
The Apache HTTP Server is a free and open-source cross-platform web server software, released under the terms of Apache License 2.0. It is developed and maintained by a community of developers under the auspices of the Apache Software Foundation.

A web server is computer software and underlying hardware that accepts requests via HTTP or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, commonly a web browser or web crawler, initiates communication by making a request for a web page or other resource using HTTP, and the server responds with the content of that resource or an error message. A web server can also accept and store resources sent from the user agent if configured to do so.

z/OS is a 64-bit operating system for IBM z/Architecture mainframes, introduced by IBM in October 2000. It derives from and is the successor to OS/390, which in turn was preceded by a string of MVS versions. Like OS/390, z/OS combines a number of formerly separate, related products, some of which are still optional. z/OS has the attributes of modern operating systems but also retains much of the older functionality originated in the 1960s and still in regular use—z/OS is designed for backward compatibility.

CUPS is a modular printing system for Unix-like computer operating systems which allows a computer to act as a print server. A computer running CUPS is a host that can accept print jobs from client computers, process them, and send them to the appropriate printer.
In computer security, a key server is a computer that receives and then serves existing cryptographic keys to users or other programs. The users' programs can be running on the same network as the key server or on another networked computer.
The Webalizer is web log analysis software, which generates web pages of analysis, from access and usage logs. It is one of the most commonly used web server administration tools. It was initiated by Bradford L. Barrett in 1997. Statistics commonly reported by Webalizer include hits, visits, referrers, the visitors' countries, and the amount of data downloaded. These statistics can be viewed graphically and presented by different time frames, such as by day, hour, or month.
Web analytics is the measurement, collection, analysis, and reporting of web data to understand and optimize web usage. Web analytics is not just a process for measuring web traffic but can be used as a tool for business and market research and assess and improve website effectiveness. Web analytics applications can also help companies measure the results of traditional print or broadcast advertising campaigns. It can be used to estimate how traffic to a website changes after launching a new advertising campaign. Web analytics provides information about the number of visitors to a website and the number of page views, or create user behavior profiles. It helps gauge traffic and popularity trends, which is useful for market research.
LXR Cross Referencer, usually known as LXR, is a general-purpose source code indexer and cross-referencer for code comprehension that provides web-based browsing of source code, with links to the definition and usage of any identifier.
ApacheBench is a single-threaded command line computer program used for benchmarking HTTP web servers. Originally it was used to test the Apache HTTP Server but it is generic enough to test any web server supporting HTTP/1.0 or HTTP/1.1 protocol versions.
pisg, short for Perl IRC Statistics Generator is a popular open-source Internet Relay Chat (IRC) log file analysis and statistical visualization program. It is written in perl by Morten Brix Pedersen. It analyzes various formats of log files from IRC clients and bots and generates HTML pages containing statistics about the channel the logs were taken from. It is often considered a competitor to mIRCStats, a similar shareware program.
Urchin was a web statistics analysis program that was developed by Urchin Software Corporation. Urchin analyzed web server log file content and displayed the traffic information on that website based upon the log data. Sales of Urchin products ended on March 28, 2012.

W3Perl is a free software logfile analyser, which can parse Web/FTP/Mail/CUPS/DHCP/SSH and Squid logfiles. Most major web logfile formats are supported, as well as split/compressed files. "Page tagging" and counter are also supported if you do not have logfiles access. The output is spread over HTML pages, with graphics and a sortable table. Stats can be run from a single command line or from a web browser.
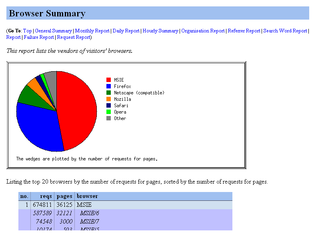
Analog is a free web log analysis computer program that runs under Windows, macOS, Linux, and most Unix-like operating systems. It was first released on June 21, 1995, by Stephen Turner as generic freeware; the license was changed to the GNU General Public License in November 2004. The software can be downloaded for several computing platforms, or the source code can be downloaded and compiled if desired.
In computing, logging is the act of keeping a log of events that occur in a computer system, such as problems, errors or just information on current operations. These events may occur in the operating system or in other software. A message or log entry is recorded for each such event. These log messages can then be used to monitor and understand the operation of the system, to debug problems, or during an audit. Logging is particularly important in multi-user software, to have a central overview of the operation of the system.

Sawmill was a software package for the statistical analysis and reporting of log files. Sawmill also incorporated real-time reporting and alerting.
Web2py is an open-source web application framework written in the Python programming language. Web2py allows web developers to program dynamic web content using Python. Web2py is designed to help reduce tedious web development tasks, such as developing web forms from scratch, although a web developer may build a form from scratch if required.
Greymatter is a free and open-source blogging software package, originally created by Noah Grey in November 2000. It was "the original opensource weblogging software". Noah Grey stopped maintaining it around 2002. Since then, it has been maintained by the community of users. It is one of the first software packages created for blogging, and had a large number of users. With the creation of WordPress and Google's Blogspot, its users have declined since 2005, but it is still in use.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Perl programming language:
Caddy is an extensible, cross-platform, open-source web server written in Go.








