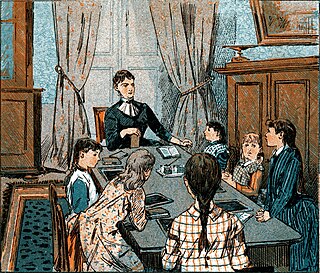
Homeschooling or home schooling, also known as home education or elective home education (EHE), is the education of school-aged children at home or a variety of places other than a school. Usually conducted by a parent, tutor, or online teacher, many homeschool families use less formal, more personalized and individualized methods of learning that are not always found in schools. The actual practice of homeschooling varies considerably. The spectrum ranges from highly structured forms based on traditional school lessons to more open, free forms such as unschooling, which is a lesson- and curriculum-free implementation of homeschooling. Some families who initially attended a school go through a deschool phase to break away from school habits and prepare for homeschooling. While "homeschooling" is the term commonly used in North America, "home education" is primarily used in Europe and many Commonwealth countries. Homeschooling should not be confused with distance education, which generally refers to the arrangement where the student is educated by and conforms to the requirements of an online school, rather than being educated independently and unrestrictedly by their parents or by themselves.

A school is both the educational institution and building designed to provide learning spaces and learning environments for the teaching of students under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of formal education, which is sometimes compulsory. In these systems, students progress through a series of schools that can be built and operated by both government and private organization. The names for these schools vary by country but generally include primary school for young children and secondary school for teenagers who have completed primary education. An institution where higher education is taught is commonly called a university college or university.
Truancy is any intentional, unjustified, unauthorized, or illegal absence from compulsory education. It is a deliberate absence by a student's own free will and usually does not refer to legitimate excused absences, such as ones related to medical conditions. Truancy is usually explicitly defined in the school's handbook of policies and procedures. Attending school but not going to class is called internal truancy. Some children whose parents claim to homeschool have also been found truant in the United States.

Education in Germany is primarily the responsibility of individual German states, with the federal government only playing a minor role.

In France, secondary education is in two stages:

Spring break, known variously as Easter vacation, Easter holiday, Easter break, spring vacation, mid-term break, study week, reading week, reading period, Easter week or March break, is a vacation period including Easter holidays in early Northern Hemisphere spring at universities and schools, which has been observed in Europe since the late 19th century, was introduced during the 1930s in the US, and is observed in many other countries. Spring Break can be associated with riotous partying at warm weather locations.
An academic term is a portion of an academic year during which an educational institution holds classes. The schedules adopted vary widely. Specific synonyms are commonly used to denote the duration or a term. In most countries, the academic year begins in late summer or early autumn and ends during the following spring or summer.

A summer camp or sleepaway camp is a supervised program for children conducted during the summer months in some countries. Children and adolescents who attend summer camps are known as campers. Summer school is usually a part of the academic curriculum for a student to make up work not accomplished during the academic year.
Tenth grade is the tenth year of formal or compulsory education. It is typically the second year of high school. In many parts of the world, students in tenth grade are usually 15 or 16 years of age.

The Republic of Austria has a free and public school system, and nine years of education are mandatory. Schools offer a series of vocational-technical and university preparatory tracks involving one to four additional years of education beyond the minimum mandatory level. The legal basis for primary and secondary education in Austria is the School Act of 1962. The Federal Ministry of Education is responsible for funding and supervising primary, secondary, and, since 2000, also tertiary education. Primary and secondary education is administered on the state level by the authorities of the respective states.

An academic year is "the year during which students attend school or university". An academic year or school year is a period that schools, colleges and universities use to measure the quantity of study. During this period, students attend classes and do relevant exams and homework. It comprises school days and school holidays. Duration of school days, school year, and holidays vary across the world.
The term summer vacation or summer break refers to a school break in the summer between school years and the break in the school academic year. Students are off anywhere between two weeks to three and a half months. Depending on the country and district, staff might be partially or fully excluded.
Summer learning loss or summer slide, is the loss of academic skills and knowledge over the course of summer vacation in countries that have lengthy breaks in the school year, such as the US and Canada. Schools see evidence of this because students are often given a standardised test prior to the summer break and again when they return to school in the autumn.
Revision week is a period in the UK and other Commonwealth countries preceding examinations in high schools, higher education institutions, and military colleges. In American colleges, this period is known as a Reading Period. Generally, this period is one week long and free of classes or assessment, permitting students to spend the period revising material, generally in preparation for final exams. With the exception of Canadian post-secondary institutions, is not often allocated for mid-semester or ongoing assessment. Each day of such a period may be referred to as a reading day. Hell week is used in many similar educational contexts, such as police or military training.

The Pennsylvania Leadership Charter School (PALCS) is a public cyber charter school approved by the Pennsylvania Department of Education, and open to all students in grades K–12 who reside in the state of Pennsylvania.

In the Dominican Republic, education is free and compulsory at the elementary level, and free but non-mandatory at the secondary level. It is divided into four stages:
Working class education is the education of working-class people.
Multi-age classrooms or composite classes are classrooms with students from more than one grade level. They are created because of a pedagogical choice of a school or school district. They are different from split classes which are formed when there are too many students for one class – but not enough to form two classes of the same grade level. Composite classes are more common in smaller schools; an extreme form is the one-room school.
Expanded learning time (ELT) is a strategy employed by schools in the United States to redesign their school days and/or years in order to provide students, particularly in communities of concentrated poverty, with substantially more and better learning time. ELT is often a core element of school improvement or turnaround efforts, such that other practices like teacher collaboration, data-driven instruction, and integrated enrichment can be more effectively implemented. ELT differs from associated efforts like after-school programs or expanded learning opportunities (ELOs) because ELT requires all students in a given school to attend the longer day and/or year, and the additional time becomes a dependent component of the school's educational practices and objectives.

High school or senior high school is the education students receive in the final stage of secondary education in the United States. In the United States most high schoolers are ages 13–18 but some ages could be delayed due to birthdays. Most comparable to secondary schools, high schools generally deliver phase three of the ISCED model of education. High schools have subject-based classes. The name high school is applied in other countries, but no universal generalization can be made as to the age range, financial status, or ability level of the pupils accepted. In North America, most high schools include grades 9 through 12. Students attend them following graduation from middle school.










