
Narendra Damodardas Modi is an Indian politician who has served as the 14th prime minister of India since May 2014. Modi was the chief minister of Gujarat from 2001 to 2014 and is the Member of Parliament (MP) for Varanasi. He is a member of the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) and of the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS), a right wing Hindu nationalist paramilitary volunteer organisation. He is the longest-serving prime minister from outside the Indian National Congress.

An Agricultural Produce Market Committee (APMC) is a marketing board established by state governments in India to ensure farmers are safeguarded from exploitation by large retailers, as well as ensuring the farm to retail price spread does not reach excessively high levels. APMCs are regulated by states through their adoption of a Agriculture Produce Marketing Regulation (APMR) Act.

Harsimrat Kaur Badal is an Indian politician and a former Union Cabinet Minister of Food Processing Industries in the Government of India and Member of Parliament in the Lok Sabha from Bathinda. She is a member of Shiromani Akali Dal Party. Her husband Sukhbir Singh Badal is former deputy chief minister of Punjab and the president of Shiromani Akali Dal. She resigned from the cabinet on 17 September 2020 to protest against few farmer related ordinances and legislation.

Agriculture in India is highly susceptible to risks like droughts and floods. It is necessary to protect the farmers from natural calamities and ensure their credit eligibility for the next season. For this purpose, the Government of India introduced many agricultural social insurances throughout the country, the most important one of them being Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana.

The Essential Commodities Act (ECA) is an act of the Parliament of India that was established to ensure the delivery of certain commodities or products, the supply of which, if obstructed due to hoarding or black marketing, would affect the normal life of the people. This includes foodstuff, drugs, fuel etc. This act was modified by the Essential Commodities (Amendment) Act, 2020 as part of the 2020 Indian farm reforms.
The following is a timeline of the Premiership of Narendra Modi from his inauguration as Prime Minister of India on 26 May 2014 till now. The following are the highlights of the major events that took place under his premiership.

The premiership of Narendra Modi began on 26 May 2014 with his swearing-in as the Prime Minister of India at the Rashtrapati Bhavan. He became the 14th Prime Minister of India, succeeding Manmohan Singh of the Indian National Congress. Modi's first cabinet consisted of 45 ministers, 25 fewer than the previous United Progressive Alliance government. 21 ministers were added to the council of ministers on 9 November 2014.
The Repealing and Amending Act, 2015 is an Act of the Parliament of India that repealed 35 obsolete Acts, and also amended the provisions of The Prohibition of Manual Scavengers Act, 2013, and the Whistle Blowers Protection Act, 2011 to correct typographical and certain patent errors. It was the first such repealing Act aimed at repealing obsolete laws tabled in Parliament by the Narendra Modi administration.

The minimum support price (MSP) is an advisory price signal that is part of a larger set of agricultural policies in parts of India. This informal "support" price is recommended by the government and aims to safeguard the farmer to a minimum profit for the harvest while at the same time increasing food security in the country. MSP was initially an incentive for farmers to adopt technology with an aim of increasing the productivity of agricultural land in the 1960s, however in the 2000s it is seen as a market intervention and farmer income scheme. The effectiveness of such a price policy has varied widely between states and commodities. Awareness among farmers of the existence of an MSP is poor at 23%, while awareness of MSP procurement agencies is also poor with only about 20–25% of wheat and paddy produce being sold at MSP.

The Second Ministry of Narendra Modi is the Council of Ministers headed by Prime Minister of India Narendra Modi that was formed after the 2019 general election which was held in seven phases in 2019. The results of the election were announced on 23 May 2019 and this led to the formation of the 17th Lok Sabha. The swearing-in ceremony was arranged in the courtyards of Rashtrapati Bhavan at Raisina Hill. The heads of the states of BIMSTEC countries were invited as guests of honor for this ceremony.

Legislative Assembly elections were held in Punjab on 20 February 2022 to elect the 117 members of the 16th Assembly of the Punjab Legislative Assembly. The votes were counted and the results were declared on 10 March 2022.
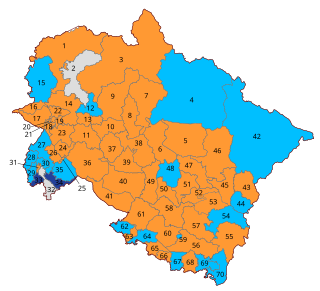
Legislative Assembly elections were held in Uttarakhand on 14 February 2022 to elect 70 members of the Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly. The votes were counted and the results were declared on 10 March 2022.

Dr. Vijoo Krishnan is an Indian peasant leader, writer on Agrarian Issues and General Secretary of the All India Kisan Sabha. He is a central committee member of Communist Party of India (Marxist). He is also part of the six-member central secretariat of CPI(M). He is one of the key organiser of Bhoomi Adhikar Andolan.

The 2020–2021 Indian farmers' protest was a protest against three farm acts that were passed by the Parliament of India in September 2020. The acts, often called the Farm Bills, had been described as "anti-farmer laws" by many farmer unions, and politicians from the opposition who said that it would leave farmers at the "mercy of corporates" since the farmer-trader disputes were taken to SDM instead of judiciary. The protests demanded the creation of a minimum support price (MSP) bill, to ensure that corporates cannot control the prices. The Union Government, however, maintained that the laws would make it effortless for farmers to sell their produce directly to big buyers, and stated that the protests are based on misinformation. Related endemic legacy issues include farmer suicides and low farmer incomes. Despite India being largely self-sufficient in foodgrain production and having welfare schemes, hunger and nutrition remain serious issues, with India ranking as one of the worst countries in the world in food security parameters. Due to unfulfilled previous demands 2024 Indian farmers' protest started on 13 of February 2024.
Events in the year 2021 in India for real time basis.
Samyukta Kisan Morcha (SKM), formed in November 2020, is a coalition of over forty Indian farmers' unions to coordinate satyagragh against the three farm acts initiated in September of the same year.

The 2021 Farmers' Republic Day protest was a protest on 26 January 2021 at Delhi. Part of the 2020–2021 Indian farmers' protest, it turned violent when a group of protestors deviated from the parade to storm the Red Fort. The protest took place on the 72nd Republic Day against the decision by Narendra Modi-led National Democratic Alliance (NDA) to implement three farm acts.

Rakesh Tikait is an Indian farmer rights activist and national spokesperson of the Bharatiya Kisan Union (BKU). He successfully led the farmer protests in 2020-2021 to cause repeal of three farmer laws implemented by the Indian government.
Joginder Singh Ugrahan is an Indian ex-army man, communist leader and farm union leader, was born in 1945 in Sunam, Punjab. He is president of farm union Bharatiya Kisan Union and one of the most popular farm leaders in the country. He founded Bharatiya Kisan Union in 2002.
The 2024 Indian farmers' protest is the second round of continuous protests and road blockades initiated by farmers in the northern states of Punjab and Haryana on 13 February 2024. The primary requests of the protests include securing legal assurance for the Minimum Support Price (MSP) for all crops and complete forgiveness of loans for all farmers.













