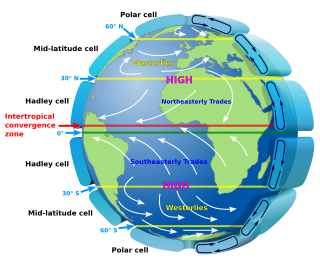
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air and together with ocean circulation is the means by which thermal energy is redistributed on the surface of the Earth. The Earth's atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, but the large-scale structure of its circulation remains fairly constant. The smaller-scale weather systems – mid-latitude depressions, or tropical convective cells – occur chaotically, and long-range weather predictions of those cannot be made beyond ten days in practice, or a month in theory.
The 42nd parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 42 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, the Mediterranean Sea, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
The 30th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 30 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It stands one-third of the way between the equator and the North Pole and crosses Africa, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America and the Atlantic Ocean. The parallel is used in some contexts to delineate Europe or what is associated with the continent of Europe as a southernmost limit, e.g. to qualify for membership of the European Broadcasting Union.
The 45th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 45 degrees north of Earth's equator. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean. The 45th parallel north is often called the halfway point between the equator and the North Pole, but the true halfway point is 16.0 km (9.9 mi) north of it because Earth is an oblate spheroid; that is, it bulges at the equator and is flattened at the poles.
The 35th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 35 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America and the Atlantic Ocean.
The 55th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 55 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.

The U.S. Army Corps of Topographical Engineers was a branch of the United States Army authorized on 4 July 1838. It consisted only of officers who were handpicked from West Point and was used for mapping and the design and construction of federal civil works such as lighthouses and other coastal fortifications and navigational routes. Members included such officers as George Meade, John C. Frémont, Thomas J. Cram and Stephen Long. It was merged with the United States Army Corps of Engineers on 31 March 1863, at which point the Corps of Engineers also assumed the Lakes Survey for the Great Lakes. In the mid-19th century, Corps of Engineers' officers ran Lighthouse Districts in tandem with U.S. Naval officers.

The 10th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 10 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Africa, the Indian Ocean, the Indian Subcontinent, Southeast Asia, the Pacific Ocean, Central America, South America and the Atlantic Ocean.

The 20th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 20 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Africa, Asia, the Indian Ocean, the Pacific Ocean, North America, the Caribbean and the Atlantic Ocean.
The 50th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 50 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
The 60th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 60 degrees north of Earth's equator. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
The 30th parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 30 degrees south of the Earth's equator. It stands one-third of the way between the equator and the South Pole and crosses Africa, the Indian Ocean, Australia, the Pacific Ocean, South America and the Atlantic Ocean.
The 60th parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 60 degrees south of Earth's equatorial plane. No land lies on the parallel—it crosses nothing but ocean. The closest land is a group of rocks north of Coronation Island of the South Orkney Islands, which are about 54 km south of the parallel, and Thule Island and Cook Island of the South Sandwich Islands, which both are about 57 km north of the parallel.
The 5th parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 5 degrees south of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean, Africa, the Indian Ocean, Southeast Asia, Australasia, the Pacific Ocean and South America.
The 15th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 15 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses the Saharan fringe in Africa, three key peninsulas of Asia, the Pacific Ocean, an isthmus of Central America, the southern Caribbean and the Atlantic Ocean.

The 25th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 25 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Africa, Asia, the Indian Ocean, the Pacific Ocean, North America and the Atlantic Ocean.

The 32nd parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 32 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Africa, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America and the Atlantic Ocean.
The 16th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 16 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Africa, Asia, the Indian Ocean, the Pacific Ocean, Central America, the Caribbean and the Atlantic Ocean.
The meridian 115° west of Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, North America, the Pacific Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole.
The 38th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 38 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, the Mediterranean Sea, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean. The 38th parallel north formed the border between North and South Korea prior to the Korean War.







