
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs were originally developed through the twentieth century for military missions too "dull, dirty or dangerous" for humans, and by the twenty-first, they had become essential assets to most militaries. As control technologies improved and costs fell, their use expanded to many non-military applications. These include aerial photography, precision agriculture, forest fire monitoring, river monitoring, environmental monitoring, policing and surveillance, infrastructure inspections, smuggling, product deliveries, entertainment, and drone racing.
LATAM Airlines Brasil, formerly TAM Linhas Aéreas, is the Brazilian brand of LATAM Airlines Group operating international and domestic flights from hubs in Rio, São Paulo, and Brasília. According to the National Civil Aviation Agency of Brazil (ANAC), between January and December 2019, LATAM had 34.7% of the domestic, and 20.9% of the international market share in terms of passenger-kilometers flown, making it the second largest domestic and largest international airline in Brazil.
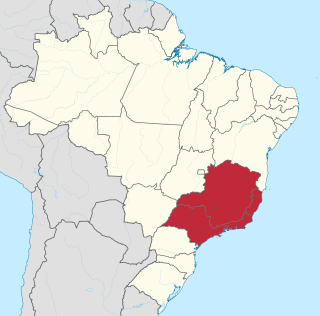
The Southeast Region of Brazil is composed of the states of Espírito Santo, Minas Gerais, Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo. It is the richest region of the country, responsible for approximately 60% of the Brazilian GDP, as São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, and Minas Gerais are the three richest states of Brazil, the top three Brazilian states in terms of GDP. The Southeast of Brazil also has the highest GDP per capita among all Brazilian regions.
Avianca Brasil S.A., officially Oceanair Linhas Aéreas S/A, was a Brazilian airline based in Congonhas Airport in São Paulo, Brazil. According to the National Civil Aviation Agency of Brazil (ANAC), which cancelled its operation, prior to cessation of operations, from January to December 2018 Avianca Brasil had 13.4% of the domestic and 7.3% of the international market share in terms of passengers per kilometer flown, making it the fourth-largest airline both in domestic and international traffic in Brazil. The company slots were redistributed by Anac. An auction on 10 July 2019 raised R$555.3 million, not enough to pay a debt of R$2.7 billion, although Avianca's bankruptcy was not officially decreed.
Pantanal Linhas Aéreas S.A. was a regional airline based in São Paulo, Brazil and incorporated by TAM Linhas Aéreas in 2013. It served destinations mainly in the southeast region of Brazil from its bases at Congonhas and Guarulhos airports in São Paulo.

Puma Air was a Brazilian airline founded in 2002. In August 2011 it ceased operations.

BRA Transportes Aéreos was a short-lived Brazilian low-fare airline based in São Paulo, Brazil, which used to operate both domestic and international scheduled services, as well as charter flights. Its main base was São Paulo/Guarulhos International Airport. BRA was the third largest airline in Brazil with 4.19% of the domestic Brazilian market as of August 2006.

The National Civil Aviation Agency, is the Brazilian civil aviation authority, created in 2005. It is headquartered in the Edifício Parque Cidade Corporate in Brasília. A part of the Brazilian Secretariat of Civil Aviation, the agency raised from the former Department of Civil Aviation (DAC) and the Civil Aviation Certification Division, the Brazilian aircraft certification authority. ANAC is responsible for regulating and overseeing civil aviation activities, aeronautics and aerodromes infrastructure.

Aurora Flight Sciences is an American aviation and aeronautics research subsidiary of Boeing which primarily specializes in the design and construction of special-purpose Unmanned aerial vehicles. Aurora has been established for 20+ years and their headquarters is at the Manassas Regional Airport in Manassas, Virginia.
The Brazilian Organization for the Development of Aeronautical Certification is a nonprofit organization, of public interest, regulated by Brazilian Law number 9.790 as of March 23, 1999, and registered at the Brazilian Ministry of Justice on November 28, 2006.

The Boeing Phantom Eye was a high altitude, long endurance (HALE) liquid hydrogen-powered unmanned aerial vehicle developed by Boeing Phantom Works. The aircraft was Boeing's proposal to meet the demand from the US military for unmanned drones designed to provide advanced intelligence and reconnaissance work, driven by the combat conditions in Afghanistan in particular. In August 2016, the Phantom Eye demonstrator was disassembled for display at the Air Force Flight Test Museum.

The Demon is an experimental unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) developed and manufactured by British defence conglomerate BAE Systems. It has been referred to as being the world's first "flapless" aircraft.

MAP Linhas Aéreas is a domestic airline based in Manaus, Brazil, founded in 2011 authorized to operate regular and non-regular charter flights within Brazil.

As of January 2014, the United States military operates a large number of unmanned aerial vehicles : 7,362 RQ-11 Ravens; 990 AeroVironment Wasp IIIs; 1,137 AeroVironment RQ-20 Pumas; 306 RQ-16 T-Hawk small UAS systems; 246 MQ-1 Predators; MQ-1C Gray Eagles; 126 MQ-9 Reapers; 491 RQ-7 Shadows; and 33 RQ-4 Global Hawk large systems.

On 11 February 2019, a Bell 206B helicopter crashed while trying to land on the Rodoanel Mário Covas highway, following an unspecified malfunction. Among the victims was journalist Ricardo Boechat. The pilot, Ronaldo Quatrucci, was also killed and one person on the ground was injured. The aircraft crashed around 12:15 pm (UTC−02:00) and the journalist and pilot were pronounced dead shortly after. The helicopter was owned by RQ Serviços Aéreo Especializados Ltda.
Abaeté Aviação is a domestic airline based in Salvador da Bahia, Brazil. Although the company was established in 1995 it was not authorized to operate regular flights until 2020.

Itapemirim Transportes Aéreos Ltda. was a Brazilian airline established in 2020 and belonged to Itapemirim Group. On 17 December 2021, the airline suspended all operations for internal restructuring. In March 2022, it was announced that the Baufaker Consulting firm bought the company, in which after the Owner Galeb Baufaker Junior defended the termination of the contract. ITA had its Air operator's certificate permanently revoked on May 5, 2022.
Flyer Indústria Aeronáutica, Eireli is a Brazilian manufacturer of light aircraft headquartered in Sumaré, São Paulo.















