
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself or by forming a template for the production of proteins. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) are nucleic acids. The nucleic acids constitute one of the four major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.
Gene knockouts are a widely used genetic engineering technique that involves the targeted removal or inactivation of a specific gene within an organism's genome. This can be done through a variety of methods, including homologous recombination, CRISPR-Cas9, and TALENs.

Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) is a private, non-profit institution with research programs focusing on cancer, neuroscience, plant biology, genomics, and quantitative biology. It is located in Laurel Hollow on Long Island, New York.

Howard Robert Horvitz ForMemRS NAS AAA&S APS NAM is an American biologist best known for his research on the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, for which he was awarded the 2002 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, together with Sydney Brenner and John E. Sulston, whose "seminal discoveries concerning the genetic regulation of organ development and programmed cell death" were "important for medical research and have shed new light on the pathogenesis of many diseases".
UMass Chan Medical School is a public medical school in Worcester, Massachusetts. It is part of the University of Massachusetts system. It is home to three schools: the T.H. Chan School of Medicine, the Morningside Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, and the Tan Chingfen Graduate School of Nursing, as well as a biomedical research enterprise and a range of public-service initiatives throughout the state.

Elizabeth Helen Blackburn, is an Australian-American Nobel laureate who is the former president of the Salk Institute for Biological Studies. In 1984, Blackburn co-discovered telomerase, the enzyme that replenishes the telomere, with Carol W. Greider. For this work, she was awarded the 2009 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, sharing it with Carol W. Greider and Jack W. Szostak, becoming the first Australian woman Nobel laureate.

Phillip Allen Sharp is an American geneticist and molecular biologist who co-discovered RNA splicing. He shared the 1993 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Richard J. Roberts for "the discovery that genes in eukaryotes are not contiguous strings but contain introns, and that the splicing of messenger RNA to delete those introns can occur in different ways, yielding different proteins from the same DNA sequence". He has been selected to receive the 2015 Othmer Gold Medal.
The RNA-induced silencing complex, or RISC, is a multiprotein complex, specifically a ribonucleoprotein, which functions in gene silencing via a variety of pathways at the transcriptional and translational levels. Using single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) fragments, such as microRNA (miRNA), or double-stranded small interfering RNA (siRNA), the complex functions as a key tool in gene regulation. The single strand of RNA acts as a template for RISC to recognize complementary messenger RNA (mRNA) transcript. Once found, one of the proteins in RISC, Argonaute, activates and cleaves the mRNA. This process is called RNA interference (RNAi) and it is found in many eukaryotes; it is a key process in defense against viral infections, as it is triggered by the presence of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA).

Eric Francis Wieschaus is an American evolutionary developmental biologist and 1995 Nobel Prize-winner.

Randy Wayne Schekman is an American cell biologist at the University of California, Berkeley, former editor-in-chief of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences and former editor of Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology. In 2011, he was announced as the editor of eLife, a new high-profile open-access journal published by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the Max Planck Society and the Wellcome Trust launching in 2012. He was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 1992. Schekman shared the 2013 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine with James Rothman and Thomas C. Südhof for their ground-breaking work on cell membrane vesicle trafficking.

Craig Cameron Mello is an American biologist and professor of molecular medicine at the University of Massachusetts Medical School in Worcester, Massachusetts. He was awarded the 2006 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine, along with Andrew Z. Fire, for the discovery of RNA interference. This research was conducted at the University of Massachusetts Medical School and published in 1998. Mello has been a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator since 2000.

Carolyn Widney Greider is an American molecular biologist and Nobel laureate. She joined the University of California, Santa Cruz as a Distinguished Professor in the department of molecular, cell, and developmental biology in October 2020.

Sir David Charles Baulcombe is a British plant scientist and geneticist. As of 2017 he is a Royal Society Research Professor. From 2007 to 2020 he was Regius Professor of Botany in the Department of Plant Sciences at the University of Cambridge.
Thomas Tuschl is a German biochemist and molecular biologist, known for his research on RNA.

Victor R. Ambros is an American developmental biologist who discovered the first known microRNA (miRNA). He is a professor at the University of Massachusetts Medical School in Worcester, Massachusetts.
Gary Bruce Ruvkun is an American molecular biologist at Massachusetts General Hospital and professor of genetics at Harvard Medical School in Boston. Ruvkun discovered the mechanism by which lin-4, the first microRNA (miRNA) discovered by Victor Ambros, regulates the translation of target messenger RNAs via imperfect base-pairing to those targets, and discovered the second miRNA, let-7, and that it is conserved across animal phylogeny, including in humans. These miRNA discoveries revealed a new world of RNA regulation at an unprecedented small size scale, and the mechanism of that regulation. Ruvkun also discovered many features of insulin-like signaling in the regulation of aging and metabolism. He was elected a Member of the American Philosophical Society in 2019.
The Wiley Prize in Biomedical Sciences is intended to recognize breakthrough research in pure or applied life science research that is distinguished by its excellence, originality and impact on our understanding of biological systems and processes. The award may recognize a specific contribution or series of contributions that demonstrate the nominee's significant leadership in the development of research concepts or their clinical application. Particular emphasis will be placed on research that champions novel approaches and challenges accepted thinking in the biomedical sciences.
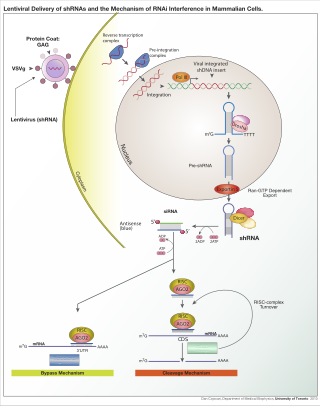
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules are involved in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression by double-stranded RNA, through translational or transcriptional repression. Historically, RNAi was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. The detailed study of each of these seemingly different processes elucidated that the identity of these phenomena were all actually RNAi. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNAi in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998. Since the discovery of RNAi and its regulatory potentials, it has become evident that RNAi has immense potential in suppression of desired genes. RNAi is now known as precise, efficient, stable and better than antisense therapy for gene suppression. Antisense RNA produced intracellularly by an expression vector may be developed and find utility as novel therapeutic agents.
The Massry Prize was established in 1996, and was administered by the Meira and Shaul G. Massry Foundation until 2019. The Prize, of $40,000 and the Massry Lectureship, is bestowed upon scientists who have made substantial recent contributions in the biomedical sciences. Shaul G. Massry, M.D., who established the Massry Foundation, is Professor Emeritus of Medicine and Physiology and Biophysics at the Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California. He served as Chief of its Division of Nephrology from 1974 to 2000. In 2009 the KECK School of Medicine was asked to administer the Prize, and has done so since that time. Ten winners of the Massry Prize have gone on to be awarded a Nobel Prize.
Richard William Carthew is a developmental biologist and quantitative biologist at Northwestern University. He is a professor of molecular biosciences and is the director of the NSF-Simons Center for Quantitative Biology.












