
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, fisheries and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in cities. While humans started gathering grains at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers only began planting them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs and cattle were domesticated around 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. In the twentieth century, industrial agriculture based on large-scale monocultures came to dominate agricultural output.

A farm is an area of land that is devoted primarily to agricultural processes with the primary objective of producing food and other crops; it is the basic facility in food production. The name is used for specialized units such as arable farms, vegetable farms, fruit farms, dairy, pig and poultry farms, and land used for the production of natural fiber, biofuel, and other commodities. It includes ranches, feedlots, orchards, plantations and estates, smallholdings, and hobby farms, and includes the farmhouse and agricultural buildings as well as the land. In modern times, the term has been extended so as to include such industrial operations as wind farms and fish farms, both of which can operate on land or at sea.

Organic farming, also known as ecological farming or biological farming, is an agricultural system that uses fertilizers of organic origin such as compost manure, green manure, and bone meal and places emphasis on techniques such as crop rotation and companion planting. It originated early in the 20th century in reaction to rapidly changing farming practices. Certified organic agriculture accounts for 70 million hectares globally, with over half of that total in Australia. Biological pest control, mixed cropping, and the fostering of insect predators are encouraged. Organic standards are designed to allow the use of naturally-occurring substances while prohibiting or strictly limiting synthetic substances. For instance, naturally-occurring pesticides such as pyrethrin are permitted, while synthetic fertilizers and pesticides are generally prohibited. Synthetic substances that are allowed include, for example, copper sulfate, elemental sulfur, and veterinary drugs. Genetically modified organisms, nanomaterials, human sewage sludge, plant growth regulators, hormones, and antibiotic use in livestock husbandry are prohibited. Organic farming advocates claim advantages in sustainability, openness, self-sufficiency, autonomy and independence, health, food security, and food safety.

Agriculture is a major industry in the United States, which is a net exporter of food. As of the 2017 census of agriculture, there were 2.04 million farms, covering an area of 900 million acres (1,400,000 sq mi), an average of 441 acres per farm.

Subsistence agriculture occurs when farmers grow crops to meet the needs of themselves and their families on smallholdings. Subsistence agriculturalists target farm output for survival and for mostly local requirements, with little or no surplus. Planting decisions occur principally with an eye toward what the family will need during the coming year, and only secondarily toward market prices. Tony Waters, a professor of Sociology, defines "subsistence peasants" as "people who grow what they eat, build their own houses, and live without regularly making purchases in the marketplace".
Agribusiness is the industry, enterprises, and the field of study of value chains in agriculture and in the bio-economy, in which case it is also called bio-business or bio-enterprise. The primary goal of agribusiness is to maximize profit while satisfying the needs of consumers for products related to natural resources such as biotechnology, farms, food, forestry, fisheries, fuel, and fiber.

A smallholding or smallholder is a small farm operating under a small-scale agriculture model. Definitions vary widely for what constitutes a smallholder or small-scale farm, including factors such as size, food production technique or technology, involvement of family in labor and economic impact. Smallholdings are usually farms supporting a single family with a mixture of cash crops and subsistence farming. As a country becomes more affluent, smallholdings may not be self-sufficient, but may be valued for the rural lifestyle. As the sustainable food and local food movements grow in affluent countries, some of these smallholdings are gaining increased economic viability. There are an estimated 500 million smallholder farms in developing countries of the world alone, supporting almost two billion people.

Traditional farming was the original type of agriculture, and has been practiced for thousands of years. All traditional farming is now considered to be "organic farming" although at the time there were no known inorganic methods. For example, forest gardening, a fully organic food production system which dates from prehistoric times, is thought to be the world's oldest and most resilient agroecosystem. The industrial revolution introduced inorganic methods, most of which were not well developed and had serious side effects. An organic movement began in the 1940s as a reaction to agriculture's growing reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. The history of this modern revival of organic farming dates back to the first half of the 20th century at a time when there was a growing reliance on these new synthetic, non-organic methods.
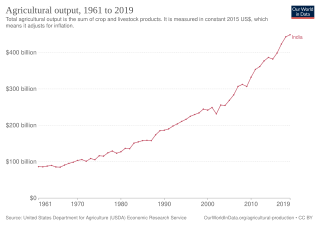
The history of agriculture in India dates back to the Neolithic period. India ranks second worldwide in farm outputs. As per the Indian economic survey 2020 -21, agriculture employed more than 50% of the Indian workforce and contributed 20.2% to the country's GDP.

China primarily produces rice, wheat, potatoes, tomato, sorghum, peanuts, tea, millet, barley, cotton, oilseed, corn and soybeans.

The Green Revolution was a period that began in the 1960s during which agriculture in India was converted into a modern industrial system by the adoption of technology, such as the use of high yielding variety (HYV) seeds, mechanised farm tools, irrigation facilities, pesticides, and fertilizers. Mainly led by agricultural scientist M. S. Swaminathan in India, this period was part of the larger Green Revolution endeavor initiated by Norman Borlaug, which leveraged agricultural research and technology to increase agricultural productivity in the developing world.

