| Yellow-billed oxpecker | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Adult in typical feeding mode | |
 | |
| On a zebra, Senegal | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Buphagidae |
| Genus: | Buphagus |
| Species: | B. africanus |
| Binomial name | |
| Buphagus africanus Linnaeus, 1766 | |
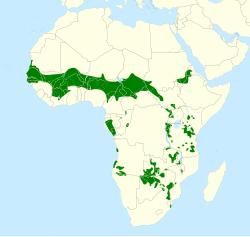 | |
| Range of the yellow-billed oxpecker | |
| Synonyms | |
Buphaga africanaLinnaeus, 1766 | |
The yellow-billed oxpecker (Buphagus africanus) is a passerine bird in the family Buphagidae. It was previously placed in the starling and myna family, Sturnidae.
Contents
It is native to the savannah of Sub-Saharan Africa from Senegal east to Sudan. It is least common in the extreme east of its range where it overlaps with the red-billed oxpecker, despite always dominating that species when feeding.
