Related Research Articles

Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines to applied disciplines. Though more often considered an academic discipline, computer science is closely related to computer programming.

A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs.
In software engineering and computer science, abstraction is the process of generalizing concrete details, such as attributes, away from the study of objects and systems to focus attention on details of greater importance. Abstraction is a fundamental concept in computer science and software engineering, especially within the object-oriented programming paradigm. Examples of this include:
Reconfigurable computing is a computer architecture combining some of the flexibility of software with the high performance of hardware by processing with flexible hardware platforms like field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs). The principal difference when compared to using ordinary microprocessors is the ability to add custom computational blocks using FPGAs. On the other hand, the main difference from custom hardware, i.e. application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) is the possibility to adapt the hardware during runtime by "loading" a new circuit on the reconfigurable fabric, thus providing new computational blocks without the need to manufacture and add new chips to the existing system.
Programming paradigms are a way to classify programming languages based on their features. Languages can be classified into multiple paradigms.
In computer science, divide and conquer is an algorithm design paradigm. A divide-and-conquer algorithm recursively breaks down a problem into two or more sub-problems of the same or related type, until these become simple enough to be solved directly. The solutions to the sub-problems are then combined to give a solution to the original problem.
Software design is the process by which an agent creates a specification of a software artifact intended to accomplish goals, using a set of primitive components and subject to constraints. The term is sometimes used broadly to refer to "all the activity involved in conceptualizing, framing, implementing, commissioning, and ultimately modifying" the software, or more specifically "the activity following requirements specification and before programming, as ... [in] a stylized software engineering process."
In computer science, evolutionary computation is a family of algorithms for global optimization inspired by biological evolution, and the subfield of artificial intelligence and soft computing studying these algorithms. In technical terms, they are a family of population-based trial and error problem solvers with a metaheuristic or stochastic optimization character.
A fifth-generation programming language (5GL) is a high-level programming language based on problem-solving using constraints given to the program, rather than using an algorithm written by a programmer. Most constraint-based and logic programming languages and some other declarative languages are fifth-generation languages.
In computer science, a parallel random-access machine is a shared-memory abstract machine. As its name indicates, the PRAM is intended as the parallel-computing analogy to the random-access machine (RAM). In the same way that the RAM is used by sequential-algorithm designers to model algorithmic performance, the PRAM is used by parallel-algorithm designers to model parallel algorithmic performance. Similar to the way in which the RAM model neglects practical issues, such as access time to cache memory versus main memory, the PRAM model neglects such issues as synchronization and communication, but provides any (problem-size-dependent) number of processors. Algorithm cost, for instance, is estimated using two parameters O(time) and O(time × processor_number).
In digital circuit design, register-transfer level (RTL) is a design abstraction which models a synchronous digital circuit in terms of the flow of digital signals (data) between hardware registers, and the logical operations performed on those signals.
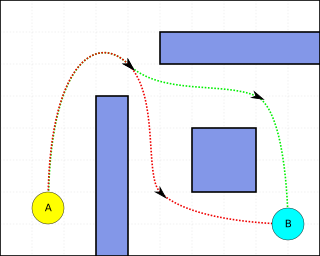
Pathfinding or pathing is the plotting, by a computer application, of the shortest route between two points. It is a more practical variant on solving mazes. This field of research is based heavily on Dijkstra's algorithm for finding the shortest path on a weighted graph.
Model-driven engineering (MDE) is a software development methodology that focuses on creating and exploiting domain models, which are conceptual models of all the topics related to a specific problem. Hence, it highlights and aims at abstract representations of the knowledge and activities that govern a particular application domain, rather than the computing concepts.
High-level synthesis (HLS), sometimes referred to as C synthesis, electronic system-level (ESL) synthesis, algorithmic synthesis, or behavioral synthesis, is an automated design process that takes an abstract behavioral specification of a digital system and finds a register-transfer level structure that realizes the given behavior.
Explicit Multi-Threading (XMT) is a computer science paradigm for building and programming parallel computers designed around the parallel random-access machine (PRAM) parallel computational model. A more direct explanation of XMT starts with the rudimentary abstraction that made serial computing simple: that any single instruction available for execution in a serial program executes immediately. A consequence of this abstraction is a step-by-step (inductive) explication of the instruction available next for execution. The rudimentary parallel abstraction behind XMT, dubbed Immediate Concurrent Execution (ICE) in Vishkin (2011), is that indefinitely many instructions available for concurrent execution execute immediately. A consequence of ICE is a step-by-step (inductive) explication of the instructions available next for concurrent execution. Moving beyond the serial von Neumann computer, the aspiration of XMT is that computer science will again be able to augment mathematical induction with a simple one-line computing abstraction.
This article attempts to set out the various similarities and differences between the various programming paradigms as a summary in both graphical and tabular format with links to the separate discussions concerning these similarities and differences in extant Wikipedia articles.
Comet is a commercial programming language designed by at-the-time Brown University professor Dr. Pascal Van Hentenryck and used to solve complex combinatorial optimization problems in areas such as resource allocation and scheduling. It offers a range of optimization algorithms: from mathematical programming to constraint programming, local search algorithms and "dynamic stochastic combinatorial optimization."
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of objects, which can contain data and code: data in the form of fields, and code in the form of procedures.
Data-intensive computing is a class of parallel computing applications which use a data parallel approach to process large volumes of data typically terabytes or petabytes in size and typically referred to as big data. Computing applications that devote most of their execution time to computational requirements are deemed compute-intensive, whereas applications are deemed data-intensive require large volumes of data and devote most of their processing time to I/O and manipulation of data.

Apache Spark is an open-source unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing. Spark provides an interface for programming clusters with implicit data parallelism and fault tolerance. Originally developed at the University of California, Berkeley's AMPLab, the Spark codebase was later donated to the Apache Software Foundation, which has maintained it since.