
Romeo and Juliet is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare early in his career about the romance between two Italian youths from feuding families. It was among Shakespeare's most popular plays during his lifetime and, along with Hamlet, is one of his most frequently performed. Today, the title characters are regarded as archetypal young lovers.

Romeo and Juliet is a 1968 period romantic tragedy film, based on the play of the same name by William Shakespeare. Directed and co-written by Franco Zeffirelli, the film stars Leonard Whiting as Romeo and Olivia Hussey as Juliet. Laurence Olivier spoke the film's prologue and epilogue and dubs the voice of Antonio Pierfederici, who played Lord Montague but was not credited on-screen. The cast also features Milo O'Shea, Michael York, John McEnery, Bruce Robinson, and Robert Stephens.

Romeo and Juliet is a 1936 American film adapted from the play by William Shakespeare, directed by George Cukor from a screenplay by Talbot Jennings. The film stars Leslie Howard as Romeo and Norma Shearer as Juliet, and the supporting cast features John Barrymore, Basil Rathbone, and Andy Devine.

Hector Guimard was a French architect and designer, and a prominent figure of the Art Nouveau style. He achieved early fame with his design for the Castel Beranger, the first Art Nouveau apartment building in Paris, which was selected in an 1899 competition as one of the best new building facades in the city. He is best known for the glass and iron edicules or canopies, with ornamental Art Nouveau curves, which he designed to cover the entrances of the first stations of the Paris Metro.

Tybalt is a character in William Shakespeare's play Romeo and Juliet. He is the son of Lady Capulet's brother, Juliet's short-tempered first cousin, and Romeo's rival. Tybalt shares the same name as the character Tibert / Tybalt "the prince of cats" in the popular story Reynard the Fox, a point of mockery in the play. Mercutio repeatedly calls Tybalt "prince of cats", in reference to his sleek, yet violent manner.

Juliet Capulet is the female protagonist in William Shakespeare's romantic tragedy Romeo and Juliet. A 13-year-old girl, Juliet is the only daughter of the patriarch of the House of Capulet. She falls in love with the male protagonist Romeo, a member of the House of Montague, with which the Capulets have a blood feud. The story has a long history that precedes Shakespeare himself.
Roméo et Juliette: de la Haine à l'Amour is a French musical based on William Shakespeare's play Romeo and Juliet, with music and lyrics by Gérard Presgurvic. It premiered in Paris on January 19, 2001. The production was directed and choreographed by Redha, with costumes by Dominique Borg and settings by Petrika Ionesco. The producers were Gérard Louvin, GLEM, and Universal Music. ! Since then, the musical has been performed in Verona, Rome, Canada, Antwerp, London, Amsterdam, Budapest, Szeged, Moscow, Vienna, Bucharest, Seoul, Pusan, Taipei, Monterrey, Japan, Hong Kong, Shanghai and Portugal and has been translated into several languages, including Dutch, Italian, Hungarian, Russian, English, German, Spanish, Romanian, Japanese, Korean, Portuguese, and Slovak.

I Capuleti e i Montecchi is an Italian opera in two acts by Vincenzo Bellini. The libretto by Felice Romani was a reworking of the story of Romeo and Juliet for an opera by Nicola Vaccai called Giulietta e Romeo and based on the play of the same name by Luigi Scevola written in 1818, thus an Italian source rather than taken directly from William Shakespeare.
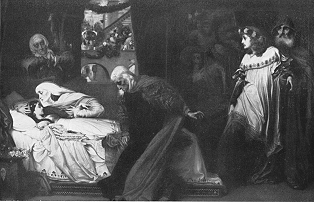
Count Paris or County Paris is a fictional character in William Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet. He is a suitor of Juliet. He is handsome, wealthy, and a kinsman to Prince Escalus.

