Related Research Articles

Altair is the brightest star in the constellation of Aquila and the twelfth-brightest star in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation Alpha Aquilae, which is Latinised from α Aquilae and abbreviated Alpha Aql or α Aql. Altair is an A-type main-sequence star with an apparent visual magnitude of 0.77 and is one of the vertices of the Summer Triangle asterism; the other two vertices are marked by Deneb and Vega. It is located at a distance of 16.7 light-years from the Sun. Altair is currently in the G-cloud—a nearby interstellar cloud, an accumulation of gas and dust.

A radio telescope is a specialized antenna and radio receiver used to detect radio waves from astronomical radio sources in the sky. Radio telescopes are the main observing instrument used in radio astronomy, which studies the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum emitted by astronomical objects, just as optical telescopes are the main observing instrument used in traditional optical astronomy which studies the light wave portion of the spectrum coming from astronomical objects. Unlike optical telescopes, radio telescopes can be used in the daytime as well as at night.

Radio astronomy is a subfield of astronomy that studies celestial objects at radio frequencies. The first detection of radio waves from an astronomical object was in 1933, when Karl Jansky at Bell Telephone Laboratories reported radiation coming from the Milky Way. Subsequent observations have identified a number of different sources of radio emission. These include stars and galaxies, as well as entirely new classes of objects, such as radio galaxies, quasars, pulsars, and masers. The discovery of the cosmic microwave background radiation, regarded as evidence for the Big Bang theory, was made through radio astronomy.

The Very Large Telescope (VLT) is an astronomical facility operated since 1998 by the European Southern Observatory, located on Cerro Paranal in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile. It consists of four individual telescopes, each equipped with a primary mirror that measures 8.2 meters in diameter. These optical telescopes, named Antu, Kueyen, Melipal, and Yepun, are generally used separately but can be combined to achieve a very high angular resolution. The VLT array is also complemented by four movable Auxiliary Telescopes (ATs) with 1.8-meter apertures.
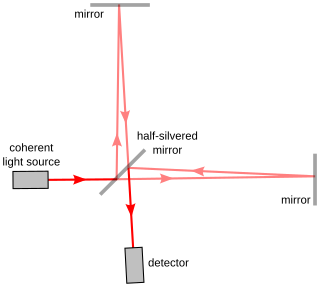
Interferometry is a technique which uses the interference of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy, quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, velocimetry, optometry, and making holograms.

Very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) is a type of astronomical interferometry used in radio astronomy. In VLBI a signal from an astronomical radio source, such as a quasar, is collected at multiple radio telescopes on Earth or in space. The distance between the radio telescopes is then calculated using the time difference between the arrivals of the radio signal at different telescopes. This allows observations of an object that are made simultaneously by many radio telescopes to be combined, emulating a telescope with a size equal to the maximum separation between the telescopes.

Observational astronomy is a division of astronomy that is concerned with recording data about the observable universe, in contrast with theoretical astronomy, which is mainly concerned with calculating the measurable implications of physical models. It is the practice and study of observing celestial objects with the use of telescopes and other astronomical instruments.
Aperture synthesis or synthesis imaging is a type of interferometry that mixes signals from a collection of telescopes to produce images having the same angular resolution as an instrument the size of the entire collection. At each separation and orientation, the lobe-pattern of the interferometer produces an output which is one component of the Fourier transform of the spatial distribution of the brightness of the observed object. The image of the source is produced from these measurements. Astronomical interferometers are commonly used for high-resolution optical, infrared, submillimetre and radio astronomy observations. For example, the Event Horizon Telescope project derived the first image of a black hole using aperture synthesis.
Darwin was a suggested ESA Cornerstone mission which would have involved a constellation of four to nine spacecraft designed to directly detect Earth-like planets orbiting nearby stars and search for evidence of life on these planets. The most recent design envisaged three free-flying space telescopes, each three to four metres in diameter, flying in formation as an astronomical interferometer. These telescopes were to redirect light from distant stars and planets to a fourth spacecraft, which would have contained the beam combiner, spectrometers, and cameras for the interferometer array, and which would have also acted as a communications hub. There was also an earlier design, called the "Robin Laurance configuration," which included six 1.5 metre telescopes, a beam combiner spacecraft, and a separate power and communications spacecraft.

The Submillimeter Array (SMA) consists of eight 6-meter (20 ft) diameter radio telescopes arranged as an interferometer for submillimeter wavelength observations. It is the first purpose-built submillimeter interferometer, constructed after successful interferometry experiments using the pre-existing 15-meter (49 ft) James Clerk Maxwell Telescope and 10.4-meter (34.1 ft) Caltech Submillimeter Observatory as an interferometer. All three of these observatories are located at Mauna Kea Observatory on Mauna Kea, Hawaii, and have been operated together as a ten element interferometer in the 230 and 345 GHz bands. The baseline lengths presently in use range from 16 to 508 meters. The radio frequencies accessible to this telescope range from 194–408 gigahertz (1.545–0.735 mm) which includes rotational transitions of dozens of molecular species as well as continuum emission from interstellar dust grains. Although the array is capable of operating both day and night, most of the observations take place at nighttime when the atmospheric phase stability is best.
Antoine Émile Henry Labeyrie is a French astronomer, who held the Observational astrophysics chair at the Collège de France between 1991 and 2014, where he is currently professor emeritus. He is working with the Hypertelescope Lise association, which aims to develop an extremely large astronomical interferometer with spherical geometry that might theoretically show features on Earth-like worlds around other suns, as its president. He is a member of the French Academy of Sciences in the Sciences of the Universe section. Between 1995 and 1999 he was director of the Haute-Provence Observatory.

