Related Research Articles

Stonemasonry or stonecraft is the creation of buildings, structures, and sculpture using stone as the primary material. Stonemasonry is the craft of shaping and arranging stones, often together with mortar and even the ancient lime mortar, to wall or cover formed structures.

Rebar, known when massed as reinforcing steel or reinforcement steel, is a steel bar used as a tension device in reinforced concrete and reinforced masonry structures to strengthen and aid the concrete under tension. Concrete is strong under compression, but has low tensile strength. Rebar significantly increases the tensile strength of the structure. Rebar's surface features a continuous series of ribs, lugs or indentations to promote a better bond with the concrete and reduce the risk of slippage.

Retaining walls are relatively rigid walls used for supporting soil laterally so that it can be retained at different levels on the two sides. Retaining walls are structures designed to restrain soil to a slope that it would not naturally keep to. They are used to bound soils between two different elevations often in areas of terrain possessing undesirable slopes or in areas where the landscape needs to be shaped severely and engineered for more specific purposes like hillside farming or roadway overpasses. A retaining wall that retains soil on the backside and water on the frontside is called a seawall or a bulkhead.

Tilt-up,tilt-slab or tilt-wall is a type of building and a construction technique using concrete. Though it is a cost-effective technique with a shorter completion time, poor performance in earthquakes has mandated significant seismic retrofit requirements in older buildings.

Seismic retrofitting is the modification of existing structures to make them more resistant to seismic activity, ground motion, or soil failure due to earthquakes. With better understanding of seismic demand on structures and with our recent experiences with large earthquakes near urban centers, the need of seismic retrofitting is well acknowledged. Prior to the introduction of modern seismic codes in the late 1960s for developed countries and late 1970s for many other parts of the world, many structures were designed without adequate detailing and reinforcement for seismic protection. In view of the imminent problem, various research work has been carried out. State-of-the-art technical guidelines for seismic assessment, retrofit and rehabilitation have been published around the world – such as the ASCE-SEI 41 and the New Zealand Society for Earthquake Engineering (NZSEE)'s guidelines. These codes must be regularly updated; the 1994 Northridge earthquake brought to light the brittleness of welded steel frames, for example.

A concrete block, also known as a cinder block in North American English, breeze block in British English, concrete masonry unit (CMU), or by various other terms, is a standard-size rectangular block used in building construction. The use of blockwork allows structures to be built in the traditional masonry style with layers of staggered blocks.
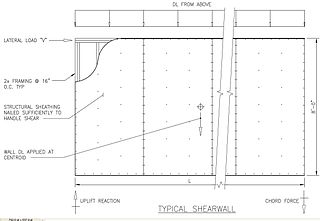
In structural engineering, a shear wall is a two-dimensional vertical element of a system that is designed to resist in-plane lateral forces, typically wind and seismic loads.

Insulating concrete form or insulated concrete form (ICF) is a system of formwork for reinforced concrete usually made with a rigid thermal insulation that stays in place as a permanent interior and exterior substrate for walls, floors, and roofs. The forms are interlocking modular units that are dry-stacked and filled with concrete. The units lock together somewhat like Lego bricks and create a form for the structural walls or floors of a building. ICF construction has become commonplace for both low rise commercial and high performance residential construction as more stringent energy efficiency and natural disaster resistant building codes are adopted.

Framing, in construction, is the fitting together of pieces to give a structure support and shape. Framing materials are usually wood, engineered wood, or structural steel. The alternative to framed construction is generally called mass wall construction, where horizontal layers of stacked materials such as log building, masonry, rammed earth, adobe, etc. are used without framing.
Earthquake engineering is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering that designs and analyzes structures, such as buildings and bridges, with earthquakes in mind. Its overall goal is to make such structures more resistant to earthquakes. An earthquake engineer aims to construct structures that will not be damaged in minor shaking and will avoid serious damage or collapse in a major earthquake. A properly engineered structure does not necessarily have to be extremely strong or expensive. It has to be properly designed to withstand the seismic effects while sustaining an acceptable level of damage.

Steel frame is a building technique with a "skeleton frame" of vertical steel columns and horizontal I-beams, constructed in a rectangular grid to support the floors, roof and walls of a building which are all attached to the frame. The development of this technique made the construction of the skyscraper possible.