Luigi Da Porto was an Italian writer and historiographer, better known as the author of the novella Historia novellamente ritrovata di due giovani amanti, with the story of Romeo and Juliet, later reprised by William Shakespeare for his famous drama.
A ghost character, in the bibliographic or scholarly study of texts of dramatic literature, is a term for an inadvertent error committed by the playwright in the act of writing. It is a character who is mentioned as appearing on stage, but who does not do anything, and who seems to have no purpose. As Kristian Smidt put it, they are characters that are "introduced in stage directions or briefly mentioned in dialogue who have no speaking parts and do not otherwise manifest their presence". It is generally interpreted as an author's mistake, indicative of an unresolved revision to the text. If the character was intended to appear and say nothing, it is assumed this would be made clear in the playscript.

Rosaline is a fictional character mentioned in William Shakespeare's tragedy Romeo and Juliet. She is the niece of Lord Capulet. Although an unseen character, her role is important: Romeo's unrequited love for Rosaline leads him to try to catch a glimpse of her at a gathering hosted by the Capulet family, during which he first spots her cousin, Juliet.

William Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet may be one of the most-screened plays of all time. The most notable theatrical releases were George Cukor's multi-Oscar-nominated 1936 production Romeo and Juliet, Franco Zeffirelli's 1968 film Romeo and Juliet, and Baz Luhrmann's 1996 MTV-inspired Romeo + Juliet. The latter two were both, at the time, the highest-grossing Shakespeare films. Cukor featured the mature actors Norma Shearer and Leslie Howard as the teenage lovers while Zeffirelli populated his film with beautiful young people, and Baz Luhrmann produced a heavily cut fast-paced version aimed at teenage audiences.

The Nurse is a character in William Shakespeare's classic drama Romeo and Juliet. She is the personal servant, guardian, and former wet nurse of Juliet Capulet, and has been since Juliet was born. She had a daughter named Susan who died in infancy, and then became wetnurse to Juliet. As the primary person to like, she is therefore Juliet's foremost confidante. She is very important to Juliet's life.
William Shakespeare's play Romeo and Juliet, set in Verona, Italy, features the eponymous protagonists Romeo Montague and Juliet Capulet. The cast of characters also includes members of their respective families and households; Prince Escalus, the city's ruler, and his kinsman, Count Paris; and various unaffiliated characters such as Friar Laurence and the Chorus. In addition, the play contains two ghost characters and an unseen character (Rosaline).

In architecture and the decorative arts, a mascaron ornament is a face, usually human, sometimes frightening or chimeric, whose alleged function was originally to frighten away evil spirits so that they would not enter the building. The concept was subsequently adapted to become a purely decorative element. The most recent architectural styles to extensively employ mascarons were Beaux Arts and Art Nouveau. In addition to architecture, mascarons are used in the other applied arts.

The Lovers of Verona is a 1949 French romantic drama mystery film co-written and directed by André Cayatte, loosely based on the William Shakespeare play Romeo and Juliet. The film was a joint project of screenwriter Jacques Prevert and director Cayatte and enjoyed great international success. It was released in Italy in 1949, then internationally in 1951.

Romeo & Juliet is a 2013 film adaptation of William Shakespeare's romantic tragedy. Written by Julian Fellowes and directed by Carlo Carlei, it stars Douglas Booth, Hailee Steinfeld, Damian Lewis, Kodi Smit-McPhee, Ed Westwick, Stellan Skarsgård and Paul Giamatti. The film opened in the United Kingdom and the United States on 11 October 2013. While remaining faithful to the original plot, it uses only some of the dialogue written by Shakespeare. This has led to several critics denouncing the film on the grounds that it loses the essence of the play. The film grossed $3 million.

Balconet or balconette is an architectural term to describe a false balcony, or railing at the outer plane of a window-opening reaching to the floor, and having, when the window is open, the appearance of a balcony. They are common in France, Portugal, Spain, and Italy. They are often referred to as Juliet balconies after the scene from Shakespeare's play Romeo and Juliet. The wall-opening appearing alongside a balconette is referred to as French window.
Julia is a 1974 erotic drama film from West Germany starring Sylvia Kristel.






































