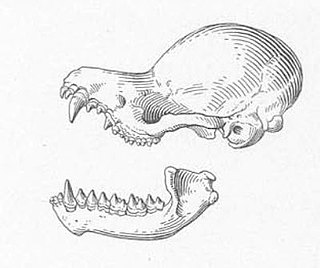
The copper woolly bat is a species of vesper bat. It is found in Cameroon, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, and Guinea. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests, subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, and subtropical or tropical swamps. It is threatened by habitat loss.
The Cameroon climbing mouse is a species of rodent in the family Nesomyidae which is endemic to the montane grasslands on three mountains in Cameroon.

The southern needle-clawed bushbaby is a species of strepsirrhine primate in the family Galagidae. Found in Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, and possibly Democratic Republic of the Congo, its natural habitat is tropical moist forests. While the species is not threatened or endangered, some local populations may be threatened by habitat destruction.

The Lady Burton's rope squirrel is a species of rodent in the family Sciuridae. It is found in Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, and Gabon. Its natural habitats are tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests and subtropical or tropical moist montane forest. It is a common species with a wide range, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated it as being of "least concern".

The red-legged sun squirrel is a species of rodent in the family Sciuridae, also commonly known as the isabelline red-legged sun squirrel. It is native to tropical western and central Africa where its range extends from Senegal in the west, through Nigeria and the Republic of Congo to Uganda and Tanzania in the east. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests and moist savanna. This species is thought to be common and has a very wide distribution, so the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated its conservation status as being of "least concern".

The forest giant squirrel or Stanger's squirrel is a species of rodent in the family Sciuridae found in Angola, Benin, Burundi, Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the Republic of the Congo, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Ghana, Kenya, Liberia, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, Tanzania, Togo, and Uganda. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests and plantations.
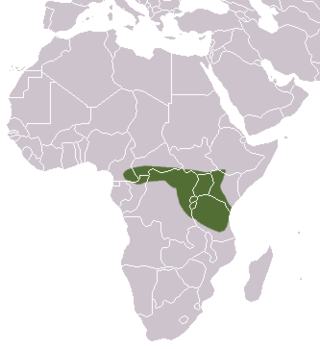
Hildegarde's shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is found in Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Kenya, Rwanda, and Tanzania. Considered by some authorities to be a subspecies of Crocidura gracilipes, it is now recognised as a separate species, with a diploid chromosome number of 2n = 52. This is one of three species of small mammal named by the British zoologist Oldfield Thomas in honour of anthropologist Hildegarde Beatrice Hinde.

The Bini free-tailed bat is a species of bat in the family Molossidae found in West and Central Africa. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests.

The halcyon horseshoe bat is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is found in Cameroon, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Liberia, Nigeria, Senegal, South Sudan, Togo, Uganda, possibly Gabon, and possibly Sierra Leone. Its natural habitats are subtropical and tropical dry and moist lowland forest, moist savanna, caves, and other subterranean habitats.

Zenker's fruit bat or Tear-drop bat is a species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. Its natural habitats are tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests and swamps.

The southern tree hyrax, also known as the southern tree dassie, is a species of mammal in the family Procaviidae. The southern tree hyrax is mainly found in the south central eastern side of Africa.

The tree hyrax or tree dassie is a small nocturnal mammal native to Africa. Distantly related to elephants and sea cows, it comprises the four species in the genus Dendrohyrax, one of only three genera in the family Procaviidae, which is the only living family within the order Hyracoidea.

The yellow-spotted rock hyrax or bush hyrax is a species of mammal in the family Procaviidae. It is found in Angola, Botswana, Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, southern Egypt, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Rwanda, Somalia, northern South Africa, South Sudan, Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Its natural habitats are dry savanna and rocky areas. Hyrax comes from the Greek word ὕραξ, or shrew-mouse.

Hyraxes, also called dassies, are small, thickset, herbivorous mammals in the order Hyracoidea. Hyraxes are well-furred, rotund animals with short tails. Typically, they measure between 30 and 70 cm long and weigh between 2 and 5 kg. They are superficially similar to pikas and marmots, but are more closely related to elephants and sea cows.

Parinari excelsa, the Guinea plum, is a species of large, evergreen tree in the family Chrysobalanaceae. It has a very wide distribution in tropical Africa and the Americas. This species grows to 50 m (160 ft) tall while the trunk is up to 1.5 m (5 ft) in diameter.

The eastern tree hyrax is a species of mammal within the family Procaviidae. The eastern tree hyrax is the most localized of the tree hyrax species, distributed patchily in a narrow band of lowland and montane forests in Kenya and Tanzania and adjacent islands.

Haumania liebrechtsiana is a species of plant in the family Marantaceae. It grows as an understorey herb or climber in tropical forests in Central Africa. The leaves and shoots are eaten by gorillas and chimpanzees, and the leaves and stems have traditional uses.





