Formwork is molds into which concrete or similar materials are either precast or cast-in-place. In the context of concrete construction, the falsework supports the shuttering molds. In specialty applications formwork may be permanently incorporated into the final structure, adding insulation or helping reinforce the finished structure.

A raised floor provides an elevated structural floor above a solid substrate to create a hidden void for the passage of mechanical and electrical services. Raised floors are widely used in modern office buildings, and in specialized areas such as command centers, Information technology data centers and computer rooms, where there is a requirement to route mechanical services and cables, wiring, and electrical supply. Such flooring can be installed at varying heights from 2 inches (51 mm) to heights above 4 feet (1.2 m) to suit services that may be accommodated beneath. Additional structural support and lighting are often provided when a floor is raised enough for a person to crawl or even walk beneath.

Fireproofing is rendering something resistant to fire, or incombustible; or material for use in making anything fire-proof. It is a passive fire protection measure. "Fireproof" or "fireproofing" can be used as a noun, verb or adjective; it may be hyphenated ("fire-proof").

Structural engineering depends on the knowledge of materials and their properties, in order to understand how different materials resist and support loads.
Tornadoes, cyclones, and other storms with strong winds damage or destroy many buildings. However, with proper design and construction, the damage to buildings by these forces can be greatly reduced. A variety of methods can help a building survive strong winds and storm surge.

Structural clay tile describes a category of burned-clay building materials used to construct roofing, walls, and flooring for structural and non-structural purposes, especially in fireproofing applications. Also called building tile, structural terra cotta, hollow tile, saltillo tile, and clay block, the material is an extruded clay shape with substantial depth that allows it to be laid in the same manner as other clay or concrete masonry. In North America it was chiefly used during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, reaching peak popularity at the turn of the century and declining around the 1950s. Structural clay tile grew in popularity in the end of the nineteenth-century because it could be constructed faster, was lighter, and required simpler flat falsework than earlier brick vaulting construction. Each unit is generally made of clay or terra-cotta with hollow cavities, or cells, inside it. The colors of terracotta transform from gray to orange, red, yellow, and cream tones. This is due to an effect of the firing process which hardens the clay so it can be used for structural purposes. The material is commonly used in floor arches, fireproofing, partition walls, and furring. It continues to be used in Europe to build fire-resistant walls and partitions. In North America the material has largely been replaced by concrete masonry units.
Hybrid masonry is a new type of building system that uses engineered, reinforced masonry to brace frame structures. Typically, hybrid masonry is implemented with concrete masonry panels used to brace steel frame structures. The basic concept is to attach a reinforced concrete masonry panel to a structural steel frame such that some combination of gravity forces, story shears and overturning moments can be transferred to the masonry. The structural engineer can choose from three different types of hybrid masonry and two different reinforcement anchorage types. In conventional steel frame building systems, the vertical force resisting steel frame system is supported in the lateral direction by steel bracing or an equivalent system. When the architectural plans call for concrete masonry walls to be placed within the frame, extra labor is required to ensure the masonry fits around the steel frame. Usually, this placement does not take advantage of the structural properties of the masonry panels. In hybrid masonry, the masonry panels take the place of conventional steel bracing, utilizing the structural properties of reinforced concrete masonry walls.

The infill wall is the supported wall that closes the perimeter of a building constructed with a three-dimensional framework structure. Therefore, the structural frame ensures the bearing function, whereas the infill wall serves to separate inner and outer space, filling up the boxes of the outer frames. The infill wall has the unique static function to bear its own weight. The infill wall is an external vertical opaque type of closure. With respect to other categories of wall, the infill wall differs from the partition that serves to separate two interior spaces, yet also non-load bearing, and from the load bearing wall. The latter performs the same functions of the infill wall, hygro-thermically and acoustically, but performs static functions too.
This glossary of structural engineering terms pertains specifically to structural engineering and its sub-disciplines. Please see glossary of engineering for a broad overview of the major concepts of engineering.
References
- ↑ Dawson, Susan. Architect's working details. vol. 10. London: Emap construct, 2004. 42. Print.
- ↑ "Advanced Masonry Design Software". MasterSeries. Retrieved 2023-01-17.
- ↑ "Masonry – Advanced Yield Line Analysis Method" (PDF). MasterSeries Technical Note. 2021 – via MasterSeries.
- ↑ "Wi System™ – Windposts & Lintels Alternative - Replace Windposts". 30 June 2017.