Related Research Articles

The Acropolis of Athens is an ancient citadel located on a rocky outcrop above the city of Athens, Greece, and contains the remains of several ancient buildings of great architectural and historical significance, the most famous being the Parthenon. The word acropolis is from the Greek words ἄκρον and πόλις. The term acropolis is generic and there are many other acropoleis in Greece. During ancient times the Acropolis of Athens was known also more properly as Cecropia, after the legendary serpent-man Cecrops, the supposed first Athenian king.

Delphi, in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), was an ancient sacred precinct and the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient classical world. The ancient Greeks considered the centre of the world to be in Delphi, marked by the stone monument known as the omphalos (navel).
The 6th century BC started on the first day of 600 BC and ended on the last day of 501 BC.
This article concerns the period 539 BC – 530 BC.
This article concerns the period 479 BC – 470 BC.
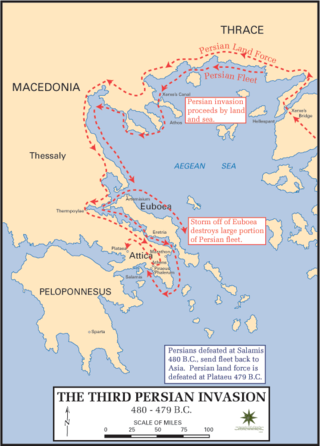
Year 480 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vibulanus and Cincinnatus. The denomination 480 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 400 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Republic, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Esquilinus, Capitolinus, Vulso, Medullinus, Saccus and Vulscus. The denomination 400 BC for this year has been used in Europe since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became prevalent there.

Year 450 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Second year of the decemviri. The denomination 450 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 410 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Mamercinus and Volusus. The denomination 410 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 470 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Potitus and Mamercus. The denomination 470 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 425 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Atratinus, Medullinus, Cincinnatus and Barbatus. The denomination 425 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The year 560 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as year 194 Ab urbe condita. The denomination 560 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 460 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Poplicola and Sabinus. The denomination 460 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 352 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Poplicola and Rutilus. The denomination 352 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The year 600 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as year 154 Ab urbe condita. The denomination 600 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The sculpture of ancient Greece is the main surviving type of fine ancient Greek art as, with the exception of painted ancient Greek pottery, almost no ancient Greek painting survives. Modern scholarship identifies three major stages in monumental sculpture in bronze and stone: the Archaic, Classical (480–323) and Hellenistic. At all periods there were great numbers of Greek terracotta figurines and small sculptures in metal and other materials.

The Siphnian Treasury was a building at the Ancient Greek cult centre of Delphi, erected to host the offerings of the polis, or city-state, of Siphnos. It was one of a number of treasuries lining the "Sacred Way", the processional route through the Sanctuary of Apollo, erected to win the favor of the gods and increase the prestige of the donor polis. It was one of the earlier surviving buildings of this type, and its date remains a matter for debate, with the most plausible date being around 525 BC. Until recently it was often confused or conflated with the neighbouring Cnidian Treasury, a similar but less elaborate building, as the remains of the two had become mixed together and earlier theoretical reconstructions used parts of both.

Amfissa is a town in Phocis, Greece, part of the municipality of Delphi, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 315.174 km2. It lies on the northern edge of the olive forest of the Crissaean plain, between two mountains, Giona to the west and Parnassus to the east, 200 km (120 mi) northwest of Athens and 20 km (12 mi) of Delphi, as well as 85 km (53 mi) northeast of Naupactus and 72 km (45 mi) south of Lamia.

Delphi Archaeological museum is one of the principal museums of Greece and one of the most visited. It is operated by the Greek Ministry of Culture. Founded in 1903, it has been rearranged several times and houses the discoveries made at the Panhellenic sanctuary of Delphi, which date from the Late Helladic (Mycenean) period to the early Byzantine era.

The Athenian Treasury at Delphi was constructed by the Athenians to house dedications and votive offerings made by their city and citizens to the sanctuary of Apollo. The entire treasury including its sculptural decoration is built of Parian marble. The date of construction is disputed, and scholarly opinions range from 510 to 480 BCE. It is located directly below the Temple of Apollo along the Sacred Way for all visitors to view the Athenian treasury on the way up to the sanctuary.