Related Research Articles

Mustard gas or sulfur mustard is any of the several chemical compounds that contain the chemical structure S(CH2CH2Cl)2. In the wider sense, compounds with the substituent S(CH2CH2X)2 and N(CH2CH2X)3 are known as sulfur mustards and nitrogen mustards, respectively, where X = Cl or Br. Such compounds are potent alkylating agents, which can interfere with several biological processes. Also known as mustard agents, this family of compounds are infamous cytotoxins and blister agents with a long history of use as chemical weapons. The name mustard gas is technically incorrect: the substances, when dispersed, are often not gases but a fine mist of liquid droplets. Sulfur mustards are viscous liquids at room temperature and have an odor resembling mustard plants, garlic, or horseradish, hence the name. When pure, they are colorless, but when used in impure forms, such as in warfare, they are usually yellow-brown. Mustard gases form blisters on exposed skin and in the lungs, often resulting in prolonged illness ending in death. The typical mustard gas is the organosulfur compound bis(2-chloroethyl) sulfide.

The use of toxic chemicals as weapons dates back thousands of years, but the first large-scale use of chemical weapons was during World War I. They were primarily used to demoralize, injure, and kill entrenched defenders, against whom the indiscriminate and generally very slow-moving or static nature of gas clouds would be most effective. The types of weapons employed ranged from disabling chemicals, such as tear gas, to lethal agents like phosgene, chlorine, and mustard gas. These chemical weapons caused medical problems. This chemical warfare was a major component of the first global war and first total war of the 20th century. The killing capacity of gas was profound, with about 90,000 fatalities from a total of 1.3 million casualties caused by gas attacks. Gas was unlike most other weapons of the period because it was possible to develop countermeasures, such as gas masks. In the later stages of the war, as the use of gas increased, its overall effectiveness diminished. The widespread use of these agents of chemical warfare, and wartime advances in the composition of high explosives, gave rise to an occasionally expressed view of World War I as "the chemist's war" and also the era where weapons of mass destruction were created.

Lewisite (L) (A-243) is an organoarsenic compound. It was once manufactured in the U.S., Japan, Germany and the Soviet Union for use as a chemical weapon, acting as a vesicant and lung irritant. Although the substance is colorless and odorless in its pure form, impure samples of lewisite are a yellow, brown, violet-black, green, or amber oily liquid with a distinctive odor that has been described as similar to geraniums.

Chlormethine, also known as mechlorethamine, mustine, HN2, and embikhin (эмбихин), is a nitrogen mustard sold under the brand name Mustargen among others. It is the prototype of alkylating agents, a group of anticancer chemotherapeutic drugs. It works by binding to DNA, crosslinking two strands and preventing cell duplication. It binds to the N7 nitrogen on the DNA base guanine. As the chemical is a blister agent, its use is strongly restricted within the Chemical Weapons Convention where it is classified as a Schedule 1 substance.
IARC group 1 Carcinogens are substances, chemical mixtures, and exposure circumstances which have been classified as carcinogenic to humans by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). This category is used when there is sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in humans. Exceptionally, an agent may be placed in this category when evidence of carcinogenicity in humans is less than sufficient, but when there is sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals and strong evidence in exposed humans that the agent (mixture) acts through a relevant mechanism of carcinogenicity.

Nitrogen mustards (NMs) are cytotoxic organic compounds with the bis(2-chloroethyl)amino ((ClC2H4)2NR) functional group. Although originally produced as chemical warfare agents, they were the first chemotherapeutic agents for treatment of cancer. Nitrogen mustards are nonspecific DNA alkylating agents.
This is the list of extremely hazardous substances defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act. The list can be found as an appendix to 40 CFR 355. Updates as of 2006 can be seen on the Federal Register, 71 FR 47121.

Sesquimustard is the organosulfur compound with the formula (ClCH2CH2SCH2)2. Although it is a colorless solid, impure samples are often brown. The compound is a type of mustard gas, a vesicant used as a chemical weapon. From the chemical perspective, the compound is both a thioether and an alkyl chloride.
Yellow Cross may refer to:
Chloroalkyl ethers are a class of organic compounds with the general structure R-O-(CH2)n-Cl, characterized as an ether connected to a chloromethyl group via an alkane chain.
The Blanc chloromethylation is the chemical reaction of aromatic rings with formaldehyde and hydrogen chloride to form chloromethyl arenes. The reaction is catalyzed by Lewis acids such as zinc chloride. The reaction was discovered by Gustave Louis Blanc (1872-1927) in 1923.
Hugo Gustav Adolf Stoltzenberg was a German chemist associated with the German government's clandestine chemical warfare activities in the early 1920s.

Green Cross (Grünkreuz) is a World War I chemical warfare pulmonary agent consisting of chloropicrin, phosgene and/or trichloromethyl chloroformate.

Chloromethyl methyl ether (CMME) is a compound with formula CH3OCH2Cl. A colorless liquid, it is a chloroalkyl ether. It is used as an alkylating agent. In organic synthesis, it is used for introducing the methoxymethyl ether (MOM) protecting group, and is thus often called MOM-Cl or MOM chloride. It also finds application as a chloromethylating agent in some variants of the Blanc chloromethylation.
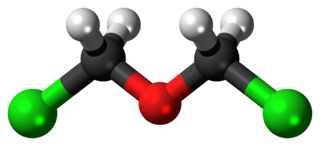
Bis(chloromethyl) ether is an organic compound with the chemical formula (ClCH2)2O. It is a colourless liquid with an unpleasant suffocating odour and it is one of the chloroalkyl ethers. Bis(chloromethyl) ether was once produced on a large scale, but was found to be highly carcinogenic and thus such production has ceased.
Bis(chloroethyl) ether is an organic compound with the formula O(CH2CH2Cl)2. It is an ether with two 2-chloroethyl substituents. It is a colorless liquid with the odor of a chlorinated solvent.
O-Mustard (T) is a vesicant chemical weapon, a type of mustard gas, with around 3 times the toxicity of the original sulfur mustard. It was developed in England in the 1930s as a thickener for mustard gas to make it more persistent when used in warm climates. A mixture of 60% sulfur mustard and 40% O-mustard also has a lower freezing point than pure sulfur mustard, and was given the code name HT. O-mustard is a Schedule I substance under the Chemical Weapons Convention.

Bis(2-chloroethyl)sulfide is the organosulfur compound with the formula (ClCH2CH2)2S. It is a prominent member of a family of cytotoxic and blister agents known as mustard agents. Sometimes referred to as mustard gas, the term is technically incorrect: bis(2-chloroethyl)sulfide is a liquid at room temperature. In warfare it was dispersed in the form of a fine mist of liquid droplets.
References
- ↑ "Chemical Weapons in World War I". www.cbwinfo.com. Archived from the original on 3 January 2014. Retrieved 22 December 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)