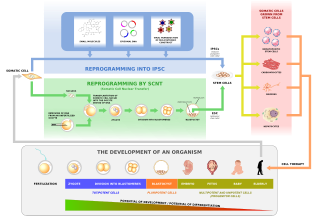
Human cloning is the creation of a genetically identical copy of a human. The term is generally used to refer to artificial human cloning, which is the reproduction of human cells and tissue. It does not refer to the natural conception and delivery of identical twins. The possibilities of human cloning have raised controversies. These ethical concerns have prompted several nations to pass laws regarding human cloning.

Monash University is a public research university based in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Named after prominent World War I general Sir John Monash, it was founded in 1958 and is the second oldest university in the state. The university has a number of campuses, four of which are in Victoria, one in Malaysia and another one in Indonesia. Monash also has a research and teaching centre in Prato, Italy, a graduate research school in Mumbai, India and graduate schools in Suzhou, China and Tangerang, Indonesia. Courses are also delivered at other locations, including South Africa.

In genetics and developmental biology, somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) is a laboratory strategy for creating a viable embryo from a body cell and an egg cell. The technique consists of taking an denucleated oocyte and implanting a donor nucleus from a somatic (body) cell. It is used in both therapeutic and reproductive cloning. In 1996, Dolly the sheep became famous for being the first successful case of the reproductive cloning of a mammal. In January 2018, a team of scientists in Shanghai announced the successful cloning of two female crab-eating macaques from foetal nuclei.
James Alexander Thomson is an American developmental biologist best known for deriving the first human embryonic stem cell line in 1998 and for deriving human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) in 2007.
Regenerative medicine deals with the "process of replacing, engineering or regenerating human or animal cells, tissues or organs to restore or establish normal function". This field holds the promise of engineering damaged tissues and organs by stimulating the body's own repair mechanisms to functionally heal previously irreparable tissues or organs.
The stem cell controversy concerns the ethics of research involving the development and use of human embryos. Most commonly, this controversy focuses on embryonic stem cells. Not all stem cell research involves human embryos. For example, adult stem cells, amniotic stem cells, and induced pluripotent stem cells do not involve creating, using, or destroying human embryos, and thus are minimally, if at all, controversial. Many less controversial sources of acquiring stem cells include using cells from the umbilical cord, breast milk, and bone marrow, which are not pluripotent.

Monash University, Clayton campus is the main campus of Monash University located in Clayton, which is a suburb of Melbourne, Australia, in the state of Victoria.

Robert Lanza is an American medical doctor and scientist, currently Head of Astellas Global Regenerative Medicine, and Chief Scientific Officer of the Astellas Institute for Regenerative Medicine. He is an Adjunct Professor at Wake Forest University School of Medicine.

Anthony Atala is an American bioengineer, urologist, and pediatric surgeon. He is the W.H. Boyce professor of urology, the founding director of the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine, and the chair of the Department of Urology at Wake Forest School of Medicine in North Carolina. His work focuses on the science of regenerative medicine: "a practice that aims to refurbish diseased or damaged tissue using the body's own healthy cells".
The Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) is a research institute affiliated with Wake Forest School of Medicine and located in Winston-Salem, North Carolina, United States
Alan Osborne Trounson is an Australian embryologist with expertise in stem cell research. Trounson was the President of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine between 2007 and 2014, a former Professor of Stem Cell Sciences and the Director of the Monash Immunology and Stem Cell Laboratories at Monash University, and retains the title of emeritus professor.
The Australian Regenerative Medicine Institute (ARMI) is an Australian medical research institute. Opened in April 2009, the institute is based at the Clayton campus of Monash University, in the Monash Science Technology Research and Innovation Precinct.
The Monash Science Technology Research and Innovation Precinct (STRIP) is a cluster of commercial and university enterprises and research centres based at Monash University's Clayton Campus. The STRIP was officially opened on 18 February 2010 by Nobel laureate Professor Elizabeth Blackburn.

Shinya Yamanaka is a Japanese stem cell researcher and a Nobel Prize laureate. He is a professor and the director emeritus of Center for iPS Cell Research and Application, Kyoto University; as a senior investigator at the UCSF-affiliated Gladstone Institutes in San Francisco, California; and as a professor of anatomy at University of California, San Francisco (UCSF). Yamanaka is also a past president of the International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR).
Samuel H. Wood is a scientist and fertility specialist. In 2008, he became the first man to clone himself, donating his own DNA via somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) to produce mature human embryos that were his clones.
Monash University is an Australian university located in Melbourne, Australia with some international campuses. It was established by an Act of the State Parliament of Victoria in 1958 as a result of the Murray Report which was commissioned in 1957 by the then Prime Minister Sir Robert Menzies to establish the second university in the state of Victoria.
The Monash Institute of Medical Research (MIMR), was an Australian medical research institute located in the Melbourne suburb of Clayton, Victoria, consisting of 400 scientists and students belonging to the Faculty of Medicine, Nursing and Health Sciences at Monash University. In January 2014 the Institute merged with Prince Henry's Institute of Medical Research and has since been renamed the Hudson Institute of Medical Research.
Stem cell laws are the law rules, and policy governance concerning the sources, research, and uses in treatment of stem cells in humans. These laws have been the source of much controversy and vary significantly by country. In the European Union, stem cell research using the human embryo is permitted in Sweden, Spain, Finland, Belgium, Greece, Britain, Denmark and the Netherlands; however, it is illegal in Germany, Austria, Ireland, Italy, and Portugal. The issue has similarly divided the United States, with several states enforcing a complete ban and others giving support. Elsewhere, Japan, India, Iran, Israel, South Korea, China, and Australia are supportive. However, New Zealand, most of Africa, and most of South America are restrictive.
Hudson Institute of Medical Research is a leading Australian medical research institute recognised internationally for discovery science and translational research.
Andrew Webster (1951–2021) was an English sociologist who was a professor of sociology at the University of York, where he established the Science and Technology Studies research unit. He studied the sociocultural and economic implications of introducing biomedical technologies, including stem cell research and regenerative medicine, into clinical settings.