DVB-T, short for Digital Video Broadcasting – Terrestrial, is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in Singapore in February, 1998. This system transmits compressed digital audio, digital video and other data in an MPEG transport stream, using coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing modulation. It is also the format widely used worldwide for Electronic News Gathering for transmission of video and audio from a mobile newsgathering vehicle to a central receive point. It is also used in the US by Amateur television operators.
A digital video recorder (DVR) is an electronic device that records video in a digital format to a disk drive, USB flash drive, SD memory card, SSD or other local or networked mass storage device. The term includes set-top boxes (STB) with direct to disk recording, portable media players and TV gateways with recording capability, and digital camcorders. Personal computers are often connected to video capture devices and used as DVRs; in such cases the application software used to record video is an integral part of the DVR. Many DVRs are classified as consumer electronic devices; such devices may alternatively be referred to as personal video recorders (PVRs), particularly in Canada. Similar small devices with built-in displays and SSD support may be used for professional film or video production, as these recorders often do not have the limitations that built-in recorders in cameras have, offering wider codec support, the removal of recording time limitations and higher bitrates.

A TV tuner card is a kind of television tuner that allows television signals to be received by a computer. Most TV tuners also function as video capture cards, allowing them to record television programs onto a hard disk much like the digital video recorder (DVR) does.
MythTV is a free and open-source home entertainment application with a simplified "10-foot user interface" design for the living room TV. It turns a computer with the necessary hardware into a network streaming digital video recorder, a digital multimedia home entertainment system, or home theater personal computer. It can be considered a free and open-source alternative to TiVo or Windows Media Center. It runs on various operating systems, primarily Linux, macOS, and FreeBSD.

Rockbox is a free and open-source software replacement for the OEM firmware in various forms of digital audio players (DAPs) with an original kernel. It offers an alternative to the player's operating system, in many cases without removing the original firmware, which provides a plug-in architecture for adding various enhancements and functions. Enhancements include personal digital assistant (PDA) functions, applications, utilities, and games. Rockbox can also retrofit video playback functions on players first released in mid-2000. Rockbox includes a voice-driven user-interface suitable for operation by visually impaired users.
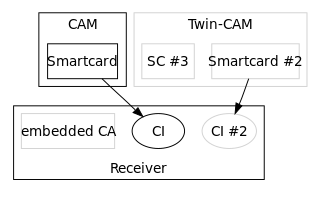
In Digital Video Broadcasting, the Common Interface is a technology which allows decryption of pay TV channels. Pay TV stations want to choose which encryption method to use. The Common Interface allows TV manufacturers to support many different pay TV stations, by allowing to plug in exchangeable conditional-access modules (CAM) for various encryption schemes.

Maemo is a software platform originally developed by Nokia, now developed by the community, for smartphones and Internet tablets. The platform comprises both the Maemo operating system and SDK. Maemo played a key role in Nokia's strategy to compete with Apple and Android, but ultimately failed to surpass both companies.Maemo is mostly based on open-source code and has been developed by Maemo Devices within Nokia in collaboration with many open-source projects such as the Linux kernel, Debian, and GNOME. Maemo is based on Debian and draws much of its GUI, frameworks, and libraries from the GNOME project. It uses the Matchbox window manager and the GTK-based Hildon framework as its GUI and application framework.

Dreambox is a series of Linux-powered DVB satellite, terrestrial and cable digital television receivers, produced by German multimedia vendor Dream Multimedia.
The Hauppauge MediaMVP is a network media player. It consists of a hardware unit with remote control, along with software for a Windows PC. Out of the box, it is capable of playing video and audio, displaying pictures, and "tuning in" to Internet radio stations. Alternative software is also available to extend its capabilities. It can be used as a front-end for various PVR projects.
TiVo digital video recorders encompass a number of digital video recorder (DVR) models that TiVo Corporation designed. Features may vary, but a common feature is that all of the units listed here require TiVo service and use its operating system.

The Pepper Pad was a family of Linux-based mobile computers with Internet capability and which doubled as a handheld game console. They also served as a portable multimedia device. The devices used Bluetooth and Wi-Fi technologies for Internet connection. Pepper Pads are now obsolete, unsupported and the parent company has ceased operations.

A free-to-air or FTA Receiver is a satellite television receiver designed to receive unencrypted broadcasts. Modern decoders are typically compliant with the MPEG-2/DVB-S and more recently the MPEG-4/DVB-S2 standard for digital television, while older FTA receivers relied on analog satellite transmissions which have declined rapidly in recent years.
Video Decode and Presentation API for Unix (VDPAU) is a royalty-free application programming interface (API) as well as its implementation as free and open-source library distributed under the MIT License. VDPAU is also supported by Nvidia.
The Eurovox is a Digital Cable set-top box, notoriously known for its ability to decode cable television services without a subscription, which has been imported into the UK from Korea since 2004.
The Vu+, is a series of Linux-powered DVB satellite, terrestrial digital television receivers, produced by Korean multimedia brand Ceru Co., Ltd.
Unibox is a satellite, cable and terrestrial digital receiver. It has been distributed widely for use with Pay TV. It also enables the receiver to store digital copies of MPEG TS on internal harddisk or networked filesystems.

The Allwinner A1X is a family of single-core SoC devices designed by Allwinner Technology from Zhuhai, China. Currently the family consists of the A10, A13, A10s and A12. The SoCs incorporate the ARM Cortex-A8 as their main processor and the Mali 400 as the GPU.
Enigma2, the second generation of Enigma software, is an application used in Linux-based Digital Video Broadcasting receivers or TV set-top boxes and Internet Protocol television receivers. It creates a graphical user interface to control the said devices using a remote control and provides features such as tuning available satellite transponders, cable channels and terrestrial television transmitters or accessing material via Internet Protocol television (IPTV), watching a TV program or listening to radio, time shifting, Digital video recorder, streaming media programs to other devices, etc. Other features are available through plugins – for example Electronic program guide (EPG), Hybrid Broadcast Broadband TV (HbbTV), access to TV archives and movie databases, playback of multimedia files, viewing photos, etc.
E2 Linux is an umbrella name for Linux distributions designed to control digital television receivers, set-top boxes and IPTV receivers. E2 Linux was originally developed for Dreambox receivers, but after 2010 a number of other manufacturers began shipping devices with E2 Linux, including Formuler, GigaBlue, Octagon, Opticum, Unibox, Vu+, and Zgemma.










