
Sagitta is a dim but distinctive constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for 'arrow', not to be confused with the significantly larger constellation Sagittarius 'the archer'. It was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. Although it dates to antiquity, Sagitta has no star brighter than 3rd magnitude and has the third-smallest area of any constellation.

GK Persei was a bright nova first observed on Earth in 1901. It was discovered by Thomas David Anderson, an Edinburgh clergyman, at 02:40 UT on 22 February 1901 when it was at magnitude 2.7. It reached a maximum magnitude of 0.2, the brightest nova of modern times until Nova Aquilae 1918. After fading into obscurity at about magnitude 12 to 13 during the early 20th century, GK Persei began displaying infrequent outbursts of 2 to 3 magnitudes. Since about 1980, these outbursts have become quite regular, typically lasting about two months and occurring about every three years. Thus, GK Persei seems to have changed from a classical nova like Nova Aquilae 1918 to something resembling a typical dwarf nova-type cataclysmic variable star.

NQ Vulpeculae also known as Nova Vulpeculae 1976, was a nova that appeared in the constellation Vulpecula in 1976. It was discovered visually at 18:20 UT on October 21, 1976 by English amateur astronomer George Alcock. Its apparent magnitude at the time of discovery was 6.5 It reached its maximum brightness of magnitude 6.0 thirteen days after its discovery, at which point it may have been faintly visible to the naked eye. A few days after maximum brightness, it had faded to magnitude 8.3.
V838 Herculis, also known as Nova Herculis 1991, was a nova which occurred in the constellation Hercules in 1991. It was discovered by George Alcock of Yaxley, Cambridgeshire, England at 4:35 UT on the morning of 25 March 1991. He found it with 10×50 binoculars, and on that morning its apparent visual magnitude was 5. Palomar Sky Survey plates showed that before the outburst, the star was at photographic magnitude 20.6 and 18.25.

V1494 Aquilae or Nova Aquilae 1999 b was a nova which occurred during 1999 in the constellation Aquila and reached a brightness of magnitude 3.9 on 2 December 1999. making it easily visible to the naked eye. The nova was discovered with 14×100 binoculars by Alfredo Pereira of Cabo da Roca, Portugal at 18:50 UT on 1 December 1999, when it had a visual magnitude of 6.0.

WZ Sagittae is a cataclysmic dwarf nova star system in the constellation Sagitta. It consists of a white dwarf primary being orbited by a low mass companion. The white dwarf is about 0.85 solar masses while the companion is only 0.08 solar masses. This implies that the companion is a spectral class L2 star, although this has yet to be confirmed. The distance to this system has been determined by parallax, yielding a distance of 45.1 parsecs.

RX Andromedae is a variable star in the constellation of Andromeda. Although it is classified as a dwarf nova of the Z Camelopardalis (UGZ) type, it has shown low-luminosity periods typical of VY Sculptoris stars. However, for most of the time it varies from an apparent visual magnitude of 15.1 at minimum brightness to a magnitude of 10.2 at maximum brightness, with a period of approximately 13 days.

Z Chamaeleontis is a dwarf nova variable star system approximately 377 light-years away from the Sun, where two stars orbit each other every 1.78 hours. The system comprises an eclipsing white dwarf and red dwarf and possibly a yet unconfirmed third low-mass substellar companion.
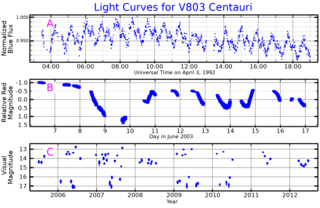
V803 Centauri is a cataclysmic binary consisting of a dwarf helium star losing mass to a white dwarf. It is an example of the AM Canum Venaticorum type of cataclysmic variable stars.
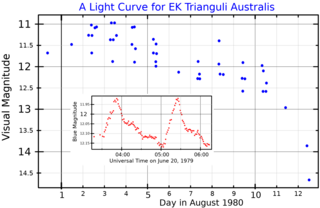
EK Trianguli Australis is a star in the constellation Triangulum Australe. It is a dwarf nova of the SU Ursae Majoris type that officially classified as such in 1980, after the characteristic eruptions of a short eruption and a supereruption were observed in May 1978 and June 1979 respectively. These systems are characterised by frequent eruptions and less frequent supereruptions. The former are smooth, while the latter exhibit short "superhumps" of heightened activity. The distance of the system has been assumed at 180 parsecs from the Solar System, for the donor star. Spectroscopic analysis and calculation gave an estimate of 125 parsecs.

