
Kofi Atta Annan was a Ghanaian diplomat who served as the seventh secretary-general of the United Nations from 1997 to 2006. Annan and the UN were the co-recipients of the 2001 Nobel Peace Prize. He was the founder and chairman of the Kofi Annan Foundation, as well as chairman of The Elders, an international organisation founded by Nelson Mandela.

The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, formerly the Organisation of the Islamic Conference, is an intergovernmental organization founded in 1969. It consists of 57 member states, 48 of which are Muslim-majority. The organisation claims to be "the collective voice of the Muslim world" and works to "safeguard and protect the interests of the Muslim world in the spirit of promoting international peace and harmony".

The Authorization for Use of Military Force Against Iraq Resolution of 2002, informally known as the Iraq Resolution, is a joint resolution passed by the United States Congress in October 2002 as Public Law No. 107-243, authorizing the use of the United States Armed Forces against Saddam Hussein's Iraq government in what would be known as Operation Iraqi Freedom.
The United States is a charter member of the United Nations and one of five permanent members of the UN Security Council.
Issues relating to the State of Israel and aspects of the Arab–Israeli conflict, and more recently the Iran–Israel conflict, occupy repeated annual debate times, resolutions and resources at the United Nations. Since its founding in 1948, the United Nations Security Council, has adopted 79 resolutions directly related to the Arab–Israeli conflict as of January 2010.

The World Peace Council (WPC) is an international organization created in 1949 by the Cominform and propped up by the Soviet Union. Throughout the Cold War, WPC engaged in propaganda efforts on behalf of the Soviet Union, whereby it criticized the United States and its allies while defending the Soviet Union's involvement in numerous conflicts.
The International law bearing on issues of Arab–Israeli conflict, which became a major arena of regional and international tension since the birth of Israel in 1948, resulting in several disputes between a number of Arab countries and Israel.
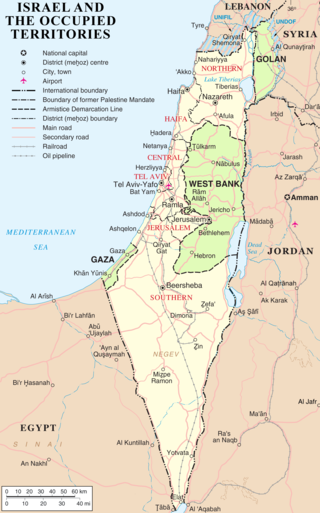
Israel has occupied the Palestinian territories and the Golan Heights since the Six-Day War of 1967. It previously occupied the Sinai Peninsula and southern Lebanon as well. Prior to 1967, the Palestinian territories was split between the Gaza Strip controlled by Egypt and the West Bank by Jordan, while the Sinai Peninsula and the Golan Heights are parts of Egypt and Syria, respectively. The Israeli occupation of the Palestinian territories and the Golan Heights, where Israel had transferred its parts of population there and built large settlements, is the longest military occupation in modern history.

The United Nations Alliance of Civilizations (UNAOC) is an initiative that attempts to "galvanize international action against extremism" through the forging of international, intercultural and interreligious dialogue and cooperation. The Alliance places a particular emphasis on defusing tensions between the Western and Islamic worlds.

Global Witness is an international NGO established on November 15 1993 that works to break the links between natural resource exploitation, conflict, poverty, corruption, and human rights abuses worldwide. The organisation has offices in London and Washington, D.C.

The United Nations Peacebuilding Commission (PBC) is a United Nations intergovernmental advisory body of both the General Assembly and the Security Council that supports peace efforts in conflict-affected countries. A key addition to the capacity of the international community in the broad peace agenda, it was established in 2005 with the passage of both A/RES/60/180 and S/RES/1645 Mr. Sérgio França Danese (Brazil) is the incumbent chair of the PBC.
Strategic Foresight Group (SFG) is a think tank based in India that works on global issues. It was established in 2002.

The International Campaign to Abolish Nuclear Weapons is a global civil society coalition working to promote adherence to and full implementation of the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons. The campaign helped bring about this treaty. ICAN was launched in 2007. In 2022, it counted 661 partner organizations in 110 countries.

The legality of the Iraq War is a contested topic that spans both domestic and international law. Political leaders in the US and the UK who supported the invasion of Iraq have claimed that the war was legal. However, legal experts and other world leaders have argued that the war lacked justification and violated the United Nations charter.
Issues relating to the State of Palestine and aspects of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict occupy continuous debates, resolutions, and resources at the United Nations. Since its founding in 1948, the United Nations Security Council, as of January 2010, has adopted 79 resolutions directly related to the Arab–Israeli conflict.

The Global Peace Foundation (GPF) is an international nonprofit organization with a stated mission to promote “an innovative, values-based approach to peacebuilding, guided by the vision of One Family under God.” GPF partners with government ministries, community and faith-based organizations, and United Nations offices to develop and execute programs in 20 countries.
Israeli settlements in the Israeli-occupied Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip, as well as in the Syrian Golan Heights, are illegal under international law. These settlements are in violation of Article 49 of the Fourth Geneva Convention, and in breach of international declarations. In a 2024 ruling by the International Court of Justice (ICJ) relating to the Palestinian territories, the court reaffirmed the illegality of the settlements and called on Israel to end its occupation, cease its settlement activity, and evacuate all its settlers.

Rajani Kannepalli Kanth is a professor, economist, philosopher, and social thinker. Though born in India, he is a U.S. citizen and has resided overseas for most of his life. His major research interests lie in the fields of Economics, Social Theory and Policy, and Women's Issues. His works have received positive endorsements from iconic intellectuals such as Ravi Batra, Roy Bhaskar, Noam Chomsky, Geoff Harcourt, Robert Heilbroner, John M. Hobson, Jonathan Joseph, Tony Lawson, Ali Mazrui, John McMurtry, Roger Owen, Warren Samuels, Gayatri Chakravorty Spivak, Paul Sweezy, and Immanuel Wallerstein. He has, across plus-three decades, taught in the areas of Anthropology, Sociology, Political Science, History, Economics, and Philosophy. He currently serves as the Trustee of the World Peace Congress that he founded in Salt Lake City, Utah, in 2007. He has also served as an advisor to the United Nations in New York, aside from being on the faculty of major universities around the world.

The Whitney R. Harris World Law Institute at Washington University School of Law, established in 2000 as the Institute for Global Legal Studies, serves as a center for instruction and research in international and comparative law.
The World Conference on Women, 1985 or the Third World Conference on Women took place between 15 and 26 July 1985 in Nairobi, Kenya, as the end-of-decade assessment of progress and failure in implementing the goals established by the World Plan of Action from the 1975 inaugural conference on women as modified by the World Programme of Action of the second conference. Of significance during the conference was the result of the Forward-looking Strategies for the Advancement of Women being adopted by consensus, unlike the previous two conferences. The conference marked the first time that lesbian rights were introduced in a UN official meeting and the turning-point for violence against women to emerge from being a hidden topic into one which needed to be addressed. Recognizing that the goals of the Decade for Women had not been met, the conference recommended and the General Assembly approved on-going evaluation of women's achievements and failures through the year 2000.