Agriculture in Ethiopia is the foundation of the country's economy, accounting for half of gross domestic product (GDP), 83.9% of exports, and 80% of total employment.

The cultivation of tobacco usually takes place annually. The tobacco is germinated in cold frames or hotbeds and then transplanted to the field until it matures. It is grown in warm climates with rich, well-drained soil. About 4.2 million hectares of tobacco were under cultivation worldwide in 2000, yielding over seven million tonnes of tobacco.

Gender roles in agriculture are a frequent subject of study by sociologists and farm economists. Historians also study them, as they are important in understanding the social structure of agrarian, and even industrial, societies. Agriculture provides many job opportunities and livelihoods around the world. It can also reflect gender inequality and uneven distribution of resources and privileges among gender.
The term food system describes the interconnected systems and processes that influence nutrition, food, health, community development, and agriculture. A food system includes all processes and infrastructure involved in feeding a population: growing, harvesting, processing, packaging, transporting, marketing, consumption, distribution, and disposal of food and food-related items. It also includes the inputs needed and outputs generated at each of these steps. Food systems fall within agri-food systems, which encompass the entire range of actors and their interlinked value-adding activities in the primary production of food and non-food agricultural products, as well as in food storage, aggregation, post-harvest handling, transportation, processing, distribution, marketing, disposal, and consumption. A food system operates within and is influenced by social, political, economic, technological and environmental contexts. It also requires human resources that provide labor, research and education. Food systems are either conventional or alternative according to their model of food lifespan from origin to plate. Food systems are dependent on a multitude of ecosystem services. For example, natural pest regulations, microorganisms providing nitrogen-fixation, and pollinators.

Farming systems in India are strategically utilized, according to the locations where they are most suitable. The farming systems that significantly contribute to the agriculture of India are subsistence farming, organic farming, industrial farming. Regions throughout India differ in types of farming they use; some are based on horticulture, ley farming, agroforestry, and many more. Due to India's geographical location, certain parts experience different climates, thus affecting each region's agricultural productivity differently. India is very dependent on its monsoon cycle for large crop yields. India's agriculture has an extensive background which goes back to at least 9 thousand years. In India, in the alluvial plains of the Indus River in Pakistan, the old cities of Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa experienced an apparent establishment of an organized farming urban culture. That society, known as the Harappan or Indus civilization, flourished until shortly after 4000 BP; it was much more comprehensive than those of Egypt or Babylonia and appeared earlier than analogous societies in northern China. Currently, the country holds the second position in agricultural production in the world. In 2007, agriculture and other industries made up more than 16% of India's GDP. Despite the steady decline in agriculture's contribution to the country's GDP, agriculture is the biggest industry in the country and plays a key role in the socio-economic growth of the country. India is the second-largest producer of wheat, rice, cotton, sugarcane, silk, groundnuts, and dozens more. It is also the second biggest harvester of vegetables and fruit, representing 8.6% and 10.9% of overall production, respectively. The major fruits produced by India are mangoes, papayas, sapota, and bananas. India also has the biggest number of livestock in the world, holding 281 million. In 2008, the country housed the second largest number of cattle in the world with 175 million.
The agricultural system in Sub-Saharan Africa is a predominantly small-scale farming system with more than 50% of the agricultural activity performed by women, producing about 60-70% of the food in this region. While women provide the majority of the labor in agricultural production, their access and control over productive resources is greatly constrained due to inequalities constructed by patriarchal norms.
In feminist economics, the feminization of agriculture refers to the measurable increase of women's participation in the agricultural sector, particularly in the developing world. The phenomenon started during the 1960s with increasing shares over time. In the 1990s, during liberalization, the phenomenon became more pronounced and negative effects appeared in the rural female population. Afterwards, agricultural markets became gendered institutions, affecting men and women differently. In 2009 World Bank, FAO & IFAD found that over 80 per cent of rural smallholder farmers worldwide were women, this was caused by men migrating to find work in other sectors. Out of all the women in the labor sector, the UN found 45-80% of them to be working in agriculture

Fair trade cocoa is an agricultural product harvested from a cocoa tree using a certified process which is followed by cocoa farmers, buyers, and chocolate manufacturers, and is designed to create sustainable incomes for farmers and their families. Companies that use fair trade certified cocoa to create products can advertise that they are contributing to social, economic, and environmental sustainability in agriculture.
Digital agriculture, sometimes known as smart farming or e-agriculture, is tools that digitally collect, store, analyze, and share electronic data and/or information in agriculture. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations has described the digitalization process of agriculture as the digital agricultural revolution. Other definitions, such as those from the United Nations Project Breakthrough, Cornell University, and Purdue University, also emphasize the role of digital technology in the optimization of food systems.












