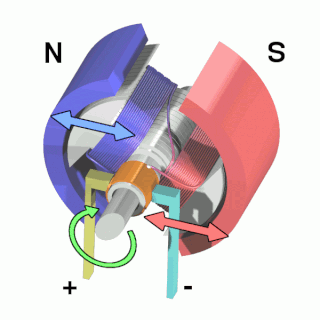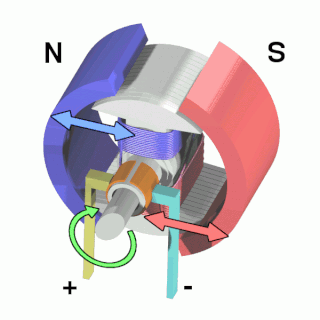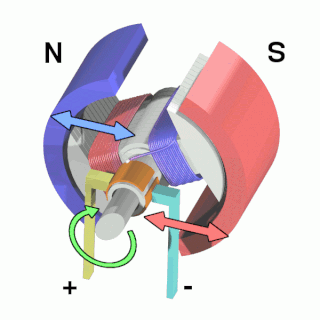
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates in reverse, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.

An induction motor or asynchronous motor is an AC electric motor in which the electric current in the rotor that produces torque is obtained by electromagnetic induction from the magnetic field of the stator winding. An induction motor therefore needs no electrical connections to the rotor. An induction motor's rotor can be either wound type or squirrel-cage type.

A compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume. An air compressor is a specific type of gas compressor.

Allgemeine Elektricitäts-Gesellschaft AG was a German producer of electrical equipment. It was founded in 1883 by Emil Rathenau as the Deutsche Edison-Gesellschaft für angewandte Elektricität in Berlin.

A brushless DC electric motor (BLDC), also known as an electronically commutated motor, is a synchronous motor using a direct current (DC) electric power supply. It uses an electronic controller to switch DC currents to the motor windings producing magnetic fields that effectively rotate in space and which the permanent magnet rotor follows. The controller adjusts the phase and amplitude of the current pulses that control the speed and torque of the motor. It is an improvement on the mechanical commutator (brushes) used in many conventional electric motors.

Turbomachinery, in mechanical engineering, describes machines that transfer energy between a rotor and a fluid, including both turbines and compressors. While a turbine transfers energy from a fluid to a rotor, a compressor transfers energy from a rotor to a fluid. It is an important application of fluid mechanics.

Vapour-compression refrigeration or vapor-compression refrigeration system (VCRS), in which the refrigerant undergoes phase changes, is one of the many refrigeration cycles and is the most widely used method for air conditioning of buildings and automobiles. It is also used in domestic and commercial refrigerators, large-scale warehouses for chilled or frozen storage of foods and meats, refrigerated trucks and railroad cars, and a host of other commercial and industrial services. Oil refineries, petrochemical and chemical processing plants, and natural gas processing plants are among the many types of industrial plants that often utilize large vapor-compression refrigeration systems. Cascade refrigeration systems may also be implemented using two compressors.

Künzelsau is a town in Baden-Württemberg, in south central Germany. It is the capital of the Hohenlohe district. It is located on the river Kocher, 19 km (12 mi) north of Schwäbisch Hall, and 37 km (23 mi) northeast of Heilbronn.

An AC motor is an electric motor driven by an alternating current (AC). The AC motor commonly consists of two basic parts, an outside stator having coils supplied with alternating current to produce a rotating magnetic field, and an inside rotor attached to the output shaft producing a second rotating magnetic field. The rotor magnetic field may be produced by permanent magnets, reluctance saliency, or DC or AC electrical windings.

WEG is a Brazilian company, operating worldwide in the electric engineering, power and automation technology areas. Headquartered in Jaraguá do Sul, Brazil, the company produces electric motors, generators, transformers, turbines, drives, and coatings. WEG has operations in around 100 countries, with approximately 39,000 employees (2023). It's one the largest manufacturers of electric motors in the world.
Wellington Drive Technologies Ltd (WDT) is a New Zealand–based company that supplies electricity-saving, electronically commutated (EC) motors and fans worldwide. Their focus is on advanced motors, electronics and software that save power.

A fan is a powered machine used to create a flow of air. A fan consists of a rotating arrangement of vanes or blades, generally made of wood, plastic, or metal, which act on the air. The rotating assembly of blades and hub is known as an impeller, rotor, or runner. Usually, it is contained within some form of housing, or case. This may direct the airflow, or increase safety by preventing objects from contacting the fan blades. Most fans are powered by electric motors, but other sources of power may be used, including hydraulic motors, handcranks, and internal combustion engines.

Maxon Group is a Swiss manufacturer and supplier of high-precision motor systems. The group, including its subsidiaries, deals in electric AC motors, DC motors, encoders, gears, motor controllers, and sensors.
Superconducting electric machines are electromechanical systems that rely on the use of one or more superconducting elements. Since superconductors have no DC resistance, they typically have greater efficiency. The most important parameter that is of utmost interest in superconducting machine is the generation of a very high magnetic field that is not possible in a conventional machine. This leads to a substantial decrease in the motor volume; which means a great increase in the power density. However, since superconductors only have zero resistance under a certain superconducting transition temperature, Tc that is hundreds of degrees lower than room temperature, cryogenics are required.
Shaft voltage occurs in electric motors and generators due to leakage, induction, or capacitive coupling with the windings of the motor. It can occur in motors powered by variable-frequency drives, as often used in heating, ventilation, air conditioning and refrigeration systems. DC machines may have leakage current from the armature windings that energizes the shaft. Currents due to shaft voltage causes deterioration of motor bearings, but can be prevented with a grounding brush on the shaft, grounding of the motor frame, insulation of the bearing supports, or shielding.
Elektrobau Mulfingen GmbH is the parent company of the ebm-papst Group, a manufacturer of electric motors and fans. The group was formed in 2003 from the merger of the companies Elektrobau Mulfingen GmbH & Co. KG (ebm), Papst Motoren GmbH and Motoren Ventilatoren Landshut GmbH and operates international production sites. The head office is located in Mulfingen in Baden-Württemberg. Ebm-papst is owned by the Ziehl, Sturm and Philippiak families.

An alternator is a type of electric generator used in modern automobiles to charge the battery and to power the electrical system when its engine is running.

Emil Ziehl was a German engineer and entrepreneur.

Günther Ziehl was a German engineer and businessman. His father, Emil Ziehl, founded ZIEHL-ABEGG, a company which was later led and rebuilt by Günther Ziehl.

An axial flux motor is a geometry of electric motor construction where the gap between the rotor and stator, and therefore the direction of magnetic flux between the two, is aligned parallel with the axis of rotation, rather than radially as with the concentric cylindrical geometry of the more common radial flux motor. With axial flux geometry torque increases with the cube of the rotor diameter, whereas in a radial flux the increase is only quadratic. Axial flux motors have a larger magnetic surface and overall surface area than radial flux motors for a given volume.

