SU Ursae Majoris, or SU UMa, is a close binary star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. It is a periodic cataclysmic variable that varies in magnitude from a peak of 10.8 down to a base of 14.96. The distance to this system, as determined from its annual parallax shift of 4.53 mas, is 719 light-years. It is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +27 km/s.
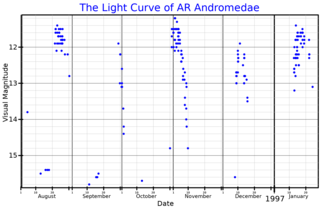
AR Andromedae is a dwarf nova of the SS Cygni type in the constellation Andromeda. Its typical apparent visual magnitude is 17.6, but increases up to 11.0 magnitude during outbursts. The outbursts occur approximately every 23 days.
OS Andromedae, known also as Nova Andromedae 1986, is a classical nova that appeared in the constellation Andromeda during 1986. It was discovered at 10:34 UT on 5 December 1986 by Mitsuri Suzuki, a 28-year-old school teacher living in Ena, Japan. He photographed the portion of the Milky Way that passes through northern Andromeda with a 200-mm telephoto lens, and found the nova when its apparent magnitude was 8.0. Two days later it reached a peak apparent visual magnitude of 6.3.

PX Andromedae is an eclipsing cataclysmic variable star in the constellation Andromeda. It has been classified as a SW Sextantis variable, and its apparent visual magnitude varies between 14.04 and 17.

V455 Andromedae is a dwarf nova in the constellation Andromeda. It has a typical apparent visual magnitude of 16.5, but reached a magnitude of 8.5 during the only observed outburst.

V1370 Aquilae, also known as Nova Aquilae 1982, is a nova that appeared in the constellation Aquila during 1982. It was discovered by Minoru Honda of Kurashiki, Japan at 20:30 UT on 27 January 1982. At that time the Sun had moved just far enough from Aquila to allow the nova to be seen in the morning sky. Although it was discovered photographically, its apparent magnitude was 6–7, making it potentially visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. A possible magnitude 20 progenitor was located on the Palomar Sky Survey prints. Spectra of the object were taken in February 1982 at Asiago Astrophysical Observatory, which confirmed that it is a nova.

BZ Ursae Majoris is a dwarf nova star system in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. It consists of a white dwarf primary in a close orbit with a red dwarf. The latter star is donating mass, which is accumulating in an accretion disk orbiting the white dwarf. The system is located at a distance of approximately 505 light years from the Sun based on parallax measurements.

RZ Leonis Minoris is a cataclysmic variable star system in the northern constellation of Leo Minor. It undergoes frequent outbursts that vary in brightness from an apparent visual magnitude of 14.4 down to 16.8. Based on parallax measurements, this system is located at a distance of approximately 2,160 light years from the Sun.

SW Ursae Majoris is a cataclysmic binary star system in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major, abbreviated SW UMa. During quiescence it has an apparent visual magnitude of 16.5–17, which is too faint to be visible to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements, it is located at a distance of approximately 526 light years from the Sun.

ER Ursae Majoris is a variable star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major, abbreviated ER UMa. It is a prototype system for a subclass of SU Ursae Majoris dwarf novae. The system ranges in brightness from a peak apparent visual magnitude of 12.4 down to 15.2, which is too faint to be visible to the naked eye. The distance to this system, based on parallax measurements, is approximately 1,163 light years.




















