
Multics is an influential early time-sharing operating system based on the concept of a single-level memory. Nathan Gregory writes that Multics "has influenced all modern operating systems since, from microcomputers to mainframes."

A mainframe computer, informally called a mainframe or big iron, is a computer used primarily by large organizations for critical applications like bulk data processing for tasks such as censuses, industry and consumer statistics, enterprise resource planning, and large-scale transaction processing. A mainframe computer is large but not as large as a supercomputer and has more processing power than some other classes of computers, such as minicomputers, servers, workstations, and personal computers. Most large-scale computer-system architectures were established in the 1960s, but they continue to evolve. Mainframe computers are often used as servers.

Computer operating systems (OSes) provide a set of functions needed and used by most application programs on a computer, and the links needed to control and synchronize computer hardware. On the first computers, with no operating system, every program needed the full hardware specification to run correctly and perform standard tasks, and its own drivers for peripheral devices like printers and punched paper card readers. The growing complexity of hardware and application programs eventually made operating systems a necessity for everyday use.
The Honeywell 6000 series computers were rebadged versions of General Electric's 600-series mainframes manufactured by Honeywell International, Inc. from 1970 to 1989. Honeywell acquired the line when it purchased GE's computer division in 1970 and continued to develop them under a variety of names for many years. In 1989, Honeywell sold its computer division to the French company Groupe Bull who continued to market compatible machines.
The GE-600 series is a family of 36-bit mainframe computers originating in the 1960s, built by General Electric (GE). When GE left the mainframe business the line was sold to Honeywell, which built similar systems into the 1990s as the division moved to Groupe Bull and then NEC.

In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit central processing units (CPU) and arithmetic logic units (ALU) are those that are based on processor registers, address buses, or data buses of that size. A computer that uses such a processor is a 64-bit computer.

General Comprehensive Operating System is a family of operating systems oriented toward the 36-bit GE-600 series and Honeywell 6000 series mainframe computers.
Cray Inc., a subsidiary of Hewlett Packard Enterprise, is an American supercomputer manufacturer headquartered in Seattle, Washington. It also manufactures systems for data storage and analytics. Several Cray supercomputer systems are listed in the TOP500, which ranks the most powerful supercomputers in the world.
This article presents a timeline of events in the history of computer operating systems from 1951 to the current day. For a narrative explaining the overall developments, see the History of operating systems.

NEC Corporation is a Japanese multinational information technology and electronics corporation, headquartered at the NEC Supertower in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. It provides IT and network solutions, including cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT) platform, and telecommunications equipment and software to business enterprises, communications services providers and to government agencies. NEC has also been the largest PC vendor in Japan since the 1980s when it launched the PC-8000 series; it currently operates its domestic PC business in a joint venture with Lenovo.

Bull SAS is a French computer company headquartered in Les Clayes-sous-Bois, in the western suburbs of Paris. The company has also been known at various times as Bull General Electric, Honeywell Bull, CII Honeywell Bull, and Bull HN. Bull was founded in 1931, as H.W. Egli - Bull, to capitalize on the punched card technology patents of Norwegian engineer Fredrik Rosing Bull (1882–1925). After a reorganization in 1933, with new investors coming in, the name was changed to Compagnie des Machines Bull (CMB). Bull has a worldwide presence in more than 100 countries and is particularly active in the defense, finance, health care, manufacturing, public, and telecommunication sectors.

NEC SX describes a series of vector supercomputers designed, manufactured, and marketed by NEC. This computer series is notable for providing the first computer to exceed 1 gigaflop, as well as the fastest supercomputer in the world between 1992–1993, and 2002–2004. The current model, as of 2018, is the SX-Aurora TSUBASA.
The Worldwide Military Command and Control System, or WWMCCS, was a military command and control system implemented for command and control of the United States Department of Defense. It was created in the days following the Cuban Missile Crisis. WWMCCS was a complex of systems that encompassed the elements of warning, communications, data collection and processing, executive decision-making tools and supporting facilities. It was decommissioned in 1996 and replaced by the Global Command and Control System.
GXS is a subsidiary of OpenText Corporation headquartered in Gaithersburg, Maryland, United States. Its GXS Trading Grid managed more than twelve billion transactions in 2011. Since 2004, GXS has invested more than $250 million in GXS Trading Grid. As of March 16, 2012, more than 550,000 businesses connect to GXS Trading Grid and, on average, more than 2,000 new businesses join each month.
PTC Scheduler is a Windows based batch scheduling application. Via the use of either "Agents" or Telnet connections, PTC Scheduler is able to schedule and monitor batch processes on the following platforms:

Japan operates a number of centers for supercomputing which hold world records in speed, with the K computer being the world's fastest from June 2011 to June 2012, and Fugaku holding the lead from June 2020 until June 2022.
IBM Power microprocessors are designed and sold by IBM for servers and supercomputers. The name "POWER" was originally presented as an acronym for "Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC". The Power line of microprocessors has been used in IBM's RS/6000, AS/400, pSeries, iSeries, System p, System i, and Power Systems lines of servers and supercomputers. They have also been used in data storage devices and workstations by IBM and by other server manufacturers like Bull and Hitachi.

The Honeywell Level 6 was a line of 16-bit minicomputers, later upgraded to 32-bit, manufactured by Honeywell, Inc. from the mid 1970s. Honeywell literature for Models 6/06, 6/34 and 6/36 say "Series 60 ". In 1979, the Level 6 was renamed the DPS 6, subsequently DPS 6 Plus and finally DPS 6000.
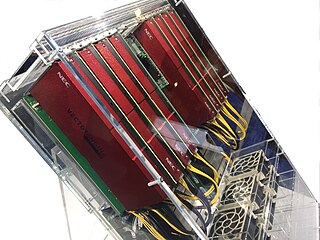
The NEC SX-Aurora TSUBASA is a vector processor of the NEC SX architecture family. Unlike previous SX supercomputers, the SX-Aurora TSUBASA is provided as a PCIe card, termed by NEC as a "Vector Engine" (VE). Eight VE cards can be inserted into a vector host (VH) which is typically a x86-64 server running the Linux operating system. The product has been announced in a press release on 25 October 2017 and NEC has started selling it in February 2018. The product succeeds the SX-ACE.










