
Seabirds are birds that are adapted to life within the marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent evolution, as the same environmental problems and feeding niches have resulted in similar adaptations. The first seabirds evolved in the Cretaceous period, and modern seabird families emerged in the Paleogene.

The family Procellariidae is a group of seabirds that comprises the fulmarine petrels, the gadfly petrels, the diving petrels, the prions, and the shearwaters. This family is part of the bird order Procellariiformes, which also includes the albatrosses and the storm petrels.

The European storm petrel, also known as British storm petrel, or just storm petrel, is a species of seabird in the northern storm petrel family, Hydrobatidae. The small, square-tailed bird is entirely black except for a broad, white rump and a white band on the under wings, and it has a fluttering, bat-like flight. The large majority of the population breeds on islands off the coasts of Europe, with the greatest numbers in the Faroe Islands, United Kingdom, Ireland, and Iceland. The Mediterranean population is a separate subspecies, but is inseparable at sea from its Atlantic relatives; its strongholds are Filfla Island (Malta), Sicily, and the Balearic Islands.

Cory's shearwater is a large shearwater in the seabird family Procellariidae. It breeds colonially of rocky islands in the eastern Atlantic. Outside the breeding season it ranges widely in the Atlantic. It was formerly considered to be conspecific with Scopoli's shearwater.

The Fea's petrel is a small seabird in the gadfly petrel genus, Pterodroma. It was previously considered to be a subspecies of the soft-plumaged petrel, but they are actually not closely related at all. However, P. feae is very closely related to Zino's petrel and Desertas petrel, two other species recently split from P. mollis. The gadfly petrels are named for their speedy weaving flight, as if evading horseflies. The flight action is also reflected in the genus name Pterodroma, from Ancient Greek pteron, "wing" and dromos, " runner". This species is named after the Italian zoologist Leonardo Fea (1852-1903).
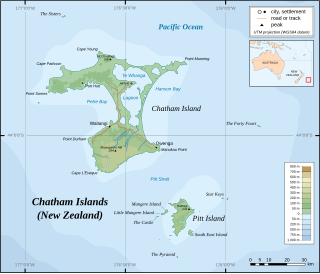
Hokorereoro, Rangatira, or South East Island is the third largest island in the Chatham Islands archipelago, and covers an area of 218 hectares. It lies 800 kilometres (497 mi) east of New Zealand's South Island off the south-east coast of Pitt Island, 55 kilometres (34 mi) south-east of the main settlement, Waitangi, on Chatham Island.

The Sisters is a group of three main islands located 16 kilometres (10 mi) north of Cape Pattison, Chatham Island. They are the northernmost members of the Chatham Archipelago, located 800 kilometres (497 mi) east of New Zealand's South Island.

The common diving petrel , also known as the smaller diving petrel or simply the diving petrel, is a diving petrel, one of four very similar auk-like small petrels of the southern oceans. It is native to South Atlantic islands and islands of the subantarctic southern Indian Ocean, islands and islets off New Zealand and south-eastern Australian islands.

The broad-billed prion is a small pelagic seabird in the shearwater and petrel family, Procellariidae. It is the largest prion, with grey upperparts plumage, and white underparts. The sexes are alike. It ranges from the southeast Atlantic to New Zealand mainly near the Antarctic Convergence. In the south Atlantic it breeds on Tristan da Cunha and Gough Island; in the south Pacific it breeds on islands off the south coast of South Island, New Zealand and on the Chatham Islands. It has many other names that have been used such as blue-billed dove-petrel, broad-billed dove-petrel, long-billed prion, common prion, icebird, and whalebird.

The Antarctic prion also known as the dove prion, or totorore in Māori, is the largest of the prions, a genus of small petrels of the Southern Ocean.

The white-bellied storm petrel is a species of seabird in the family Oceanitidae. It is found in Angola, Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Chile, Ecuador, French Polynesia, French Southern Territories, Maldives, Namibia, New Zealand, Perú, Saint Helena, and South Africa. Its natural habitat is open seas.

The grey-backed storm petrel is a species of seabird in the austral storm petrel family Oceanitidae. It is monotypic within the genus Garrodia. It is found in Antarctica, Argentina, Australia, Chile, Falkland Islands, French Southern Territories, New Zealand, Saint Helena, South Africa, and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands. Its natural habitat is open seas. It is highly attracted to bright lights, especially in conditions of low visibility.

The fulmar prion is a species of seabird in the family Procellariidae, found in the southern oceans.

Motunau Island is a small, 3 ha, island nature reserve lying 1.2 km (0.75 mi) off the coast of New Zealand's South Island, at the northern end of Pegasus Bay, south of the mouth of the Motunau River. The reserve is managed by the Department of Conservation and access is by permit only.



















