
The Centaurus was the final development of the Bristol Engine Company's series of sleeve valve radial aircraft engines. The Centaurus is an 18-cylinder, two-row design that eventually delivered over 3,000 hp (2,200 kW). The engine was introduced into service late in the Second World War and was one of the most powerful aircraft piston engines to see service.

The Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone is an American twin-row, supercharged, air-cooled, radial aircraft engine with 18 cylinders displacing nearly 3,350 cubic inches (54.9 L). Power ranged from 2,200 to over 3,700 hp, depending on the model. Developed before World War II, the R-3350's design required a long time to mature before finally being used to power the Boeing B-29 Superfortress.
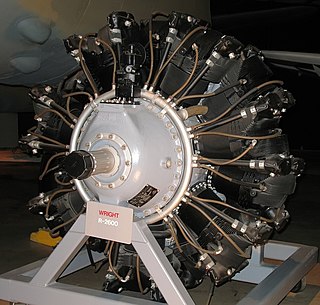
The Wright R-2600 Cyclone 14 is an American radial engine developed by Curtiss-Wright and widely used in aircraft in the 1930s and 1940s.

The Pratt & Whitney Wasp was the civilian name of a family of air-cooled radial piston engines developed in the 1920s, 1930s and 1940s.

The Pratt & Whitney R-1690 Hornet was a widely used American aircraft engine. Developed by Pratt & Whitney, 2,944 were produced from 1926 through 1942. It first flew in 1927. It was a single-row, 9-cylinder air-cooled radial design. Displacement was 1,690 cubic inches. It was built under license in Italy as the Fiat A.59. In Germany, the BMW 132 was a developed version of this engine. The R-1860 Hornet B was an enlarged version produced from 1929.
The BMW 802 was a large air-cooled radial aircraft engine, built using two rows of nine cylinders to produce what was essentially an 18-cylinder version of the 14-cylinder BMW 801. Although promising at first, development dragged on and the project was eventually cancelled to concentrate on jet engines instead.

The Wright R-1300 Cyclone 7 is an American air-cooled seven-cylinder supercharged radial aircraft engine produced by Curtiss-Wright.

The Shvetsov ASh-62 is a nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial aircraft engine produced in the Soviet Union. A version of this engine is produced in Poland as the ASz-62 and the People's Republic of China as the HS-5.

The Gnome et Rhône 18L was a French-designed twin-row 18-cylinder air-cooled radial engine. The 18L was a large step up in terms of displacement, power and number of cylinders. The majority of Gnome-Rhone engines were either 7, 9 or 14 cylinders. The engine proved not to be a success, and it was dropped in 1939 due to a poor power-to-weight ratio.

The Shvetsov M-25 was an aircraft radial engine produced in the Soviet Union (USSR) in the 1930s and 1940s, a licensed production variant of the Wright R-1820-F3.

The Shvetsov ASh-21 is a seven-cylinder single-row air-cooled radial aero engine.
The Armstrong Siddeley Hyena was a British aero engine developed by Armstrong Siddeley. Designed in the 1930s, it was an unusual experimental radial engine with inline cylinder banks. It was flown using an Armstrong Whitworth A.W.16 fighter aircraft as a test bed. Unresolved problems with cooling of the rear cylinders prevented the engine from going into production. Few details of this engine survive as company records were lost.

The Armstrong Siddeley Deerhound was a large aero engine developed by Armstrong Siddeley between 1935 and 1941. An increased capacity variant known as the Boarhound was never flown, and a related, much larger, design known as the Wolfhound existed on paper only. Development of these engines was interrupted in April 1941, when the company's factory was bombed, and on 3 October 1941 the project was cancelled by the Air Ministry.
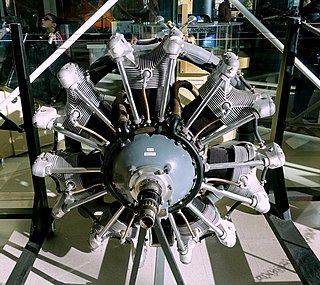
The Jacobs R-915 or Jacobs L-6 is a seven-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine for aircraft manufactured in the United States, production started in 1936.
The Jacobs R-830 or L-5 is a seven-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine for aircraft manufactured in the United States, production started in 1935.

The Alvis Pelides was an unflown British air-cooled radial aero engine first developed in 1936. The Pelides Major was a projected but unbuilt development as were the Alcides, Alcides Major and the Maeonides Major, the Alvis aircraft engine range taking their names from Greek mythology.

Alessandro Anzani developed the first two-row radial from his earlier 3- cylinder Y engine by merging two onto the same crankshaft with a common crankweb.
The RAF 2 was a British air-cooled, nine-cylinder radial engine developed for aircraft use just prior to World War I; it was designed and built by the Royal Aircraft Factory.
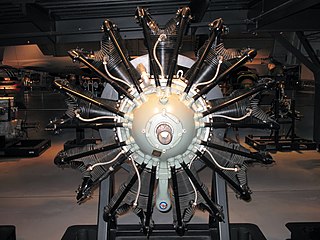
The Pratt & Whitney R-1860 Hornet B was a relatively uncommon aircraft engine. It was a development of Pratt & Whitney's earlier R-1690 Hornet and was basically similar, but enlarged in capacity from 1,690 to 1,860 cubic inches (30.5 L). Cylinder bore was increased by 1/8" and the crankshaft stroke by 3/8". Both engines were air-cooled radial engines, with a single row of nine cylinders.
The Wright R-4090 Cyclone 22 was an American experimental radial piston engine designed and built in prototype form by Wright Aeronautical during the 1940s.


















