
The National Diet Library (NDL) is the national library of Japan and among the largest libraries in the world. It was established in 1948 for the purpose of assisting members of the National Diet of Japan in researching matters of public policy. The library is similar in purpose and scope to the United States Library of Congress.

Interactive television is a form of media convergence, adding data services to traditional television technology. It has included on-demand delivery of content, online shopping, and viewer polls. Interactive TV is an example of how new information technology can be integrated vertically into established technologies and commercial structures.

Kodi is a free and open-source media player and technology convergence software application developed by the Kodi Foundation, a non-profit technology consortium. Kodi is available for multiple operating systems and hardware platforms, with a software 10-foot user interface for use with televisions and remote controls. It allows users to play and view most streaming media, such as videos, music, podcasts, and videos from the Internet, as well as all common digital media files from local and network storage media, or TV gateway viewer.

Human interface guidelines (HIG) are software development documents which offer application developers a set of recommendations. Their aim is to improve the experience for the users by making application interfaces more intuitive, learnable, and consistent. Most guides limit themselves to defining a common look and feel for applications in a particular desktop environment. The guides enumerate specific policies. Policies are sometimes based on studies of human–computer interaction, but most are based on conventions chosen by the platform developers preferences.

Toda Katsushige(戸田 勝成, 1557 – October 21, 1600) or Toda Shigemasa was a daimyō in Sengoku and Azuchi–Momoyama periods. At first, Shigemasa served Niwa Nagahide. In 1585, after Nagahide died, Shigemasa served Toyotomi Hideyoshi and was given 10,000 koku at Echizen Province.
A voice-user interface (VUI) enables spoken human interaction with computers, using speech recognition to understand spoken commands and answer questions, and typically text to speech to play a reply. A voice command device is a device controlled with a voice user interface.

LaLa is a monthly Japanese shōjo manga magazine published by Hakusensha on the 24th of each month. The magazine's bonus contents are usually calendars for New Year issues, drama CDs, and so on. In a 2006 survey conducted by Oricon, Japanese girls selected LaLa as their fifth favorite manga anthology, along with Shogakukan's Shōjo Comic and Kodansha's Weekly Shōnen Magazine.
Mobile app development is the act or process by which a mobile app is developed for one or more mobile devices, which can include personal digital assistants (PDA), enterprise digital assistants (EDA), or mobile phones. Such software applications are specifically designed to run on mobile devices, taking numerous hardware constraints into consideration. Common constraints include CPU architecture and speeds, available memory (RAM), limited data storage capacities, and considerable variation in displays and input methods. These applications can be pre-installed on phones during manufacturing or delivered as web applications, using server-side or client-side processing to provide an "application-like" experience within a web browser.

A digital media player is a type of consumer electronics device designed for the storage, playback, or viewing of digital media content. They are typically designed to be integrated into a home cinema configuration, and attached to a television or AV receiver or both.
A mobile operating system is an operating system used for smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, smartglasses, or other non-laptop personal mobile computing devices. While computers such as typical/mobile laptops are "mobile", the operating systems used on them are generally not considered mobile, as they were originally designed for desktop computers that historically did not have or need specific mobile features. This line distinguishing mobile and other forms has become blurred in recent years, due to the fact that newer devices have become smaller and more mobile unlike hardware of the past. Key notabilities blurring this line are the introduction of tablet computers, light laptops, and the hybridization of the two in 2-in-1 PCs.

A smart TV, also known as a connected TV (CTV), is a traditional television set with integrated Internet and interactive Web 2.0 features that allow users to stream music and videos, browse the internet, and view photos. Smart TVs are a technological convergence of computers, televisions, and digital media players. Besides the traditional functions of television sets provided through traditional broadcasting media, these devices can provide access to over-the-top media services such as streaming television and internet radio, along with home networking access.
A mobile application or app is a computer program or software application designed to run on a mobile device such as a phone, tablet, or watch. Mobile applications often stand in contrast to desktop applications which are designed to run on desktop computers, and web applications which run in mobile web browsers rather than directly on the mobile device.

Chromecast is a line of digital media players developed by Google. The devices, designed as small dongles, can play Internet-streamed audio-visual content on a high-definition television or home audio system. The user can control playback with a mobile device or personal computer through mobile and web apps that can use the Google Cast protocol, or by issuing commands via Google Assistant; later models introduced an interactive user interface and remote control. Content can be mirrored to video models from the Google Chrome web browser on a personal computer or from the screen of some Android devices.
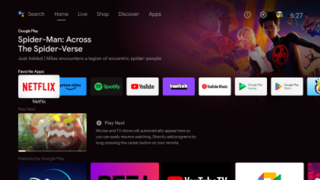
Android TV is a smart TV operating system based on Android and developed by Google. It is available on television sets, soundbars, set-top boxes and digital media players. A successor to Google TV, it features a user interface designed around content discovery and voice search, content aggregation from various media apps and services, and integration with other recent Google technologies such as Assistant, Cast, and Knowledge Graph.
Flutter is an open-source UI software development kit created by Google. It can be used to develop cross platform applications from a single codebase for the web, Fuchsia, Android, iOS, Linux, macOS, and Windows. First described in 2015, Flutter was released in May 2017. Flutter is used internally by Google in apps such as Google Pay and Google Earth as well as by other software developers including ByteDance and Alibaba.

EMUI (formerly known as Emotion UI, and also known as MagicOS is a HarmonyOS/Android mobile operating system developed by Chinese technology company Huawei. It is used on the company's smartphones and tablet computers.

One UI is a user interface (UI) developed by Samsung Electronics for its Android devices running Android 9 "Pie" and later. Succeeding Samsung Experience and TouchWiz, it is designed to make using larger smartphones easier and be more visually appealing. To provide more clarity, some elements of the UI are tweaked to match colors that are based on the color of the user's phone. It was announced at Samsung Developer Conference in 2018, and was unveiled in Galaxy Unpacked in February 2019 alongside the Galaxy S10 series, Galaxy Buds and the Galaxy Fold.

HarmonyOS (HMOS) is a distributed operating system developed by Huawei for smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, smart watches, personal computers and other smart devices. It has a multi-kernel design with dual frameworks: the operating system selects suitable kernels from the abstraction layer in the case of devices that use diverse resources. The operating system was officially launched by Huawei in August 2019.
Realme is a Chinese consumer electronics manufacturer based in Shenzhen, Guangdong. It was founded by Li Bingzhong on May 4, 2018, who was a former vice president of Oppo. Starting originally as a sub-brand of Oppo, Realme eventually ventured as its own brand. Realme then became the fastest-growing 5G smartphone brand in Q3 2021.
The Hidden Supplies Incident was an event during which the former Imperial Japanese Armed Forces issued a notice to sell off precious metals, diamonds, and munitions, and other valuables which were confiscated from civilians during the Second World War before the Allied occupation.














