
State Bank of India (SBI) is an Indian multinational public sector bank and financial services statutory body headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra. SBI is the 48th largest bank in the world by total assets and ranked 221st in the Fortune Global 500 list of the world's biggest corporations of 2020, being the only Indian bank on the list. It is a public sector bank and the largest bank in India with a 23% market share by assets and a 25% share of the total loan and deposits market. It is also the tenth largest employer in India with nearly 250,000 employees. In 2023, the company’s seat in Forbes Global 2000 was 77.

Bank of Baroda (BOB) is a government of India owned Multinational Public Sector Bank headquartered in Vadodara, Gujarat. It is the second largest Public Sector Bank in India after State Bank of India, with 153 million customers(March 2023), a total business of US$291 billion(March 2024), and a global presence of 100 overseas offices. Based on 2023 data, it is ranked 586 on the Forbes Global 2000 list.

Punjab National Bank is an Indian government public sector bank based in New Delhi.It was founded in May 1894 and is the second-largest public sector bank in India in terms of its business volumes, with over 180 million customers, 12,248 branches, and 13,000+ ATMs.

Indian Bank is an Indian public sector bank, established in 1907 and headquartered in Chennai. It serves over 100 million customers with 41,645 employees, 5,814 branches with 4,929 ATMs and Cash deposit machines. Total business of the bank has touched ₹1,094,752 crore (US$140 billion) as onfMarch 231, 023.

Indian Overseas Bank (IOB) is an Indian public sector bank based in Chennai. During the nationalisation, IOB was one of the 14 major banks taken over by the government of India. On 5 December 2021, IOB got Degidhan Award 2020–21 by Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology for achieving second highest percentage of digital payment transaction among public sector banks. As on 31 March 2022, IOB's total business stands at ₹417,960 crore (US$52 billion). It has about 3,220 domestic branches, 2 DBUs about 4 foreign branches and representative office. Founded in February 1937 by M. Ct. M. Chidambaram Chettyar with twin objectives of specializing in FOREX and overseas banking.
Events in the year 1857 in India.

Samuel Bourne was a British photographer known for his prolific seven years' work in India, from 1863 to 1870. Together with Charles Shepherd, he set up Bourne & Shepherd first in Shimla in 1863 and later in Kolkata (Calcutta); the company closed in June 2016.
The high courts of India are the highest courts of appellate jurisdiction in each state and union territory of India. However, a high court exercises its original civil and criminal jurisdiction only if the subordinate courts are not authorized by law to try such matters for lack of peculiar or territorial jurisdiction. High courts may also enjoy original jurisdiction in certain matters, if so designated, especially by the constitution, a state law or union law.

The Central Bank of India (CBI) is an Indian public sector bank based in Mumbai. Despite its name, it is not the central bank of India. The Indian central bank is the Reserve Bank of India.

British Punjab was a province of British India. Most of the Punjab region was annexed by the British East India Company on 29 March 1849, and declared a province of British colonial rule; it was one of the last areas of the Indian subcontinent to fall under British control. In 1858, the Punjab, along with the rest of British Raj, came under the direct colonial rule of the British Crown. It had a land area of 358,355 square kilometers.

The Bank of Calcutta was founded on 2 June 1806, mainly to fund General Arthur Wellesley's wars against Tipu Sultan and the Marathas. It was the tenth oldest bank in India and was renamed Bank of Bengal on 2 January 1809.

The historic overseas bank was established in London in 1828 as Leslie & Grindlay, agents and bankers to the British army and business community in India. Banking operations expanded to include the Indian subcontinent, the Middle East and elements of Africa and Southeast Asia. It was styled Grindlay, Christian & Matthews in 1839, Grindlay & Co from 1843, Grindlay & Co Ltd from 1924 and Grindlays Bank Ltd in 1947 until its merger with the National Bank of India.
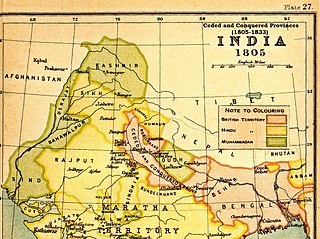
The Ceded and Conquered Provinces constituted a region in northern India that was ruled by the British East India Company from 1805 to 1834; it corresponded approximately—in present-day India—to all regions in Uttar Pradesh state with the exception of the Lucknow and Faizabad divisions of Awadh; in addition, it included the Delhi territory and, after 1816, the Kumaun division and a large part of the Garhwal division of present-day Uttarakhand state. In 1836, the region became the North-Western Provinces, and in 1904, the Agra Province within the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh.

Sir Thomas Douglas Forsyth was an Anglo-Indian administrator and diplomat.

The Delhi and London Bank was a bank that operated in British India.
Agra Bank was an Indian bank that was founded in 1833 in Agra, with a capital of £1,000,000 and was finally liquidated in 1900.

The Currency Building is an early 19th-century building in the B. B. D. Bagh central business district of Kolkata in West Bengal, India. The building was originally built in 1833 to house the Calcutta branch of the Agra Bank. In 1868, it was converted for use by the Office of the Issue and Exchange of Government Currency, an office of the Controller of the Currency under the British Raj. From 1935 until 1937, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) used the building as its first central office. The building remained in use, and was used at one time by the Central Public Works Department (CPWD) as a storehouse. Authorities decided to demolish it in 1994.
The Punjab Banking Company (1889) was a bank founded in the year 1889 in British India. The bank became defunct in the year 1916, when it was acquired by the Alliance Bank of Simla.
The Simla Bank Limited (1844) was a bank founded in the year 1844 in British India. The bank became defunct in the year 1893 with the winding down of its operations. The bank was notable for being the twenty ninth oldest bank in India.














