
The Lophophorata or Tentaculata are a Lophotrochozoan clade consisting of the Brachiozoa and the Bryozoa. They have a lophophore. Molecular phylogenetic analyses suggest that lophophorates are protostomes, but on morphological grounds they have been assessed as deuterostomes. Fossil finds of the "tommotiid" Wufengella suggest that they evolved from worm-like animals that resembled annelids.

The Mesozoa are minuscule, worm-like parasites of marine invertebrates. Generally, these tiny, elusive creatures consist of a somatoderm of ciliated cells surrounding one or more reproductive cells.

Vetulicolia is a phylum of animals encompassing several extinct species belonging to the Cambrian Period. The phylum was created by Degan Shu and his research team in 2001, and named after Vetulicola cuneata, the first species of the phylum described in 1987. The vetulicolian body comprises two parts: a voluminous anterior forebody, tipped with an anteriorly positioned mouth and lined with a row of five round to oval-shaped features on each lateral side, which have been interpreted as gills ; and a posterior section that primitively comprises seven segments and functions as a tail. All vetulicolians lack preserved appendages of any kind, having no legs, feelers or even eyes. The area where the anterior and posterior parts join is constricted.
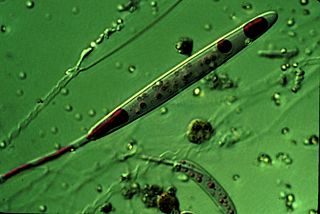
A cnidocyte is an explosive cell containing one large secretory organelle called a cnidocyst that can deliver a sting to other organisms. The presence of this cell defines the phylum Cnidaria. Cnidae are used to capture prey and as a defense against predators. A cnidocyte fires a structure that contains a toxin within the cnidocyst; this is responsible for the stings delivered by a cnidarian.

Panarthropoda is a proposed animal clade containing the extant phyla Arthropoda, Tardigrada and Onychophora. Panarthropods also include extinct marine legged worms known as lobopodians ("Lobopodia"), a paraphyletic group where the last common ancestor and basal members (stem-group) of each extant panarthropod phylum are thought to have risen. However the term "Lobopodia" is sometimes expanded to include tardigrades and onychophorans as well.

Lophotrochozoa is a clade of protostome animals within the Spiralia. The taxon was established as a monophyletic group based on molecular evidence. The clade includes animals like annelids, molluscs, bryozoans, brachiopods, and platyhelminthes.

Acoelomorpha is a subphylum of very simple and small soft-bodied animals with planula-like features which live in marine or brackish waters. They usually live between grains of sediment, swimming as plankton, or crawling on other organisms, such as algae and corals. With the exception of two acoel freshwater species, all known Acoelomorphs are marine.
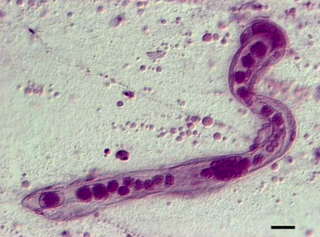
Dicyemida, also known as Rhombozoa, is a phylum of tiny parasites that live in the renal appendages of cephalopods.

Xenoturbella is a genus of very simple bilaterians up to a few centimeters long. It contains a small number of marine benthic worm-like species.

Acropora is a genus of small polyp stony coral in the phylum Cnidaria. Some of its species are known as table coral, elkhorn coral, and staghorn coral. Over 149 species are described. Acropora species are some of the major reef corals responsible for building the immense calcium carbonate substructure that supports the thin living skin of a reef.

Deuterostomes are bilaterian animals of the superphylum Deuterostomia, typically characterized by their anus forming before the mouth during embryonic development. The three major clades of extant deuterostomes include chordates, echinoderms and hemichordates.

The origin of the brachiopods is uncertain; they either arose from reduction of a multi-plated tubular organism, or from the folding of a slug-like organism with a protective shell on either end. Since their Cambrian origin, the phylum rose to a Palaeozoic dominance, but dwindled during the Mesozoic.

The Spiralia are a morphologically diverse clade of protostome animals, including within their number the molluscs, annelids, platyhelminths and other taxa. The term Spiralia is applied to those phyla that exhibit canonical spiral cleavage, a pattern of early development found in most members of the Lophotrochozoa.

Indostomus is a genus of small fishes native to slow moving or stagnant freshwater habitats in Indochina. It is the sole genus of the monogeneric family Indostomidae, Long considered to be sticklebacks, within the order Gasterosteiformes, modern analyses place the Indostomids within the order Synbranchiformes, related to the spiny eels and swamp eels.

Xenoturbella bocki is a marine benthic worm-like species from the genus Xenoturbella. It is found in saltwater sea floor habitats off the coast of Europe, predominantly Sweden. It was the first species in the genus discovered. Initially it was collected by Swedish zoologist Sixten Bock in 1915, and described in 1949 by Swedish zoologist Einar Westblad. The unusual digestive structure of this species, in which a single opening is used to eat food and excrete waste, has led to considerable study and controversy as to its classification. It is a bottom-dwelling, burrowing carnivore that eats mollusks.

Xenoturbella churro is a marine, benthic, deep-water worm-like species that belongs to the genus Xenoturbella. It was discovered in eastern Pacific Ocean by a group of Californian and Australian scientists. The species was described in 2016 from a single specimen.

Xenoturbella profunda, the purple sock or sock worm, is a marine, benthic, deep-water worm-like species that belongs to the genus Xenoturbella. It was discovered in eastern Pacific Ocean by a group of Californian and Australian scientists. The species was described in 2016 from seven specimens.

Xenoturbella monstrosa, a deep-sea giant purple sock worm, is a marine, benthic, deep-water worm-like species that belongs to the genus Xenoturbella. It was discovered in eastern Pacific Ocean by a group of Californian and Australian scientists. The species was described in 2016 from several specimens.

Xenoturbella hollandorum is a marine, benthic worm-like species that belongs to the genus Xenoturbella. It was discovered in eastern Pacific Ocean by a group of Californian and Australian scientists. The species was described in 2016.
















