
My Lucky Stars is a 1985 Hong Kong action comedy film directed by Sammo Hung, written by Barry Wong, and starring Hung, Jackie Chan and Yuen Biao. It was released as 5 Lucky Stars in Japan and as Ninja Encounter in the Philippines. My Lucky Stars is the second film in the Lucky Stars series, and a semi-sequel to Winners and Sinners, with many of the same actors returning as the "Five Lucky Stars" troupe, albeit with different character names and slightly different roles.

Sir Reginald Edward Stubbs was a British colonial governor, who was once the Governor of Hong Kong. He caused controversy while Governor of Ceylon over the Bracegirdle Incident.

The Hong Kong Confederation of Trade Unions (HKCTU) was a pro-democracy labour and political group in the Hong Kong. It was established on 29 July 1990. It had 160,000 members in 61 affiliates and representation in the Legislative Council of Hong Kong (LegCo) to challenge government policies and push for legal protection of worker and trade union rights. It was one of the two most influential labour groups in Hong Kong, with the other one being the pro-Beijing Hong Kong Federation of Trade Unions.

The National Union of Seamen (NUS) was the principal trade union of merchant seafarers in the United Kingdom from the late 1880s to 1990. In 1990, the union amalgamated with the National Union of Railwaymen to form the National Union of Rail, Maritime and Transport Workers (RMT).

Sean Lau Ching-wan is a Hong Kong actor who has acted in both films and television series. He won Best Actor in the 2007, 2015 and 2023 Hong Kong Film Awards and in the 2000 and 2007 Golden Bauhinia Awards.

C'est la vie, mon chéri is a 1993 Hong Kong romance film directed by Derek Yee and starring Lau Ching-wan, Anita Yuen and Carina Lau. It won six awards, including Best Film, during the 13th Hong Kong Film Awards.

The Crazy Companies is a 1988 Hong Kong comedy film directed by Wong Jing, and starring Andy Lau and Natalis Chan. It was followed by a sequel, The Crazy Companies II, which was released in 1989.

The Political Appointments System is a scheme introduced in 2008 by the Hong Kong Government to reinforce its ministerial team by superseding the Principal Officials Accountability System and inserting two layers of politically appointed officials below the secretaries, who are political appointees. These appointees report only to the secretaries, but not the permanent secretaries, the highest-ranking civil servants. The appointment of undersecretaries and political assistants is an extension of the previous RPAS that was initially confined to principal officials. Prior to the introduction, there were 14 political appointees—3 Secretaries of Departments and 11 Directors of Bureaux.

The Legend of the Condor Heroes is a Hong Kong television series adapted from Louis Cha's novel of the same title. The series was first broadcast on TVB Jade in 1994.

The Canton–Hong Kong strike was a strike and boycott that took place in British Hong Kong and Guangzhou (Canton), Republic of China, from June 1925 to October 1926. It started out as a response to the May 30 Movement shooting incidents in which Chinese protesters were fired upon by Sikh detachments of the Shanghai Municipal Police in Shanghai.
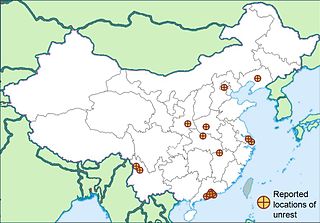
The 2010 Chinese labour unrest was a series of labour disputes, strike actions, and protests in the south of the People's Republic of China that saw striking workers successfully receive higher pay packages.

The 2013 Hong Kong dock strike was a 40-day labour strike at the Kwai Tsing Container Terminal. It was called by the Union of Hong Kong Dockers (UHKD), an affiliate of the Hong Kong Confederation of Trade Unions (HKCTU) on 28 March 2013, against contracting companies to whom workforce management had been out-sourced by the Hongkong International Terminals Ltd. (HIT), subsidiary of Hutchison Port Holdings Trust (HPHT), which is in turn owned by Hutchison Whampoa Ltd (HWL), flagship company of Li Ka-shing, Hong Kong's richest man. The strike workers demanded better pay and working conditions. The strike ended on 6 May 2013 when the strikers accepted the offer of 9.8% pay rise. It was the longest running industrial action in Hong Kong in years. Public support and media attention on the strike were unprecedented in the city's history. Some observers marked this as the rejuvenation of political engagement.

Lau Chü-pak was a Hong Kong merchant and politician.

Lifeline is a 1997 Hong Kong action disaster drama film directed by Johnnie To and starring Sean Lau, Alex Fong and Carman Lee.
Socialism in Hong Kong is a political trend taking root from Marxism and Leninism which was imported to Hong Kong in the early 1920s. Socialist trends have taken various forms, including Marxism–Leninism, Maoism, Trotskyism, democratic socialism and liberal socialism, with the Marxist–Leninists being the most dominant faction due to the influence of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) regime in the mainland. The "traditional leftists" became the largest force representing the pro-Beijing camp in the post-war decades, which had an uneasy relationship with the colonial authorities. As the Chinese Communist Party adopted capitalist economic reforms from 1978 onwards and the pro-Beijing faction became increasingly conservative, the socialist agenda has been slowly taken up by the liberal-dominated pro-democratic camp.

The pro-Republic of China camp, or the pro-Kuomintang camp (親國民黨派), is a political alignment in Hong Kong. It generally pledges allegiance to the Republic of China (ROC) in Taiwan and the Kuomintang.

The Emergency Regulations Ordinance is a law of Hong Kong that confers on the Chief Executive in Council the power to make regulations on occasions that the Chief Executive believes to be an emergency or public danger. It was first introduced in Colonial Hong Kong in 1922 to combat the seamen's strikes which had immobilised the city's ports, and was invoked on several occasions during the colonial rule.
Anarchism in Hong Kong emerged as part of the Chinese anarchist movement, when many anarchists sought refuge from the Qing Empire in the territory. It grew alongside the Chinese revolutionary movement, before the territory again became a safe haven for anarchists, following the Communist victory in the Chinese Civil War. Since then anarchists have formed a part of the Hong Kong opposition movement, first to British colonial rule and then to the rising authoritarianism of the Government of Hong Kong.
Home Office 213/926 or HO 213/926 is a Home Office file which records the secret deportation from the United Kingdom of thousands of seafarers to China in 1945 and 1946, permanently separating them from their families. It was officially entitled "Compulsory repatriation of undesirable Chinese seamen."
















