High commissioner is the title of various high-ranking, special executive positions held by a commission of appointment.
Resident commissioner was or is an official title of several different types of commissioners, who were or are representatives of any level of government. Historically, they were appointed by the British Crown in overseas protectorates, or colonies, and some still exist in this capacity. The United States of America once had a resident commissioner in the Philippines and the Puerto Rico resident commissioner resides in Washington DC. State governments of today's Republic of India have a resident commissioner to represent them in New Delhi.
A resident minister, or resident for short, is a government official required to take up permanent residence in another country. A representative of his government, he officially has diplomatic functions which are often seen as a form of indirect rule.

The Bight of Benin or Bay of Benin is a bight in the Gulf of Guinea area on the western African coast that derives its name from the historical Kingdom of Benin.

The Bight of Biafra, also known as the Bight of Bonny, is a bight off the west-central African coast, in the easternmost part of the Gulf of Guinea.

Togoland was a German Empire protectorate in West Africa from 1884 to 1914, encompassing what is now the nation of Togo and most of what is now the Volta Region of Ghana, approximately 90,400 km2 in size. During the period known as the "Scramble for Africa", the colony was established in 1884 and was gradually extended inland.

Wilhelm Heinrich Solf was a German scholar, diplomat, jurist and statesman.
John Beecroft was an explorer, governor of Fernando Po and British Consul of the Bight of Benin and Biafra.

The islands of Samoa were originally inhabited by humans as early as 850 BC. After being invaded by European explorers in the 18th century, by the 20th and 21st century, the islands were incorporated into Samoa and American Samoa.

A consulate is the office of a consul. A type of diplomatic mission, it is usually subordinate to the state's main representation in the capital of that foreign country, usually an embassy. The term "consulate" may refer not only to the office of a consul, but also to the building occupied by the consul and the consul's staff. The consulate may share premises with the embassy itself.
Sapele is a primary town and one of the Local Government Areas of Delta State, Nigeria.

Colonial Nigeria was ruled by the British Empire from the mid-nineteenth century until 1960 when Nigeria achieved independence. Britain annexed Lagos in 1861 and established the Oil River Protectorate in 1884. British influence in the Niger area increased gradually over the 19th century, but Britain did not effectively occupy the area until 1885. Other European powers acknowledged Britain's dominance over the area in the 1885 Berlin Conference.

There are 122 diplomatic missions in Hong Kong, of which 61 are consulates-general and 61 are consulates and six officially recognised bodies in Hong Kong. As Hong Kong has the status of a Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China, some consuls-general in Hong Kong report directly to their respective foreign ministries, rather than to their Embassies in Beijing.

Diplomatic relations exist between Australia and Germany, as well as the historical contacts, shared values of democracy and human rights, substantial commercial links, and a keen interest in each other's culture. As part of a strategic partnership concluded in 2013, both nations are also increasingly cooperating on security policy issues. Both countries also maintain diplomatic relations in each other's countries.

Lagos Colony was a British colonial possession centred on the port of Lagos in what is now southern Nigeria. Lagos was annexed on 6 August 1861 under the threat of force by Commander Beddingfield of HMS Prometheus who was accompanied by the Acting British Consul, William McCoskry. Oba Dosunmu of Lagos resisted the cession for 11 days while facing the threat of violence on Lagos and its people, but capitulated and signed the Lagos Treaty of Cession. Lagos was declared a colony on 5 March 1862. By 1872, Lagos was a cosmopolitan trading centre with a population over 60,000. In the aftermath of prolonged wars between the mainland Yoruba states, the colony established a protectorate over most of Yorubaland between 1890 and 1897. The protectorate was incorporated into the new Southern Nigeria Protectorate in February 1906, and Lagos became the capital of the Protectorate of Nigeria in January 1914. Since then, Lagos has grown to become the largest city in West Africa, with an estimated metropolitan population of over 9,000,000 as of 2011.
The Treaty of Cession, 6 August 1861 or the Lagos Treaty of Cession was a treaty between the British Empire and Oba Dosunmu of Lagos wherein Dosunmu, under the threat of military bombardment, ceded Lagos Island to Britain, whilst retaining the title and powers of Oba, subject to English laws.
The Treaty Between Great Britain and Lagos, 1 January 1852 was an agreement between Great Britain and Oba Akitoye, the newly installed Oba of Lagos. The treaty was signed following British victory during the Reduction of Lagos.
The Embassy of Switzerland in New Zealand is the official representation of Switzerland in New Zealand and in a number of Pacific island countries.

The Reduction of Lagos or Bombardment of Lagos was a British naval operation in late 1851 that involved the Royal Navy bombarding Lagos under the justification of suppressing the Atlantic slave trade and deposing the King (Oba) of Lagos, Kosoko, for refusing to end the slave trade.
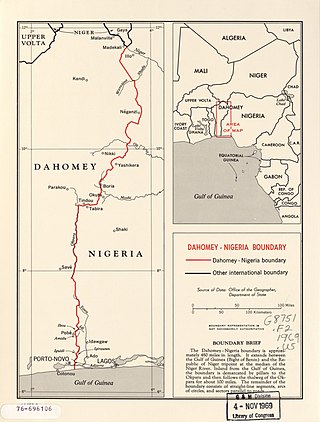
The Benin–Nigeria border is 809 km in length and runs from the tripoint with Niger in the north down to the Bight of Benin in the south.










