
A sailing ship is a sea-going vessel that uses sails mounted on masts to harness the power of wind and propel the vessel. There is a variety of sail plans that propel sailing ships, employing square-rigged or fore-and-aft sails. Some ships carry square sails on each mast—the brig and full-rigged ship, said to be "ship-rigged" when there are three or more masts. Others carry only fore-and-aft sails on each mast, for instance some schooners. Still others employ a combination of square and fore-and-aft sails, including the barque, barquentine, and brigantine.

A sailing vessel's rig is its arrangement of masts, sails and rigging. Examples include a schooner rig, cutter rig, junk rig, etc. A rig may be broadly categorized as "fore-and-aft", "square", or a combination of both. Within the fore-and-aft category there is a variety of triangular and quadrilateral sail shapes. Spars or battens may be used to help shape a given kind of sail. Each rig may be described with a sail plan—formally, a drawing of a vessel, viewed from the side.

A brigantine is a two-masted sailing vessel with a fully square-rigged foremast and at least two sails on the main mast: a square topsail and a gaff sail mainsail. The main mast is the second and taller of the two masts.

A brig is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: two masts which are both square-rigged. Brigs originated in the second half of the 18th century and were a common type of smaller merchant vessel or warship from then until the latter part of the 19th century. In commercial use, they were gradually replaced by fore-and-aft rigged vessels such as schooners, as owners sought to reduce crew costs by having rigs that could be handled by fewer men. In Royal Navy use, brigs were retained for training use when the battle fleets consisted almost entirely of iron-hulled steamships.

A barque, barc, or bark is a type of sailing vessel with three or more masts and mainmasts rigged square and only the mizzen rigged fore and aft. Sometimes, the mizzen is only partly fore-and-aft rigged, bearing a square-rigged sail above.

A cutter is a name for various types of watercraft. It can apply to the rig of a sailing vessel, to a governmental enforcement agency vessel, to a type of ship's boat which can be used under sail or oars, or, historically, to a type of fast-sailing vessel introduced in the 18th century, some of which were used as small warships.

A barquentine or schooner barque is a sailing vessel with three or more masts; with a square rigged foremast and fore-and-aft rigged main, mizzen and any other masts.

Gaff rig is a sailing rig in which the sail is four-cornered, fore-and-aft rigged, controlled at its peak and, usually, its entire head by a spar (pole) called the gaff. Because of the size and shape of the sail, a gaff rig will have running backstays rather than permanent backstays.

The Polish Scouting and Guiding Association is the coeducational Polish Scouting organization recognized by the World Organization of the Scout Movement and the World Association of Girl Guides and Girl Scouts. It was founded in 1918 and currently is the largest Scouting organization in Poland. The first ZHP was founded in 1916, the current one is the fourth organization with this name. It is a public benefit organization as defined by Polish law.

The mast of a sailing vessel is a tall spar, or arrangement of spars, erected more or less vertically on the centre-line of a ship or boat. Its purposes include carrying sails, spars, and derricks, giving necessary height to a navigation light, look-out position, signal yard, control position, radio aerial or signal lamp. Large ships have several masts, with the size and configuration depending on the style of ship. Nearly all sailing masts are guyed.

A Thames sailing barge is a type of commercial sailing boat once common on the River Thames in London. The flat-bottomed barges, with a shallow draught and leeboards, were perfectly adapted to the Thames Estuary, with its shallow waters and narrow tributary rivers. The larger barges were seaworthy vessels, and were the largest sailing vessel to be handled by just two men. The average size was about 120 tons and they carried 4,200 square feet (390 m2) of canvas sail in six working sails. The mainsail was loose-footed and set up with a sprit, and was brailed to the mast when not needed. It is sheeted to a horse, as is the foresail; they require no attention when tacking. The foresail is often held back by the mate to help the vessel come about more swiftly.

"Grey Ranks" was a codename for the underground paramilitary Polish Scouting Association during World War II.
Zawisza or Záviš is a Slavic name and may refer to:
A mast-aft rig is a sailboat sail-plan that uses a single mast set in the aft half of the hull. The mast supports fore-sails that may consist of a single jib, multiple staysails, or a crab claw sail. The mainsail is either small or completely absent. Mast-aft rigs are uncommon, but are found on a few custom, and production sailboats.

Mariusz Zaruski was a brigadier-general in the Polish Army, a pioneer of Polish sports yachting, an outstanding climber of the winter and caves of Tatra Mountains. He was a photographer, painter, poet and writer, a seamen and traveler, a conspirator, legionnaire and lancer in Polish cavalry.

A sailing yacht, is a leisure craft that uses sails as its primary means of propulsion. A yacht may be a sail or power vessel used for pleasure, cruising, or racing. There is no standard definition, so the term applies here to sailing vessels that have a cabin with amenities that accommodate overnight use. To be termed a "yacht", as opposed to a "boat", such a vessel is likely to be at least 33 feet (10 m) in length and have been judged to have good aesthetic qualities. Sailboats that do not accommodate overnight use or are smaller than 30 feet (9.1 m) are not universally called yachts. Sailing yachts in excess of 130 feet (40 m) are generally considered to be superyachts.

A wishbone rig, sometimes also known as fishbone ketch, is a type of rigging on sailboats. This rigging is most popular on heavy two-masted vessels. The rig gets its name from the wishbone, a V- or Y-shaped bone similar to the rig's gaff. A ketch rigged in this fashion is called wishbone ketch. Examples of wishbone-rigged boats include the Zawisza Czarny and the Norda.

The Tall Ships Races are races for sail training "tall ships". The races are designed to encourage international friendship and training for young people in the art of sailing. The races are held annually in European waters and consists of two racing legs of several hundred nautical miles, and a "cruise in company" between the legs. Over one half of the crew of each ship participating in the races must consist of young people.
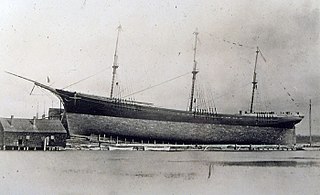
The Down Easter or Downeaster was a type of 19th-century sailing ship built in Maine, and used largely in the California grain trade. It was a modification of the clipper ship using a similar bow but with better cargo handling. It achieved a balance between speed and tonnage such that it made the wheat trade between California and Great Britain competitive with east coast grain trade via steam ship. It could make the trip between San Francisco and Liverpool in 100 days, despite rounding Cape Horn and crossing the equator twice. A more unusual name for the rig was shipentine.
This glossary of nautical terms is an alphabetical listing of terms and expressions connected with ships, shipping, seamanship and navigation on water. Some remain current, while many date from the 17th to 19th centuries. The word nautical derives from the Latin nauticus, from Greek nautikos, from nautēs: "sailor", from naus: "ship".

















