
Entamoeba is a genus of Amoebozoa found as internal parasites or commensals of animals. In 1875, Fedor Lösch described the first proven case of amoebic dysentery in St. Petersburg, Russia. He referred to the amoeba he observed microscopically as Amoeba coli; however, it is not clear whether he was using this as a descriptive term or intended it as a formal taxonomic name. The genus Entamoeba was defined by Casagrandi and Barbagallo for the species Entamoeba coli, which is known to be a commensal organism. Lösch's organism was renamed Entamoeba histolytica by Fritz Schaudinn in 1903; he later died, in 1906, from a self-inflicted infection when studying this amoeba. For a time during the first half of the 20th century the entire genus Entamoeba was transferred to Endamoeba, a genus of amoebas infecting invertebrates about which little is known. This move was reversed by the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature in the late 1950s, and Entamoeba has stayed 'stable' ever since.

Entamoeba histolytica is an anaerobic parasitic amoebozoan, part of the genus Entamoeba. Predominantly infecting humans and other primates causing amoebiasis, E. histolytica is estimated to infect about 35-50 million people worldwide. E. histolytica infection is estimated to kill more than 55,000 people each year. Previously, it was thought that 10% of the world population was infected, but these figures predate the recognition that at least 90% of these infections were due to a second species, E. dispar. Mammals such as dogs and cats can become infected transiently, but are not thought to contribute significantly to transmission.

Mimivirus is a genus of giant viruses, in the family Mimiviridae. Amoeba serve as their natural hosts. This genus contains a single identified species named Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus (APMV). It also refers to a group of phylogenetically related large viruses.

Naegleria is a genus consisting of 47 described species of protozoa often found in warm aquatic environments as well as soil habitats worldwide. It has three life cycle forms: the amoeboid stage, the cyst stage, and the flagellated stage, and has been routinely studied for its ease in change from amoeboid to flagellated stages. The Naegleria genera became famous when Naegleria fowleri, the causative agent of the usually fatal human and animal disease primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM), was discovered in 1965. Most species in the genus, however, are incapable of causing disease.
A chimera or chimeric virus is a virus that contains genetic material derived from two or more distinct viruses. It is defined by the Center for Veterinary Biologics as a "new hybrid microorganism created by joining nucleic acid fragments from two or more different microorganisms in which each of at least two of the fragments contain essential genes necessary for replication." The term genetic chimera had already been defined to mean: an individual organism whose body contained cell populations from different zygotes or an organism that developed from portions of different embryos. Chimeric flaviviruses have been created in an attempt to make novel live attenuated vaccines.

Lake Pampulha is an artificial lake located in Pampulha, Belo Horizonte, Brazil. It is also the name of an administrative region of Belo Horizonte, and the name of one of 29 neighborhoods (bairros) within the administrative region of the same name. The lake was built in the early 1940s during the mayoralty of Juscelino Kubitschek, later president of Brazil from 1956 to 1961. Pampulha was created as a source of water for the city of Belo Horizonte, but quickly became polluted.

Virophages are small, double-stranded DNA viral phages that require the co-infection of another virus. The co-infecting viruses are typically giant viruses. Virophages rely on the viral replication factory of the co-infecting giant virus for their own replication. One of the characteristics of virophages is that they have a parasitic relationship with the co-infecting virus. Their dependence upon the giant virus for replication often results in the deactivation of the giant viruses. The virophage may improve the recovery and survival of the host organism.

Mimivirus-dependent virus Sputnik is a subviral agent that reproduces in amoeba cells that are already infected by a certain helper virus; Sputnik uses the helper virus's machinery for reproduction and inhibits replication of the helper virus. It is known as a virophage, in analogy to the term bacteriophage.

