
The Eighth Amendment to the United States Constitution protects against imposing excessive bail, excessive fines, or cruel and unusual punishments. This amendment was adopted on December 15, 1791, along with the rest of the United States Bill of Rights. The amendment serves as a limitation upon the state or federal government to impose unduly harsh penalties on criminal defendants before and after a conviction. This limitation applies equally to the price for obtaining pretrial release and the punishment for crime after conviction. The phrases in this amendment originated in the English Bill of Rights of 1689.

Lethal injection is the practice of injecting one or more drugs into a person for the express purpose of causing rapid death. The main application for this procedure is capital punishment, but the term may also be applied in a broader sense to include euthanasia and other forms of suicide. The drugs cause the person to become unconscious, stops their breathing, and causes a heart arrhythmia, in that order.

The electric chair is a specialized device employed for carrying out capital punishment through the process of electrocution. During its use, the individual sentenced to death is securely strapped to a specially designed wooden chair and electrocuted via strategically positioned electrodes affixed to the head and leg. This method of execution was conceptualized by Alfred P. Southwick, a dentist based in Buffalo, New York, in 1881. Over the following decade, this execution technique was developed further, aiming to provide a more humane alternative to the conventional forms of execution, particularly hanging. The electric chair was first utilized in 1890 and subsequently became known as a symbol of this method of execution.
Furman v. Georgia, 408 U.S. 238 (1972), was a landmark criminal case in which the United States Supreme Court invalidated all then existing legal constructions for the death penalty in the United States. It was a 5–4 decision, with each member of the majority writing a separate opinion. Following Furman, in order to reinstate the death penalty, states had to at least remove arbitrary and discriminatory effects in order to satisfy the Eighth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution.
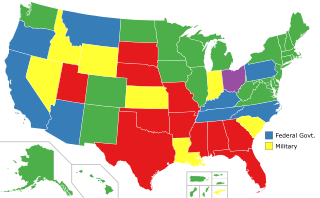
In the United States, capital punishment is a legal penalty throughout the country at the federal level, in 27 states, and in American Samoa. It is also a legal penalty for some military offenses. Capital punishment has been abolished in 23 states and in the federal capital, Washington, D.C. It is usually applied for only the most serious crimes, such as aggravated murder. Although it is a legal penalty in 27 states, 20 states currently have the ability to execute death sentences, with the other seven, as well as the federal government, being subject to different types of moratoriums.
The death row phenomenon is the emotional distress felt by prisoners on death row. Concerns about the ethics of inflicting this distress upon prisoners have led to some legal concerns about the constitutionality of the death penalty in the United States and other countries. In relation to the use of solitary confinement with death row inmates, death row phenomenon and death row syndrome are two concepts that are gaining recognition. The death row syndrome is a distinct concept, which is the enduring psychological effects of the death row phenomenon, which merely refers to the triggers of the syndrome.
Uttecht v. Brown, 551 U.S. 1 (2007), was a case dealing with jury selection in capital cases in which the Supreme Court of the United States held that appeals courts must defer to a trial judge’s decision on whether a potential juror would be able to overcome demur about capital punishment and be open to voting to impose a death sentence.
Ralph Baze is a convicted murderer who sued the Kentucky State Department of Corrections along with fellow inmate Thomas Clyde Bowling Jr. to challenge their impending execution. He and Bowling sued on the grounds that execution by lethal injection using the "cocktail" prescribed by Kentucky law constitutes cruel and unusual punishment in violation of the 8th Amendment. Baze's court case was Baze v. Rees.
Thomas Clyde Bowling Jr. was an American convicted murderer who unsuccessfully challenged the constitutionality of his death sentence.

The Supreme Court of the United States handed down six per curiam opinions during its 2007 term, which began October 1, 2007 and concluded September 30, 2008.
Wilkerson v. Utah, 99 U.S. 130 (1879), is a United States Supreme Court case in which the Court affirmed the judgment of the Supreme Court of the Territory of Utah in stating that execution by firing squad, as prescribed by the Utah territorial statute, was not cruel and unusual punishment under the Eighth Amendment to the United States Constitution.
Davis v. Federal Election Commission, 554 U.S. 724 (2008), is a decision by the Supreme Court of the United States which held that section 319 of the Bipartisan Campaign Reform Act of 2002 unconstitutionally infringed on candidates' rights as provided by First Amendment.
Participation of medical professionals in American executions is a controversial topic, due to its moral and legal implications. The practice is proscribed by the American Medical Association, as defined in its Code of Medical Ethics. The American Society of Anesthesiologists endorses this position, stating that lethal injections "can never conform to the science, art and practice of anesthesiology".
The Death Penalty Information Center (DPIC) is a non-profit organization based in Washington, D.C., that focuses on disseminating studies and reports related to the death penalty. Founded in 1990, DPIC is primarily focused on the application of capital punishment in the United States.
Padilla v. Commonwealth of Kentucky, 559 U.S. 356 (2010), is a case in which the United States Supreme Court decided that criminal defense attorneys must advise noncitizen clients about the deportation risks of a guilty plea. The case extended the Supreme Court's prior decisions on criminal defendants' Sixth Amendment right to counsel to immigration consequences.
Glossip v. Gross, 576 U.S. 863 (2015), was a United States Supreme Court case in which the Court held, 5–4, that lethal injections using midazolam to kill prisoners convicted of capital crimes do not constitute cruel and unusual punishment under the Eighth Amendment to the United States Constitution. The Court found that condemned prisoners can only challenge their method of execution after providing a known and available alternative method.
Richard Eugene Glossip is an American prisoner currently on death row at Oklahoma State Penitentiary after being convicted of commissioning the 1997 murder of Barry Van Treese. The man who murdered Van Treese, Justin Sneed, had a "meth habit" and agreed to plead guilty in exchange for testifying against Glossip. Sneed received a life sentence without parole. Glossip's case has attracted international attention due to the unusual nature of his conviction, namely that there was little or no corroborating evidence, with the first case against him described as "extremely weak" by the Oklahoma Court of Criminal Appeals.
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in the U.S. state of Kentucky.
Bucklew v. Precythe, 587 U.S. ___ (2019), was a United States Supreme Court case regarding the standards for challenging methods of capital punishment under the Eighth Amendment to the United States Constitution. In a 5–4 decision, the Court held that when a convict sentenced to death challenges the State's method of execution due to claims of excessive pain, the convict must show that other alternative methods of execution exist and clearly demonstrate they would cause less pain than the state-determined one. The Court's opinion emphasized the precedential force of its prior decisions in Baze v. Rees and Glossip v. Gross.

Glossip v. Chandler is a United States District Court for the Western District of Oklahoma case in which the plaintiffs challenged the State of Oklahoma's execution protocol. The initial lawsuit, Glossip v. Gross, rose to the United States Supreme Court in 2015 at the preliminary injunction stage and involved an earlier version of Oklahoma's lethal injection protocol. The case was reopened in the District Court in 2020 following an end to Oklahoma's moratorium on executions.