The Dunn Solar Telescope also known as the Richard B. Dunn Solar Telescope is a unique vertical-axis solar telescope, in Sunspot, New Mexico located at Sacramento Peak, New Mexico. It is the main telescope at the Sunspot Solar Observatory, operated by New Mexico State University in partnership with the National Solar Observatory through funding by the National Science Foundation, the state of New Mexico and private funds from other partners. The Dunn Solar Telescope specializes in high-resolution imaging and spectroscopy to help astrophysicists worldwide obtain a better understanding of how the Sun affects the Earth. Completed in 1969, it was upgraded with high-order adaptive optics in 2004 and remains a highly versatile astrophysical observatory which serves as an important test platform for developing new instrumentation and technologies. The Dunn Solar Telescope, located in Sunspot, New Mexico, is a vertical-axis solar telescope that specializes in high-resolution imaging and spectroscopy. It was completed in 1969 and received a significant upgrade with high-order adaptive optics in 2004.
An astronomical interferometer or telescope array is a set of separate telescopes, mirror segments, or radio telescope antennas that work together as a single telescope to provide higher resolution images of astronomical objects such as stars, nebulas and galaxies by means of interferometry. The advantage of this technique is that it can theoretically produce images with the angular resolution of a huge telescope with an aperture equal to the separation, called baseline, between the component telescopes. The main drawback is that it does not collect as much light as the complete instrument's mirror. Thus it is mainly useful for fine resolution of more luminous astronomical objects, such as close binary stars. Another drawback is that the maximum angular size of a detectable emission source is limited by the minimum gap between detectors in the collector array.

The Dominion Radio Astrophysical Observatory is a research facility founded in 1960 and located at Kaleden, British Columbia, Canada. The site houses four radio telescopes: an interferometric radio telescope, a 26-m single-dish antenna, a solar flux monitor, and the Canadian Hydrogen Intensity Mapping Experiment (CHIME) — as well as support engineering laboratories. The DRAO is operated by the Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics of the National Research Council of the Government of Canada. The observatory was named an IEEE Milestone for first radio astronomical observations using VLBI.

A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally it was an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe distant objects – an optical telescope. Nowadays, the word "telescope" is defined as a wide range of instruments capable of detecting different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, and in some cases other types of detectors.

A gravitational-wave detector is any device designed to measure tiny distortions of spacetime called gravitational waves. Since the 1960s, various kinds of gravitational-wave detectors have been built and constantly improved. The present-day generation of laser interferometers has reached the necessary sensitivity to detect gravitational waves from astronomical sources, thus forming the primary tool of gravitational-wave astronomy.
In optical astronomy, interferometry is used to combine signals from two or more telescopes to obtain measurements with higher resolution than could be obtained with either telescopes individually. This technique is the basis for astronomical interferometer arrays, which can make measurements of very small astronomical objects if the telescopes are spread out over a wide area. If a large number of telescopes are used a picture can be produced which has resolution similar to a single telescope with the diameter of the combined spread of telescopes. These include radio telescope arrays such as VLA, VLBI, SMA, astronomical optical interferometer arrays such as COAST, NPOI and IOTA, resulting in the highest resolution optical images ever achieved in astronomy. The VLT Interferometer is expected to produce its first images using aperture synthesis soon, followed by other interferometers such as the CHARA array and the Magdalena Ridge Observatory Interferometer which may consist of up to 10 optical telescopes. If outrigger telescopes are built at the Keck Interferometer, it will also become capable of interferometric imaging.

3C 286, also known by its position as 1328+307 or 1331+305, is a quasar at redshift 0.8493 with a radial velocity of 164,137 km/s. It is part of the Third Cambridge Catalogue of Radio Sources.

Psi Phoenicis is a star in the constellation Phoenix. Its apparent magnitude varies from 4.3 to 4.5 with a period of about 30 days and it is approximately 342 light years away based on parallax.

The Northern Extended Millimeter Array (NOEMA) is one of the largest astronomical facilities on European ground and the most powerful radio telescope in the Northern Hemisphere operating at millimeter wavelengths. It consists of a large array of twelve 15-meter antennas that can spread over distances of up to 1.7 kilometers, working together as a single telescope.
References
- ↑ "Zero-spacing Problem". www.gmrt.ncra.tifr.res.in. Retrieved 2024-05-11.
- ↑ "ALMA Configurations". www.cv.nrao.edu. Retrieved 2024-05-11.
- ↑ Wenger, S.; Magnor, M.; Pihlström, Y.; Bhatnagar, S.; Rau, U. (2010-11-01). "SparseRI: A Compressed Sensing Framework for Aperture Synthesis Imaging in Radio Astronomy". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 122 (897): 1367. doi:10.1086/657252. ISSN 1538-3873.
- ↑ Soida, M.; Krause, M.; Dettmar, R.-J.; Urbanik, M. (2011-07-01). "The large scale magnetic field structure of the spiral galaxy NGC 5775". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 531: A127. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200810763. ISSN 0004-6361.