Mimiviridae is a family of viruses. Amoeba and other protists serve as natural hosts. The family is divided in up to 4 subfamilies. Viruses in this family belong to the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA virus clade (NCLDV), also referred to as giant viruses.
Mamavirus is a large and complex virus in the Group I family Mimiviridae. The virus is exceptionally large, and larger than many bacteria. Mamavirus and other mimiviridae belong to nucleocytoplasmic large DNA virus (NCLDVs) family. Mamavirus can be compared to the similar complex virus mimivirus; mamavirus was so named because it is similar to but larger than mimivirus.
Marseillevirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Marseilleviridae. There are two species in this genus. It is the prototype of a family of nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses (NCLDV) of eukaryotes. It was isolated from amoeba.
Organic Lake is a lake in the Vestfold Hills in eastern Antarctica. It was formed 6,000 years ago when sea levels were higher; it is isolated, rather shallow 7.5 metres (25 ft), meromictic, a few hundred meters in diameter and has extremely salty water. It has the highest recorded concentration of dimethyl sulfide in any natural body of water.
A giant virus, sometimes referred to as a girus, is a very large virus, some of which are larger than typical bacteria. All known giant viruses belong to the phylum Nucleocytoviricota.

Pandoravirus is a genus of giant virus, first discovered in 2013. It is the second largest in physical size of any known viral genus, behind only Pithovirus. Pandoraviruses have double stranded DNA genomes, with the largest genome size of any known viral genus.
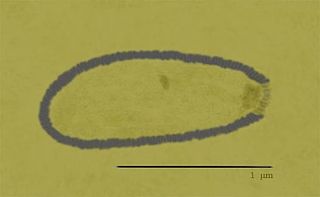
Pithovirus, first described in a 2014 paper, is a genus of giant virus known from two species, Pithovirus sibericum, which infects amoebas and Pithovirus massiliensis. It is a DNA based virus and is a member of the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses clade. The 2014 discovery was made when a viable specimen was found in a 30,000-year-old ice core harvested from permafrost in Siberia, Russia.

Faustovirus is a genus of giant virus which infects amoebae associated with humans. The virus was first isolated in 2015 and shown to be around 0.2 micrometers in diameter with a double stranded DNA genome of 466 kilobases predicted to encode 451 proteins. Although classified as a nucleocytoplasmic large DNA virus (NCLDV), faustoviruses share less than a quarter of their genes with other NCLDVs; however, ~46% are homologous to bacterial genes and the remainder are orphan genes (ORFans). Specifically, the gene encoding the major capsid protein (MCP) of faustovirus is different than that of its most closely related giant virus, asfivirus, as well as other NCLDVs. In asfivirus, the gene encoding MCP is a single genomic fragment of ~2000 base pairs (bp), however, in faustovirus the MCP is encoded by 13 exons separated by 12 large introns. The exons have a mean length of 149 bp and the introns have a mean length of 1,273 bp. The presence of introns in faustovirus genes is highly unusual for viruses.

Tupanvirus is a genus of viruses first described in 2018. The genus is composed of two species of virus that are in the giant virus group. Researchers discovered the first isolate in 2012 from deep water sediment samples taken at 3000m depth off the coast of Brazil. The second isolate was collected from a soda lake in Southern Nhecolândia, Brazil in 2014. They are named after Tupã (Tupan), a Guaraní thunder god, and the places they were found. These are the first viruses reported to possess genes for amino-acyl tRNA synthetases for all 20 standard amino acids.

Medusavirus is a nucleocytoplasmic large DNA virus first isolated from a Japanese hot spring in 2019. It notably encodes all five types of histones — H1, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 — which are involved in DNA packaging in eukaryotes, raising the possibility that they may have been involved in the origin of eukaryotes. The virus can harden amoebas of the species Acanthamoeba castellanii into stone-like cysts, but infection usually causes infected amoebas to burst open. The virus was named after Medusa, the monster in Greek mythology whose gaze turned people to stone.

Varidnaviria is a realm of viruses that includes all DNA viruses that encode major capsid proteins that contain a vertical jelly roll fold. The major capsid proteins (MCP) form into pseudohexameric subunits of the viral capsid, which stores the viral deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), and are perpendicular, or vertical, to the surface of the capsid. Apart from this, viruses in the realm also share many other characteristics, such as minor capsid proteins (mCP) with the vertical jelly roll fold, an ATPase that packages viral DNA into the capsid, and a DNA polymerase that replicates the viral genome.
Nucleocytoviricota is a phylum of viruses. Members of the phylum are also known as the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses (NCLDV), which serves as the basis of the name of the phylum with the suffix -viricota for virus phylum. These viruses are referred to as nucleocytoplasmic because they are often able to replicate in both the host's cell nucleus and cytoplasm.











