
This is a bibliography of works on the Provinces and territories of Canada .

This is a bibliography of works on the Provinces and territories of Canada .
Ontario., general survey emphasizing politics
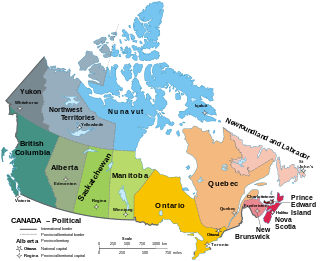
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada —united to form a federation, becoming a fully independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the world's second-largest country by area.
The Canadian order of precedence is a nominal and symbolic hierarchy of important positions within the governing institutions of Canada. It has no legal standing, but is used to dictate ceremonial protocol.
Canadian Senate divisions refers to two aspects of the Senate of Canada. First, it refers to the division of Canada into four regional Senate divisions of 24 senators each, as set out in section 22 of the Constitution Act, 1867. The four regions are the Western Provinces, Ontario, Quebec and the Maritimes. These regions are intended to serve the Senate's purpose of providing regional representation in the Parliament of Canada, in contrast to the popular representation that the House of Commons is intended to provide. While not within any of the original four Senate divisions, Senate seats are also allocated to Newfoundland and Labrador and the three territories. The four divisions can be expanded when the need arises to have an extra two senators appointed to each regional division.
The orders, decorations, and medals of the Canadian provinces, in which each province of Canada has devised a system of orders and other awards to honour residents for actions or deeds that benefit their local community or province, are in turn subsumed within the Canadian honours system. Each province sets its own rules and criteria for eligibility and also for how each award is presented. Most of the awards allow for the recipients to wear their awards in public, and most grant the recipients the use of post-nominal letters after their names. Not all of the awards listed below are part of the Canadian honours system, thus some of them may not be worn or court mounted with awards that are part of the Canadian honours system.

The history of post-confederation Canada began on July 1, 1867, when the British North American colonies of Canada, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia were united to form a single Dominion within the British Empire. Upon Confederation, the United Province of Canada was immediately split into the provinces of Ontario and Quebec. The colonies of Prince Edward Island and British Columbia joined shortly after, and Canada acquired the vast expanse of the continent controlled by the Hudson's Bay Company, which was eventually divided into new territories and provinces. Canada evolved into a fully sovereign state by 1982.
Crown corporations in Canada are government organizations with a mixture of commercial and public-policy objectives. They are directly and wholly owned by the Crown.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Canada:
This is a list of elections in Canada in 2009. Included are provincial, municipal and federal elections, by-elections on any level, referendums and party leadership races at any level.

The 2010 Canadian Mixed Curling Championship was held Nov. 14–21, 2009 at the Burlington Golf and Country Club in Burlington, Ontario. Nova Scotia won its seventh Mixed title, and skip Mark Dacey won his second title with then-wife, Heather Smith-Dacey as his mate who won her third. The team's front end of Andrew Gibson and Jill Mouzar won their first mixed title.

The men's soccer tournament at the 2013 Canada Summer Games was held at the Université de Sherbrooke Stadium and Bishop's University in Sherbrooke, Quebec.
The Canadian Association of Social Workers (CASW) is the national association for the social work profession in Canada.

The 2016 Tim Hortons Brier, Canada's national men's curling championship, was held from March 5–13, 2016 at TD Place Arena in Ottawa, Ontario.

The Prime Minister's Youth Council is an advisory board created by the Prime Minister of Canada Justin Trudeau in 2016. Currently, 10 Canadian youth aged 16 to 24 comprise the non-partisan board. Members advise the prime minister on education, economy, climate change and other issues affecting youth.
The quadrennial Canada Winter Games competition has an ice hockey tournament. The participants are the provincial and territorial ice hockey associations.