
Delta Scuti, Latinized from δ Scuti, is a variable star in the southern constellation Scutum. With an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 4.72, it is the fifth-brightest star in this small and otherwise undistinguished constellation. Analysis of the parallax measurements place this star at a distance of about 199 light-years from Earth. It is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −45 km/s.

28 Andromedae is a Delta Scuti variable star in the constellation Andromeda. 28 Andromedae is the Flamsteed designation. It also bears the variable star name GN Andromedae. Its apparent magnitude is 5.214, varying by less than 0.1 magnitudes.

RT Aurigae is a yellow supergiant variable star in the constellation Auriga, about 1,500 light years from Earth.

38 Cancri is a variable star in the zodiac constellation Cancer, located around 607 light years from the Sun. This object has the variable star designation BT Cancri; 38 Cancri is the Flamsteed designation. It is a member of the Praesepe cluster but is a challenge to view with the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 6.65. The star is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +32 km/s.
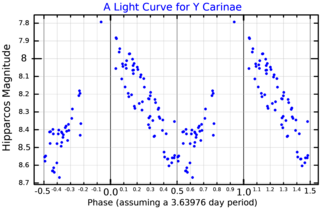
Y Carinae is a Classical Cepheid variable, a type of variable star, in the constellation Carina. Its apparent magnitude varies from 7.53 to 8.48.

FF Aquilae is a classical Cepheid variable star located in the constellation Aquila. It ranges from apparent magnitude 5.18 to 5.51 over a period of 4.470848 days, meaning it is faintly visible to the unaided eye in rural or suburban settings.

HD 15082 is a star located roughly 399 light years away in the northern constellation of Andromeda. The star is a Delta Scuti variable and a planetary transit variable. A hot Jupiter type extrasolar planet, named WASP-33b or HD 15082b, orbits this star with an orbital period of 1.22 days. It is the first Delta Scuti variable known to host a planet.

64 Eridani is a single, yellow-white hued star in the constellation Eridanus having variable star designation S Eridani. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.77. The annual parallax shift is measured at 12.01 mas, which equates to a distance of about 272 light years. In addition to its proper motion, it is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of around −9 km/s.

V529 Andromedae, also known as HD 8801, is a variable star in the constellation of Andromeda. It has a 13th magnitude visual companion star 15" away, which is just a distant star on the same line of sight.
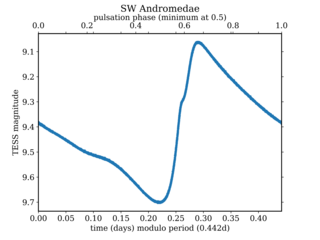
SW Andromedae is a variable star in the constellation of Andromeda. It is classified as an RR Lyrae star, and varies from an apparent magnitude of 10.09 at minimum brightness to a magnitude of 9.14 at maximum brightness with a period of 0.44226 days.

R Sagittae is an RV Tauri variable star in the constellation Sagitta that varies from magnitude 8.0 to 10.5 in 70.77 days. It is a post-AGB low mass yellow supergiant that varies between spectral types G0Ib and G8Ib as it pulsates. Its variable star designation of "R" indicates that it was the first star discovered to be variable in the constellation. It was discovered in 1859 by Joseph Baxendell, though classified as a semi regular variable until RV Tauri variables were identified as a distinct class in 1905.

CC Andromedae is a variable star in the constellation Andromeda. It is a pulsating star of the Delta Scuti type, with an apparent visual magnitude that varies between 9.19 and 9.46 with a periodicity of 3 hours.
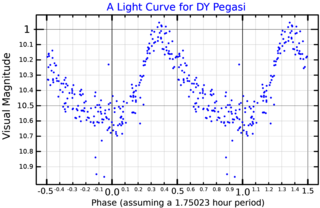
DY Pegasi, abbreviated DY Peg, is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Pegasus. It is a well-studied SX Phoenicis variable star with a brightness that ranges from an apparent visual magnitude of 9.95 down to 10.62 with a period of 1.75 hours. This system is much too faint to be seen with the naked eye, but can be viewed with large binoculars or a telescope. Based on its high space motion and low abundances of heavier elements, it is a population II star system.
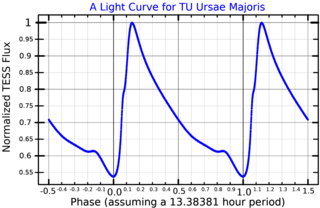
TU Ursae Majoris is a variable star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. It is classified as a Bailey-type 'ab' RR Lyrae variable with a period of 0.557648 days that ranges in brightness from apparent visual magnitude of 9.26 down to 10.24. The distance to this star is approximately 2,090 light years based on parallax measurements. It is located near the north galactic pole at a distance that indicates this is a member of the galactic halo.

SZ Tauri is a variable star in the equatorial constellation of Taurus. The brightness of this star varies from an apparent visual magnitude of 6.39 down to 6.69 with a period of 3.149 days, which is near the lower limit of visibility to the naked eye. The distance to this star is approximately 2,070 light years based on parallax measurements. There is some indication this may be a binary system, but the evidence is inconclusive.

FG Virginis is a well-studied variable star in the equatorial constellation of Virgo. It is a dim star, near the lower limit of visibility to the naked eye, with an apparent visual magnitude that ranges from 6.53 down to 6.58. The star is located at a distance of 273.5 light years from the Sun based on parallax measurements, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +16 km/s. Because of its position near the ecliptic, it is subject to lunar occultations.

AI Velorum is a variable star in the southern constellation of Vela, abbreviated AI Vel. It is a prototype for a class of high amplitude Delta Scuti variables. The apparent visual magnitude of this star fluctuates around 6.56, which is just bright enough to be dimly visible to the naked eye. The distance to AI Vel is approximately 327 light years based on parallax measurements, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of about 9 km/s.

VZ Cancri is a variable star in the constellation Cancer, abbreviated VZ Cnc. It varies in brightness with a period of 0.178364 days, from an apparent visual magnitude of 7.18 down to 7.91, which lies below the typical threshold of visibility for the naked eye. The distance to this star is approximately 724 light years based on parallax measurements, and it is receding from the Sun with a radial velocity of 25 km/s.
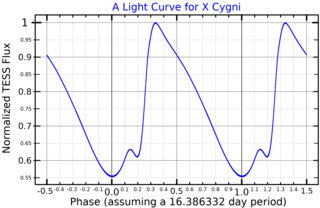
X Cygni is a variable star in the northern constellation of Cygnus, abbreviated X Cyg. This is a Delta Cephei variable that ranges in brightness from an apparent visual magnitude of 5.85 down to 6.91 with a period of 16.386332 days. At it brightest, this star is dimly visible to the naked eye. The distance to this star is approximately 628 light years based on parallax measurements. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of 8.1 km/s. This star is a likely member of the open cluster Ruprecht 173.

SU Cygni is a triple star system in the northern constellation of Cygnus, abbreviated SU Cyg. The primary component of the system is a classical Cepheid variable with a period of 3.8455473 days. The changing luminosity of this star causes the system to vary in brightness from a peak apparent visual magnitude of 6.44 down to magnitude 7.22 over the course of its cycle. The distance to this system is approximately 3,200 light years based on parallax measurements. It is a member of the Turner 9 open cluster of stars.




















